为什么需要读写分离
当项目越来越大和并发越来大的情况下,单个数据库服务器的压力肯定也是越来越大,最终演变成数据库成为性能的瓶颈,而且当数据越来越多时,查询也更加耗费时间,当然数据库数据过大时,可以采用数据库分库分表,同时数据库压力过大时,也可以采用Redis等缓存技术来降低压力,但是任何一种技术都不是万金油,很多时候都是通过多种技术搭配使用,而本文主要就是介绍通过读写分离来加快数据库读取速度
实现方式
读写分离实现的方式有多种,但是多种都需要配置数据库的主从复制
方式一
数据库中间件实现,如Mycat等数据库中间件,对于项目本身来说,只有一个数据源,就是链接到Mycat,再由mycat根据规则去选择从哪个库获取数据
方式二
代码中配置多数据源,通过代码控制使用哪个数据源,本文也是主要介绍这种方式
优点
1.降低数据库读取压力,尤其是有些需要大量计算的实时报表类应用
2.增强数据安全性,读写分离有个好处就是数据近乎实时备份,一旦某台服务器硬盘发生了损坏,从库的数据可以无限接近主库
3.可以实现高可用,当然只是配置了读写分离并不能实现搞可用,最多就是在Master(主库)宕机了还能进行查询操作,具体高可用还需要其他操作
缺点
1.增大成本,一台数据库服务器和多台数据库的成本肯定是不一样的
2.增大代码复杂度,不过这点还比较轻微吧,但是也的确会一定程度上加重
3.增大写入成本,虽然降低了读取成本,但是写入成本却是一点也没有降低,毕竟还有从库一直在向主库请求数据
实践:
项目结构:
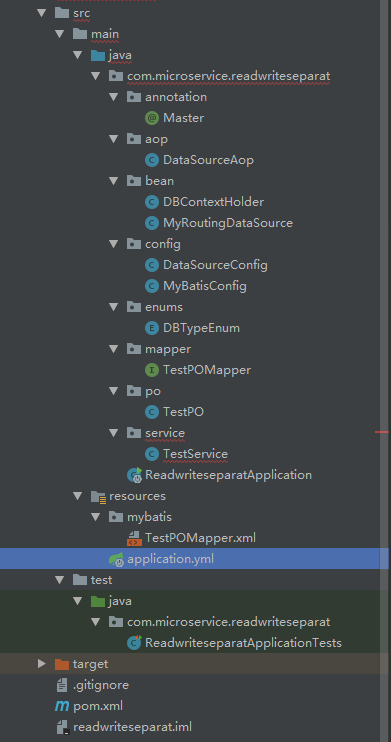
application.yml
spring: datasource: master: # 写账户 jdbc-url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/otadb?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&useSSL=false username: root password: 123456 slave1: # 只读账户 jdbc-url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/otadb1?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&useSSL=false username: root password: 123456 slave2: # 只读账户 jdbc-url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/otadb2?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&useSSL=false username: root password: 123456
多数据源配置
import com.microservice.readwriteseparat.bean.MyRoutingDataSource; import com.microservice.readwriteseparat.enums.DBTypeEnum; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.boot.jdbc.DataSourceBuilder; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import javax.sql.DataSource; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; @Configuration public class DataSourceConfig { /** * 写库 * @return */ @Bean @ConfigurationProperties("spring.datasource.master") public DataSource masterDataSource() { return DataSourceBuilder.create().build(); } /** * 读库 * @return */ @Bean @ConfigurationProperties("spring.datasource.slave1") public DataSource slave1DataSource() { return DataSourceBuilder.create().build(); } /** * 读库 * @return */ @Bean @ConfigurationProperties("spring.datasource.slave2") public DataSource slave2DataSource() { return DataSourceBuilder.create().build(); } @Bean public DataSource myRoutingDataSource(@Qualifier("masterDataSource") DataSource masterDataSource, @Qualifier("slave1DataSource") DataSource slave1DataSource, @Qualifier("slave2DataSource") DataSource slave2DataSource) { Map<Object, Object> targetDataSources = new HashMap<>(); targetDataSources.put(DBTypeEnum.MASTER, masterDataSource); targetDataSources.put(DBTypeEnum.SLAVE1, slave1DataSource); targetDataSources.put(DBTypeEnum.SLAVE2, slave2DataSource); MyRoutingDataSource myRoutingDataSource = new MyRoutingDataSource(); myRoutingDataSource.setDefaultTargetDataSource(masterDataSource); myRoutingDataSource.setTargetDataSources(targetDataSources); return myRoutingDataSource; } }
这里,我们配置了4个数据源,1个master,2两个slave,1个路由数据源。前3个数据源都是为了生成第4个数据源,而且后续我们只用这最后一个路由数据源myRoutingDataSource。
MyBatis配置
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory; import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver; import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager; import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement; import javax.annotation.Resource; import javax.sql.DataSource; @EnableTransactionManagement @Configuration public class MyBatisConfig { @Resource(name = "myRoutingDataSource") private DataSource myRoutingDataSource; /** * 扫描mybatis下的xml文件 * @return * @throws Exception */ @Bean public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory() throws Exception { SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactoryBean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean(); sqlSessionFactoryBean.setDataSource(myRoutingDataSource); sqlSessionFactoryBean.setMapperLocations(new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources("classpath:mybatis/*.xml")); return sqlSessionFactoryBean.getObject(); } @Bean public PlatformTransactionManager platformTransactionManager() { return new DataSourceTransactionManager(myRoutingDataSource);//由于Spring容器中现在有4个数据源,所以我们需要为事务管理器和MyBatis手动指定一个明确的数据源。 } }
定义一个枚举来代表这三个数据源
public enum DBTypeEnum { MASTER,SLAVE1,SLAVE2 }
通过ThreadLocal将数据源设置到每个线程上下文中
import com.microservice.readwriteseparat.enums.DBTypeEnum; import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger; public class DBContextHolder { private static final ThreadLocal<DBTypeEnum> contextHolder = new ThreadLocal<>(); private static final AtomicInteger counter = new AtomicInteger(-1); public static void set(DBTypeEnum dbType) { contextHolder.set(dbType); } public static DBTypeEnum get() { return contextHolder.get(); } public static void master() { set(DBTypeEnum.MASTER); System.out.println("切换到master"); } public static void slave() { // 轮询 int index = counter.getAndIncrement() % 2; if (counter.get() > 9999) { counter.set(-1); } if (index == 0) { set(DBTypeEnum.SLAVE1); System.out.println("切换到slave1"); }else { set(DBTypeEnum.SLAVE2); System.out.println("切换到slave2"); } } }
获取路由key
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.lookup.AbstractRoutingDataSource; import org.springframework.lang.Nullable; public class MyRoutingDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource { @Nullable @Override protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() { return DBContextHolder.get(); } }
默认情况下,所有的查询都走从库,插入/修改/删除走主库。我们通过方法名来区分操作类型(CRUD)
import com.microservice.readwriteseparat.bean.DBContextHolder; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Aspect @Component public class DataSourceAop { /** * 只读: * 不是Master注解的对象或方法 && select开头的方法 || get开头的方法 */ @Pointcut("!@annotation(com.microservice.readwriteseparat.annotation.Master) " + "&& (execution(* com.microservice.readwriteseparat.service..*.select*(..)) " + "|| execution(* com.microservice.readwriteseparat.service..*.get*(..)))") public void readPointcut() { } /** * 写: * Master注解的对象或方法 || insert开头的方法 || add开头的方法 || update开头的方法 * || edlt开头的方法 || delete开头的方法 || remove开头的方法 */ @Pointcut("@annotation(com.microservice.readwriteseparat.annotation.Master) " + "|| execution(* com.microservice.readwriteseparat.service..*.insert*(..)) " + "|| execution(* com.microservice.readwriteseparat.service..*.add*(..)) " + "|| execution(* com.microservice.readwriteseparat.service..*.update*(..)) " + "|| execution(* com.microservice.readwriteseparat.service..*.edit*(..)) " + "|| execution(* com.microservice.readwriteseparat.service..*.delete*(..)) " + "|| execution(* com.microservice.readwriteseparat..*.remove*(..))") public void writePointcut() { } @Before("readPointcut()") public void read() { DBContextHolder.slave(); } @Before("writePointcut()") public void write() { DBContextHolder.master(); } }
有一般情况就有特殊情况,特殊情况是某些情况下我们需要强制读主库,针对这种情况,我们定义一个主键,用该注解标注的就读主库
public @interface Master { }
mapper:
import com.microservice.readwriteseparat.po.TestPO; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper; @Mapper public interface TestPOMapper { int deleteByPrimaryKey(Long id); int insert(TestPO record); int insertSelective(TestPO record); TestPO selectByPrimaryKey(Long id); int updateByPrimaryKeySelective(TestPO record); int updateByPrimaryKey(TestPO record); }
po:
public class TestPO { private Long id; private String name; public Long getId() { return id; } public void setId(Long id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name == null ? null : name.trim(); } }
service:
import com.microservice.readwriteseparat.annotation.Master; import com.microservice.readwriteseparat.mapper.TestPOMapper; import com.microservice.readwriteseparat.po.TestPO; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service public class TestService{ @Autowired private TestPOMapper testPOMapper; public int insert(TestPO aaa) { return testPOMapper.insert(aaa); } @Master public int save(TestPO aaa) { return testPOMapper.insert(aaa); } public TestPO selectByPrimaryKey(Long id) { return testPOMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(id); } @Master public TestPO getById(Long id) { // 有些读操作必须读主数据库 // 比如,获取微信access_token,因为高峰时期主从同步可能延迟 // 这种情况下就必须强制从主数据读 return testPOMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(id); } }
测试:
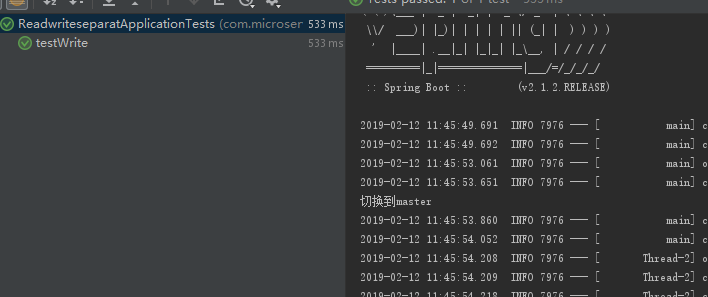
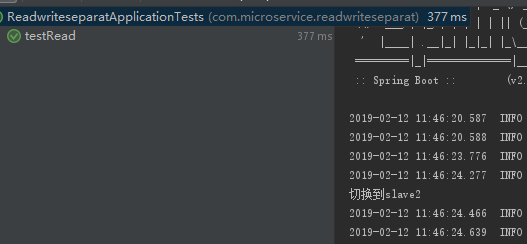
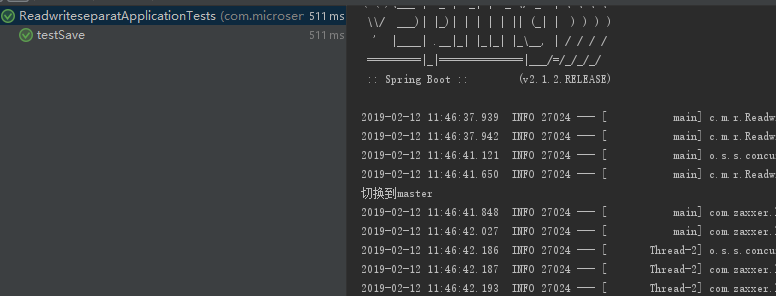
import com.microservice.readwriteseparat.po.TestPO; import com.microservice.readwriteseparat.service.TestService; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner; @RunWith(SpringRunner.class) @SpringBootTest public class ReadwriteseparatApplicationTests { private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ReadwriteseparatApplicationTests.class); @Autowired private TestService aaaService; /** * 写库进行写入 */ @Test public void testWrite() { TestPO aaa = new TestPO(); aaaService.insert(aaa); } /** * 读库(otadb1和otadb2随机)进行读取 */ @Test public void testRead() { TestPO aaa = aaaService.selectByPrimaryKey(1l); logger.info("aaa="+aaa.toString()); } /** * 写库进行写入 */ @Test public void testSave() { TestPO aaa = new TestPO(); aaaService.save(aaa); } /** * 写库进行读取 */ @Test public void testReadFromMaster() { aaaService.getById(10001l); } }
查看控制台:
源码地址:https://github.com/qjm201000/micro_service_readwriteseparat.git
参考资料:https://www.cnblogs.com/cjsblog/p/9712457.html