组件设计初衷就是要配合使用的,最常见的就是形成父子组件的关系:组件 A 在它的模板中使用了组件 B。
1 <html> 2 <head> 3 <title>Vue组件 A 在它的模板中使用了组件 B的例子</title> 4 <script src="vue.js"></script> 5 <style type="text/css"> 6 </style> 7 </head> 8 <body> 9 <div id="app"> 10 <my-item :list="list"></my-item> 11 </div> 12 13 14 <script> 15 new Vue({ 16 el:"#app", 17 data:{ 18 list:["第一项","第二项","第三项"] 19 }, 20 components:{
// 组件A 21 "my-item":{ 22 template : ` 23 <div> 24 <ul> 25 <li v-for="item in list">{{ item }}</li> 26 </ul> 27 <my-list :list="list"></my-list> 28 </div> 29 `, 30 props:['list'], 31 32 components:{
// 组件B 33 "my-list":{ 34 template : ` 35 <div> 36 <ul> 37 <li v-for="item in list">{{ item }}</li> 38 </ul> 39 </div> 40 `, 41 props:['list'] 42 } 43 44 } 45 46 }, 47 } 48 }) 49 </script> 50 </body> 51 </html>
在 Vue 中,父子组件的关系可以总结为 prop 向下传递,事件向上传递。父组件通过 prop 给子组件下发数据,子组件通过事件给父组件发送消息。看看它们是怎么工作的。

Prop
使用 Prop 传递数据
组件实例的作用域是孤立的。这意味着不能 (也不应该) 在子组件的模板内直接引用父组件的数据。父组件的数据需要通过 prop 才能下发到子组件中。
我们来看一个例子:
1 <html> 2 <head> 3 <title>Vue子组件的模板内直接引用父组件的数据</title> 4 <script src="vue.js"></script> 5 <style type="text/css"> 6 </style> 7 </head> 8 <body> 9 <div id="app"> 10 <child></child> 11 </div> 12 13 14 <script> 15 new Vue({ 16 el:"#app", 17 data:{ 18 message:"Hello" 19 20 }, 21 components:{ 22 "child":{ 23 template:"<p>{{ message }}</p>" 24 } 25 26 } 27 28 }) 29 </script> 30 </body> 31 </html>
这样子组件直接引用父组件的数据会出错!

子组件要显式地用 props 选项声明它预期的数据:
1 <html> 2 <head> 3 <title>Vue props父子之间通信</title> 4 <script src="vue.js"></script> 5 <style type="text/css"> 6 </style> 7 </head> 8 <body> 9 <div id="app"> 10 <child message="Hello Vue!!!"></child> 11 </div> 12 13 14 <script> 15 new Vue({ 16 el:"#app", 17 components:{ 18 "child":{ 19 template:"<p>{{ message }}</p>" , 20 props:['message'] 21 }, 22 } 23 24 }) 25 </script> 26 </body> 27 </html>
这样就可以正常显示我们想要的结果

模板的要求
注意:组件的模板只能有一个根元素。下面的情况是不允许的。
template: `<div>这是一个局部的自定义组件,只能在当前Vue实例中使用</div>
<button>hello</button>`,camelCase vs. kebab-case
HTML 特性是不区分大小写的。所以,当使用的不是字符串模板时,camelCase (驼峰式命名) 的 prop 需要转换为相对应的 kebab-case (短横线分隔式命名):
<div id="example"> <child myMessage="Hello Vue!!!"></child> </div> <script> new Vue({ el:"#example", components:{ "child":{ template:"<p>{{ myMessage }}</p>", props:["myMessage"] } } }) </script>
这样就会报错
应改为
<div id="example"> <child my-Message="Hello Vue!!!"></child> </div>
动态prop:
与绑定到任何普通的 HTML 特性相类似,我们可以用 v-bind 来动态地将 prop 绑定到父组件的数据。每当父组件的数据变化时,该变化也会传导给子组件:
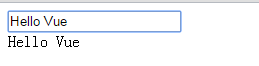
1 <div id="example"> 2 <input v-model="parentMsg"><br> 3 <child :message="parentMsg"></child> 4 </div> 5 <script> 6 Vue.component("child",{ 7 template:"<span>{{ message }}</span>", 8 props:["message"] 9 10 }) 11 new Vue({ 12 el:"#example", 13 data:{ 14 parentMsg:"" 15 } 16 }) 17 </script>
浏览器打开显示
如果你想把一个对象的所有属性作为 prop 进行传递,可以使用不带任何参数的 v-bind (即用 v-bind 而不是 v-bind:prop-name)。
这句话怎么理解呢?我们看一个例子
1 <div id="app"> 2 <my-component v-bind="todo"></my-component> <!--重点就是这-->
<!--不用将对象的属性写成 v-bind:first="todo.first" v-bind:second="todo.second"-->
3 </div>
Vue.component("my-component", { template: "<div><span>第一个值是:{{first}},第二个值是:{{ second }}</span></div>", props:["first","second"] }) new Vue({ el:"#app", data:{ todo:{ first:"Hello world", second:"Hello Vue" } } })
字面量语法 vs 动态语法
初学者常犯的一个错误是使用字面量语法传递数值:
<!-- 传递了一个字符串 "1" -->
|
因为它是一个字面量 prop,它的值是字符串 "1" 而不是一个数值。如果想传递一个真正的 JavaScript 数值,则需要使用 v-bind,从而让它的值被当作 JavaScript 表达式计算:
<!-- 传递真正的数值 -->
|
例子如下:
<div id="example"> <child num1="4" v-bind:num2="4"></child> </div> <script> Vue.component("child", { template:"<p>使用了字面量传递数值+2得出结果:{{num1 + 2}}<br>使用了动态语法传递数值+2的结果:{{num2 + 2}}</p>", props:["num1","num2"] }) new Vue({ el:"#example", }) </script>
浏览器打开显示:

单向数据流
Prop 是单向绑定的:当父组件的属性变化时,将传导给子组件,但是反过来不会。这是为了防止子组件无意间修改了父组件的状态,来避免应用的数据流变得难以理解。
另外,每次父组件更新时,子组件的所有 prop 都会更新为最新值。这意味着你不应该在子组件内部改变 prop。如果你这么做了,Vue 会在控制台给出警告。
1 <html> 2 <head> 3 <title>Vue单向数据流</title> 4 <script src="vue.js"></script> 5 </head> 6 <body> 7 <div id="example"> 8 <my-button :count="count"></my-button> 9 </div> 10 <script> 11 Vue.component("my-button", { 12 props:["count"], 13 template:"<button @click='changeMessage'>{{ count }}</button>", 14 methods:{ 15 changeMessage:function(){ 16 this.count++ 17 } 18 } 19 }) 20 new Vue({ 21 el:"#example", 22 data:{ 23 count:0 24 } 25 }) 26 </script> 27 28 </body> 29 </html>
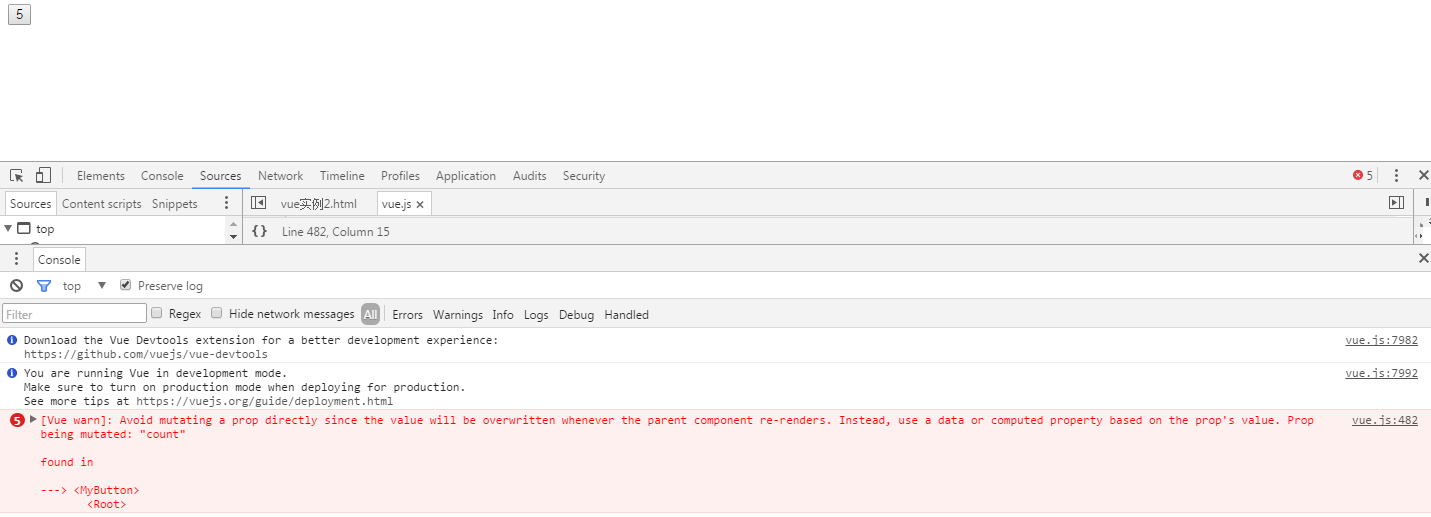
虽然想要做的功能实现了但vue报了个错,你不应该在子组件内部改变 prop
在两种情况下,我们很容易忍不住想去修改 prop 中数据:
-
Prop 作为初始值传入后,子组件想把它当作局部数据来用;
-
Prop 作为原始数据传入,由子组件处理成其它数据输出。
上面的例子就是第一种情况子组件怎么把它当局部数据用?
定义一个局部变量,并用 prop 的值初始化它:
data:function(){
return {
initCount: this.count
}
}
1 <html> 2 <head> 3 <title>Vue单向数据流</title> 4 <script src="vue.js"></script> 5 </head> 6 <body> 7 <div id="example"> 8 <my-button :count="count"></my-button> 9 </div> 10 <script> 11 Vue.component("my-button", { 12 props:["count"], 13 template:"<button @click='changeMessage'>{{ initCount }}</button>",//别忘了这里也需要修改 14 data:function(){ 15 return { 16 initCount: this.count 17 } 18 }, 19 methods:{ 20 changeMessage:function(){ 21 this.initCount++ 22 } 23 } 24 }) 25 new Vue({ 26 el:"#example", 27 data:{ 28 count:0 29 } 30 }) 31 </script> 32 33 </body> 34 </html>
这样就ok了!
第二种情况请看下面例子:
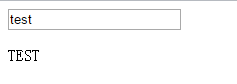
1 <html> 2 <head> 3 <title>Vue单向数据流</title> 4 <script src="vue.js"></script> 5 </head> 6 <body> 7 <div id="example"> 8 <input v-model="message"> 9 <child :message="message"></child> 10 </div> 11 <script> 12 Vue.component("child", { 13 props:["message"], 14 template:"<p>{{ message }}</p>" 15 }) 16 new Vue({ 17 el:"#example", 18 data:{ 19 message:"test" 20 } 21 }) 22 </script> 23 </body> 24 </html>

这是一个双向绑定的例子,我们如何把输入的值将它用p标签转化成大写显示出来!
computed:{
changeMessage:function(){
return this.message.trim().toUpperCase();
}
}
1 <html> 2 <head> 3 <title>Vue单向数据流</title> 4 <script src="vue.js"></script> 5 </head> 6 <body> 7 <div id="example"> 8 <input v-model="message"> 9 <child :message="message"></child> 10 </div> 11 <script> 12 Vue.component("child", { 13 props:["message"], 14 template:"<p>{{ changeMessage }}</p>", 15 computed:{ 16 changeMessage:function(){ 17 return this.message.trim().toUpperCase(); 18 } 19 } 20 }) 21 new Vue({ 22 el:"#example", 23 data:{ 24 message:"test" 25 } 26 }) 27 </script> 28 </body> 29 </html>
props验证
我们可以为组件的 prop 指定验证规则。如果传入的数据不符合要求,Vue 会发出警告。这对于开发给他人使用的组件非常有用。
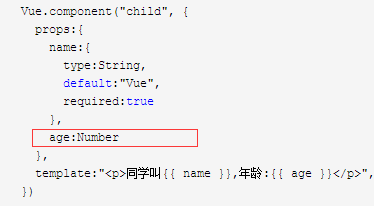
<html> <head> <title>Vueprops验证</title> <script src="vue.js"></script> </head> <body> <div id="example"> <child :name="name" :age="age" ></child> </div> <script> Vue.component("child", { props:{ name:{ type:String, default:"Vue", required:true }, age:Number }, template:"<p>同学叫{{ name }},年龄:{{ age }}</p>", }) new Vue({ el:"#example", data:{ name:"胡小明", age:18, } }) </script> </body> </html>
就从这个简单的例子分析一下用法:
type:可以使用type来声明这个参数可以接受的数据的类型,当检查规则只有一个的时候type可以略写如
当参数可以是多种类型的其中一个的时候,使用数组来表示
message:[String,Number]
type可以是以下原生类型:
String
Number
Boolean
Function
Object
Array
Symbol
required:可以使用required选项来声明这个参数是否必须传入。如果是true则为必填项,如不填则报出警告
defaule:使用default选项来指定当父组件未传入参数时props变量的默认值:
validator:当校验规则很复杂,默认提供的校验规则无法满足的时候可以使用自定义函数来校验。(上面代码没有写这个例子)
举例当小明可以去网吧上网的时候必定年龄是>=18的
1 props:{ 2 age:{ 3 validator:function(value){ 4 return value >= 18 5 } 6 } 7 8 }