在Spring Security之前
我曾经使用 Interceptor 实现了一个简单网站Demo的登录拦截和Session处理工作,虽然能够实现相应的功能,但是无疑Spring Security提供的配置方法更加简单明确,能够更好的保护Web应用。
Spring Security的相关结构
这里大家可以参考Spring Security的官方介绍文档:spring-security-architecture
简单的来说:
-
Spring Security是一个单一的
Filter,其具体的类型是FilterChainProxy,其是作为@Bean在ApplicationContext中配置的。 -
从容器的角度来看,Spring Security是一个单一的Filter,但是在其中有很多额外的Filter,每一个都扮演着他们各自的角色,如下图所示:
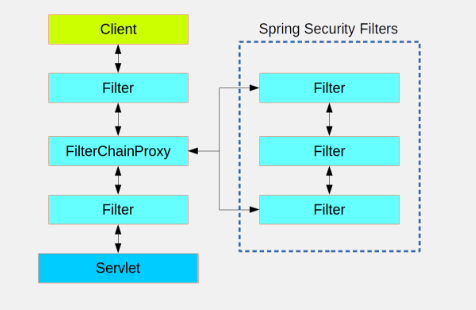
-
Spring Security的身份验证,主要由
AuthenticationManager这个接口完成,其验证的主要方法是authenticate()
public interface AuthenticationManager {
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException;
}
- 该方法可以完成三件事:
- 如果它可以验证输入代表一个有效的主体,就返回一个
Authentication(通常包含authenticated=true) - 如果它可以验证输入代表一个无效的主体,就throw一个
AuthenticationException - 如果它不能决断,就返回
null
- 如果它可以验证输入代表一个有效的主体,就返回一个
- 最常用的
AuthicationManager的实现是ProviderManager,它将其委托给AuthticationProvider这个实例,AuthenticationProvider和AuthenticationManager有一点像,但是含有一些额外的方法,来允许调用者来查询是否支持该Authenticaion形式。
public interface AuthenticationProvider {
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException;
boolean supports(Class<?> authentication);
}
supports()方法中的Class<?>参数是Class<? extends Authentication>,它只会询问其是否支持传递给authenticate()方法。
-
在同一个程序中,一个
ProviderManager通过委托一系列的AuthenticaitonProviders,以此来支支持多个不同的认证机制,如果ProviderManager无法识别一个特定的Authentication实例类型,则会跳过它。 -
很多时候,一个程序含有多个资源保护逻辑组,每一个组都有他们独有的
AuthenticationManager,通常他们共享父级,那么父级就成为了了一个"global"资源,作为所有provider的后背。
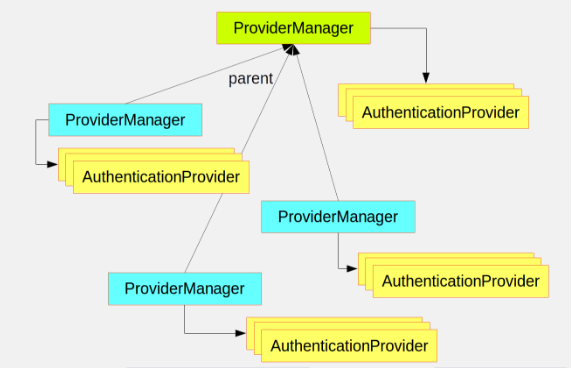
-
Spring Security提供了一些配置帮助我们快速的开启验证功能,最常用的就是
AuthenticationManagerBuiler,它在内存(in-memory)、JDBC、LDAP或者个人定制的UserDetailService这些领域都很擅长。
使用Spring Security实现访问和权限控制
注意:本后续代码以SpringBoot为框架实现,其DEMO Git: Spring-Security-Demo
- 主要通过重载WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter的configure方法进行访问和权限控制
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| configure(WebSecurity) | 通过重载,配置Spring Security的Filter链 |
| configure(HttpSecurity) | 通过重载,配置如何拦截器保护请求 |
| configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder) | 通过重载,配置user-detail服务 |
- 我们重写如下方法:
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/index").hasAnyAuthority("ROLE_USER","ROLE_ADMIN")
.antMatchers("/oss").hasAuthority("ROLE_ADMIN")
.antMatchers(HttpMethod.GET, "/login").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.loginPage("/login")
.permitAll()//.successHandler(successHandler)
.and()
.logout()
.logoutSuccessUrl("/")
.permitAll();
}
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.inMemoryAuthentication().passwordEncoder(new BCryptPasswordEncoder())
.withUser("root").password(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("root")).roles("USER","ADMIN").and()
.withUser("normal").password(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("normal")).roles("USER");
//auth.authenticationProvider(userProvider);
//auth.authenticationProvider(afterProvider);
}
- 通过`antMatchers()`进行URL匹配,再进行相应的处理,比如见上代码,我们将**/index**和**/oss**两个链接进行了拦截,并分别要求拥有`ROLE_USER`或`ROLE_ADMIN`、`ROLE_ADMIN`这两个身份才能访问。
- `anyRequest().authenticated()`指其他请求都会需要验证
- `formLogin()`使其有了登录页面,如果没有后面的`loginPage()`,则会默认生成一个Spring Security的页面,而后面注释掉的`successHandler`则是后续会讲到的。
- `permitAll()`则表示当前连接不需要认证。
- `logout()`会拦截所以的**logout**请求,完成登出操作,`logoutSuccessUrl()`则是登出后的重定向地址。
- `and()`在其中起连接作用。
-
一些常用的保护路径配置方法
- authenticated() : 允许认证过的用户访问
- denyAll() : 无条件拒绝所有访问
- fullyAuthenticated() : 如果用户是完整认证(不通过Remeber me)访问
- hasIpAdress(String) : 如果骑牛来自给定IP地址,就可以访问
- hasAnyAuthority(String ...) : 如果用于具备任意一个给定角色,就可以访问
- hasAnthority(String) : 如果用户具备给定角色,就可以访问
- permitAl() : 无条件允许方法
- remeberMe():如果用户是通过Remeber-me认证的,就可以访问
- 另外,与Autheority对应有一个Role,两者是一个概念,Autheority必须以“ROLE_”开头,而Role不需要,见上代码。
-
则此时我们的root账号既能够访问index也能够访问oss,而normal账号只能访问index,不能访问oss,如果访问oss会出现:
There was an unexpected error (type=Forbidden, status=403). -
上面我们通过重载configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth)生成了两个内存用户root和normal,我们也可以通过jdbc等方法实现。
通过AuthenticationSuccessHandler实现认证成功后的处理
- 通过实现AuthenticationSuccessHandler接口,我们可以在验证成功后执行相应的代码,比如
Token的设置等等,比如我现在打印一条登录信息,并将请求重定向到首页
@Component
public class SuccessHandler implements AuthenticationSuccessHandler{
@Override
public void onAuthenticationSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
Authentication authentication) throws IOException, ServletException {
System.out.println(authentication.getName()+" is loging , role is"+authentication.getAuthorities());
response.sendRedirect("/");
}
- 并将其添加到
formLogin()后,即:
.formLogin()
.loginPage("/login")
.permitAll().successHandler(successHandler)
- 再次登录root账户,则会在控制台看到: root is loging , role is[ROLE_ADMIN, ROLE_USER]
通过AuthenticationProvider实现个性化认证
- 我们建立一个
UserAuthProvider,并让其实现AuthenticationProvider接口:
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------------------------------------");
System.out.println("This is UserAuthProvider");
System.out.println("starting authenticate ... ...");
System.out.println("Credentials:"+authentication.getCredentials());
System.out.println("Name:"+authentication.getName());
System.out.println("Class:"+authentication.getClass());
System.out.println("Details:"+authentication.getDetails());
System.out.println("Principal:"+authentication.getPrincipal());
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------------------------------------");
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken auth=new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(authentication.getPrincipal(), authentication.getCredentials());
return auth;
}
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> authentication) {
System.out.println("This is UserAuthProvider");
System.out.println("starting supports");
System.out.println(authentication.getClass());
return false;
}
- 同时,我们注释掉以前的
auth.inMemoryAuthentication(),将UserAuthProvider加入到AuthenticationManagerBuilder中,即:
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
// auth.inMemoryAuthentication().passwordEncoder(new BCryptPasswordEncoder())
// .withUser("root").password(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("root")).roles("USER","ADMIN").and()
// .withUser("normal").password(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("normal")).roles("USER");
auth.authenticationProvider(userProvider);
auth.authenticationProvider(afterProvider);
}
- 此时我们再次登录,会发现控制台会输出
This is UserAuthProvider
starting supports
java.lang. Class
- 其原因是我们重写的
supports()方法,永远返回false,而返回false时,即不会再调用authenticate()进行认证操作(正如上面所介绍的),我们将supports()的返回值变成true,再次登录(username: root password: 1234),则控制台会输出
This is UserAuthProvider
starting supports
class java.lang.Class
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
This is UserAuthProvider
starting authenticate ... ...
Credentials:1234
Name:root
Class:class org.springframework.security.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken
Details:org.springframework.security.web.authentication.WebAuthenticationDetails@166c8: RemoteIpAddress: 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1; SessionId: node04v47liue6knt1oghnzgiqb9dx0
Principal:root
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
root is loging , role is[]
-
即成功登录了,因为我们在
authenticate()方法中直接声明了一个Authentication的实例UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken,并返回了,正如上面所说,当返回Authentication实例时,则默认为授权成功,而如果我们返回null,则说明无法判断,不会登录成功。 -
此时我们再创建一个对象
UserAfterProvider,其也实现AuthenticationProvider接口,并将UserAfterProvider和UserAuthProvider的authenticate()返回值都设置为null,我们再次使用上面的数据进行登录,控制台输出如下:
This is UserAuthProvider
starting supports
class java.lang.Class
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
This is UserAuthProvider
starting authenticate ... ...
Credentials:1234
Name:root
Class:class org.springframework.security.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken
Details:org.springframework.security.web.authentication.WebAuthenticationDetails@43458: RemoteIpAddress: 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1; SessionId: node01m47f3t6xq5a470fu07jaipzb0
Principal:root
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
This is UserAfterProvider
starting supports
class java.lang.Class
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
This is UserAfterProvider
starting authenticate ... ...
Credentials:1234
Name:root
Class:class org.springframework.security.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken
Details:org.springframework.security.web.authentication.WebAuthenticationDetails@43458: RemoteIpAddress: 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1; SessionId: node01m47f3t6xq5a470fu07jaipzb0
Principal:root
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
- 即两个Porvider都进行了验证,都没有通过(返回null),说明所有加入
AuthenticationManagerBuilder的验证都会进行一遍,那么如果我们将其中一个Provider的authenticate()返回值还原为Authentication实例,再次登录,则控制台会输出如下结果:
This is UserAuthProvider
starting supports
class java.lang.Class
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
This is UserAuthProvider
starting authenticate ... ...
Credentials:1234
Name:root
Class:class org.springframework.security.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken
Details:org.springframework.security.web.authentication.WebAuthenticationDetails@166c8: RemoteIpAddress: 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1; SessionId: node04v47liue6knt1oghnzgiqb9dx0
Principal:root
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
root is loging , role is[]
This is UserAuthProvider
starting supports
class java.lang.Class
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
This is UserAuthProvider
starting authenticate ... ...
Credentials:null
Name:root
Class:class org.springframework.security.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken
Details:org.springframework.security.web.authentication.WebAuthenticationDetails@166c8: RemoteIpAddress: 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1; SessionId: node04v47liue6knt1oghnzgiqb9dx0
Principal:root
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
-
因为我们重写了
AuthenticationSuccessHandler,所以验证成功后悔重定向到/,而我Controller里对/又做了一次重定向到/index,所以发生了两次验证,而这次我们发现因为UserAuthProvider通过了,所以UserAfterProvider并没有进行验证,所以我们可以知道,只要有一个Provider通过了验证我们就可以认为通过了验证。 -
因此,我们可以通过实现
AuthenticationProvider来写入自己的一些认证逻辑,甚至可以@Autowire相关Service来辅助实现。
我的博客即将搬运同步至腾讯云+社区,邀请大家一同入驻:https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/support-plan?invite_code=1353hw8jzy7ee