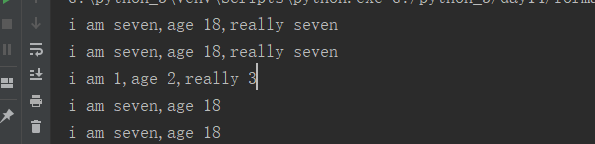
1.format()格式方法传值时,必须要一一对应,如果不对应则会报错
# format()格式方法传值时,必须要一一对应,如果不对应则会报错 tpl = "i am {},age {},{}".format("seven",18,'alex') print(tpl) #可以通过索引来传值 tpl = "i am {0},age {1},{2}".format("seven",18,'alex') print(tpl) #索引位置不同,则传过来的值不同 tpl = "i am {2},age {1},{0}".format("seven",18,'alex') print(tpl)
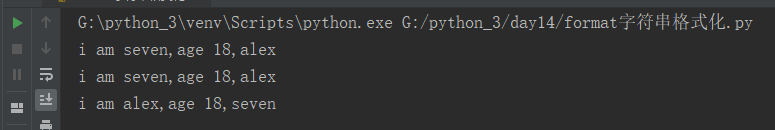
2.其他传值方式
# 可通过字典的方式传值 tpl = "i am {name},age {age},really {name}".format(name ='seven',age =18) print(tpl) tpl = "i am {name},age {age},really {name}".format(**{"name" :'seven',"age" :18}) print(tpl) #可通过列表的方式传值 tpl = "i am {0[0]},age {0[1]},really {0[2]}".format([1,2,3],[11,22,33]) print(tpl) # 字典与类型取值联合使用 tpl = "i am {name:s},age {age:d}".format(name="seven",age =18) print(tpl) tpl = "i am {:s},age {:d}".format("seven",18) print(tpl)