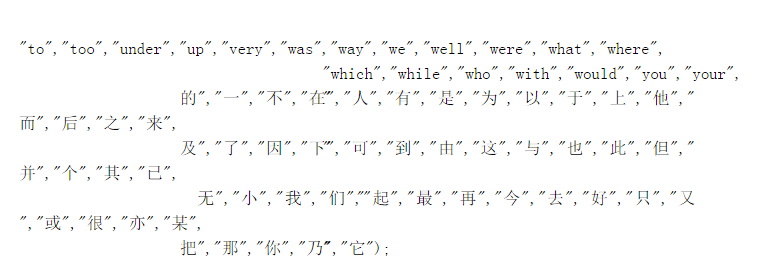二 倒排索引
倒排索引(英语:Inverted index),也常被称为反向索引、置入档案或反向档案,是一种索引方法,被用来存储在全文搜索下某个单词在一个文档或者一组文档中的存储位置的映射。它是文档检索系统中最常用的数据结构。
有两种不同的反向索引形式:
后者的形式提供了更多的兼容性(比如短语搜索),但是需要更多的时间和空间来创建。

使用场景:
倒排索引通常用在需要快速搜索查询响应的场景。可以对一个查询的结果进行预处理并存储在一个数据库中。
以英文为例,下面是要被索引的文本:
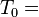
"it is what it is"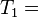
"what is it"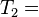
"it is a banana"
我们就能得到下面的反向文件索引:
"a": {2}
"banana": {2}
"is": {0, 1, 2}
"it": {0, 1, 2}
"what": {0, 1}
检索的条件"what", "is" 和 "it" 将对应这个集合: 。
。
对相同的文字,我们得到后面这些完全反向索引,有文档数量和当前查询的单词结果组成的的成对数据。 同样,文档数量和当前查询的单词结果都从零开始。所以,"banana": {(2, 3)} 就是说 "banana"在第三个文档里 (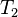 ),而且在第三个文档的位置是第四个单词(地址为 3)。
),而且在第三个文档的位置是第四个单词(地址为 3)。
"a": {(2, 2)}
"banana": {(2, 3)}
"is": {(0, 1), (0, 4), (1, 1), (2, 1)}
"it": {(0, 0), (0, 3), (1, 2), (2, 0)}
"what": {(0, 2), (1, 0)}
如果我们执行短语搜索"what is it" 我们得到这个短语的全部单词各自的结果所在文档为文档0和文档1。但是这个短语检索的连续的条件仅仅在文档1得到。
2.分析和设计
(1)Map过程
首先使用默认的TextInputFormat类对输入文件进行处理,得到文本中每行的偏移量及其内容,Map过程首先必须分析输入的<key, value>对,得到倒排索引中需要的三个信息:单词、文档URI和词频,如图所示:

存在两个问题,第一:<key, value>对只能有两个值,在不使用Hadoop自定义数据类型的情况下,需要根据情况将其中的两个值合并成一个值,作为value或key值;
第二,通过一个Reduce过程无法同时完成词频统计和生成文档列表,所以必须增加一个Combine过程完成词频统计
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | public static class InvertedIndexMapper extends Mapper<Object, Text, Text, Text> { private Text keyInfo = new Text(); //存储单词和URI的组合 private Text valueInfo = new Text();//存储词频 private FileSplit split; //存储Split对象 public void map(Object key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { //获得<key,value>对所属的FileSplit对象 split = (FileSplit)context.getInputSplit(); StringTokenizer itr = new StringTokenizer(value.toString()); while(itr.hasMoreTokens()) { //key值由单词和URI组成,如"MapReduce:1.txt" keyInfo.set(itr.nextToken() + ":" + split.getPath().toString()); // 词频初始为1 valueInfo.set("1"); context.write(keyInfo, valueInfo); } }} |
(2)Combine过程
将key值相同的value值累加,得到一个单词在文档中的词频,如图
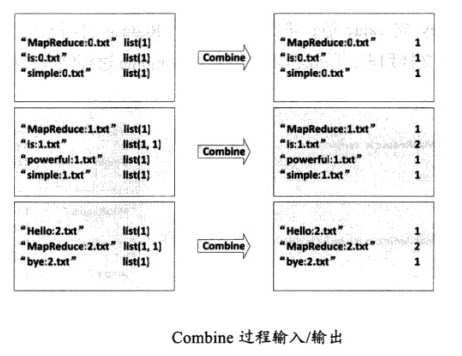
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | public static class InvertedIndexCombiner extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, Text> { private Text info = new Text(); public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<Text>values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { //统计词频 int sum = 0; for(Text value : values) { sum += Integer.parseInt(value.toString()); } int splitIndex= key.toString().indexOf(":"); //重新设置value值由URI和词频组成 info.set(key.toString().substring(splitIndex + 1) + ":" + sum); //重新设置key值为单词 key.set(key.toString().substring(0, splitIndex)); context.write(key, info); }} |
(3)Reduce过程
讲过上述两个过程后,Reduce过程只需将相同key值的value值组合成倒排索引文件所需的格式即可,剩下的事情就可以直接交给MapReduce框架进行处理了

1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | public static class InvertedIndexReducer extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, Text> { private Text result = new Text(); public void reducer(Text key, Iterable<Text>values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { //生成文档列表 String fileList = new String(); for(Text value : values) { fileList += value.toString() + ";"; } result.set(fileList); context.write(key, result); }} |
完整代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 | import java.io.IOException;import java.util.StringTokenizer;import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileSplit;import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;import org.apache.hadoop.util.GenericOptionsParser;public class InvertedIndex { public static class InvertedIndexMapper extends Mapper<Object, Text, Text, Text> { private Text keyInfo = new Text(); private Text valueInfo = new Text(); private FileSplit split; public void map(Object key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { split = (FileSplit)context.getInputSplit(); StringTokenizer itr = new StringTokenizer(value.toString()); while(itr.hasMoreTokens()) { keyInfo.set(itr.nextToken() + ":" + split.getPath().toString()); valueInfo.set("1"); context.write(keyInfo, valueInfo); } } } public static class InvertedIndexCombiner extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, Text> { private Text info = new Text(); public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<Text>values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { int sum = 0; for(Text value : values) { sum += Integer.parseInt(value.toString()); } int splitIndex= key.toString().indexOf(":"); info.set(key.toString().substring(splitIndex + 1) + ":" + sum); key.set(key.toString().substring(0, splitIndex)); context.write(key, info); } } public static class InvertedIndexReducer extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, Text> { private Text result = new Text(); public void reducer(Text key, Iterable<Text>values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { String fileList = new String(); for(Text value : values) { fileList += value.toString() + ";"; } result.set(fileList); context.write(key, result); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ // TODO Auto-generated method stub Configuration conf = new Configuration(); String[] otherArgs = new GenericOptionsParser(conf, args).getRemainingArgs(); if(otherArgs.length != 2) { System.err.println("Usage: wordcount <in> <out>"); System.exit(2); } Job job = new Job(conf, "InvertedIndex"); job.setJarByClass(InvertedIndex.class); job.setMapperClass(InvertedIndexMapper.class); job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class); job.setCombinerClass(InvertedIndexCombiner.class); job.setReducerClass(InvertedIndexReducer.class); job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class); FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[0])); FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[1])); System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1); }} |
建立一个倒排索引的性能分析:
Mapper 端内容解析的计算成本;需要索引的键的基数;每一个键对应的内容标识符的数目。
解决方案: mapper 中对文本或者其他格式的内容解析有时是 MR job 中计算最密集的操作。特别是对类似 XML 或者 JSON 这样的半结构化数据来说更是如此,因为这些数据通常需要将任意数量的信息解析成可用对象。 如果唯一键的数目非常巨大,那么 会有更多的数据发送至 Reduce。 这时候应该通过增加 reduce 的数目来提高 reduce 阶段的并行处理能力。
热点分析:倒排索引计算经常会出现索引存在热点的情况,因为索引键很少均匀分布。如:and,the,are 中文 “一”,“的”等。 由于这些词出现的频率非常高,那么这个reduce 将会异常繁忙, 这将拖累整个 job 的 map 并行进度。 为了规避这个问题。可以选择忽略一些对最终结果没有意义的高词频索引词(索引干扰词)。 如果还要更快,需要定制 partitioner 来均匀处理较高词频有意义词。