题目:已知两个链表head1 和head2 各自有序,请把它们合并成一个链表依然有序。(保留所有结点,即便大小相同)
循环实现:
1.重新申请一个头结点,使用指针p指向他,每新加一个结点,就将指针p后移一位,即指针p永远指向新链表的尾结点
2.由于所用链表第一个结点不赋值,因此指针需要开始从头结点的下一个结点开始判断,如果两个指针都为非空,将data域较小的指针连在新链表的末尾
3.当两个指针有一个到达链表的结尾时,将没有到达末尾的链表连接到新链表之后
递归实现:
1.函数返回条件是有一个链表结束,则返回另一个链表
2.取两个指针data域较小的作为新的头结点,递归调用
实现代码如下:
#include<iostream> using namespace std; struct listnode { int data; listnode *next; }; //尾插法创建链表 listnode *init() { listnode *head=new listnode; head->next=NULL; listnode *p=head; cout<<"please input a number(按-1结束)"<<endl; int data; cin>>data; while(data!=-1) { listnode *temp=(listnode *)malloc(sizeof(listnode)); temp->data=data; temp->next=p->next; p->next=temp; p=temp; cout<<"please input a number(按-1结束)"<<endl; cin>>data; } return head; } //打印链表 void print(listnode *head) { listnode *p=head->next; while(p) { cout<<p->data<<" "; p=p->next; } cout<<endl; } //将两个有序链表合并(循环实现) listnode *hebing(listnode *head1,listnode *head2) { listnode *head=new listnode; head->next=NULL; //声明两个指针分别指向两个链表的数据开始部分 listnode *p1=head1->next; listnode *p2=head2->next; //声明一个指针来指向新链表的最后一个结点,开始时指向head listnode *last=head; while(p1!=NULL && p2!=NULL) { //p1结点的数据小:将last指向p1结点,last和p1分别后移 if(p1->data<p2->data) { last->next=p1; p1=p1->next; last=last->next; } //p2结点数据小:将last指向p2结点,last和p2分别后移 else { last->next=p2; p2=p2->next; last=last->next; } } //当有一个链表结束时候,将last指向还未结束的链表 if(p1==NULL) last->next=p2; else if(p2==NULL) last->next=p1; return head; } //将两个有序链表合并(递归实现) listnode *hebing2(listnode *head1,listnode *head2) { //循环结束条件:当一个链表到达结尾 if(head1==NULL) return head2; if(head2==NULL) return head1; listnode *head=NULL; //选择两个头结点中较小的作为头结点 if(head1->data>head2->data) { head=head2; head->next=hebing2(head1,head2->next); } else { head=head1; head->next=hebing2(head1->next,head2); } return head; } //因为输出时候第一个结点时空的,需要填加一个空的头结点 listnode *diguihebing(listnode *head1,listnode *head2) { listnode *head=new listnode; head->next=hebing2(head1->next,head2->next); return head; }
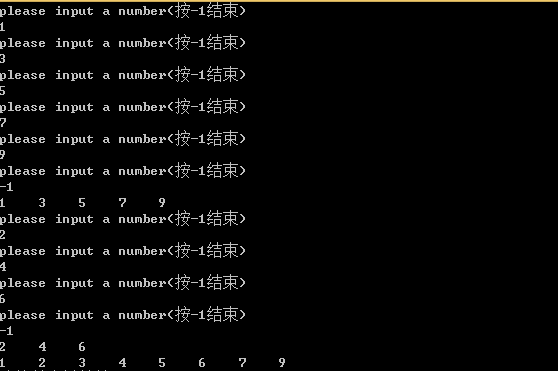
测试代码以及运行结果:
int main() { listnode *head1=init(); print(head1); listnode *head2=init(); print(head2); //listnode *head=hebing(head1,head2);//测试循环代码 //print(head); listnode *head=diguihebing(head1,head2);//测试递归代码 print(head); delete head,head1,head2; return 0; }