要学好C#,基础知识的重要性不言而喻,现将常用到的一些基础进行总结,总结如下:
01. 数据类型转换:
强制类型转换(Chart--> int):
char cr='A'; int i = (int)(cr);
02. 委托/匿名函数/Lamda表达式:
委托是匿名函数的起源,Lamda表达式又是匿名函数的升华。这些又是如何体现的呢,请看:
委托示例:

namespace Delegate { class Program { public delegate void TDelegate(int i, int j); static void Caculator(int i, int j) { Console.WriteLine(i * j * i * j); } public static void InvokeDE() { TDelegate td = new TDelegate(Caculator); td.Invoke(3, 5); } static void Main(string[] args) { InvokeDE(); Console.ReadLine(); } } }
匿名函数示例:

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace CSP { class Program { public delegate void MyDelegate(int x, int y); static void Main(string[] args) { MyDelegate md = delegate(int x, int y) { Console.WriteLine(x + y); }; md(10, 100); Console.ReadLine(); } } }
Lamda表达式(实际就是一个函数)示例:

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace CSP { class Program { private static void LamdaExpression() { int[] InitArr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 }; int ResCount = InitArr.Where(n => n > 6).Count(); Console.WriteLine(ResCount); } static void Main(string[] args) { LamdaExpression(); Console.ReadLine(); } } }
03. 泛型Gereric:
泛型是C#一个非常重要的用法,必须熟记于心:

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace CSP { class Program { public static void GenericFunction() { int i = 10; string HI = "Hello World!"; TestGC<int> tg_int = new TestGC<int>(i); TestGC<string> tg_string = new TestGC<string>(HI); Console.WriteLine(tg_int.t.ToString()); Console.WriteLine(tg_string.t.ToString()); } static void Main(string[] args) { GenericFunction(); Console.ReadLine(); } } public class TestGC<T> { public T t; public TestGC(T t) { this.t = t; } } }
04. 虚方法Virtual:
以前总觉得自己掌握的很好了,最近看了一些文章才对Virtual的执行顺序有了更深的理解,为了加深印象,我添加了示例图并特地将本篇文章在此处进行了引用:

class A { public virtual void Func() // 注意virtual,表明这是一个虚拟函数 { Console.WriteLine("Func In A"); } } class B : A // 注意B是从A类继承,所以A是父类,B是子类 { public override void Func() // 注意override ,表明重新实现了虚函数 { Console.WriteLine("Func In B"); } } class C : B // 注意C是从B类继承,所以B是父类,C是子类 { } class D : A // 注意D是从A类继承,所以A是父类,D是子类 { public new void Func() // 注意new,表明覆盖父类里的同名类,而不是重新实现 { Console.WriteLine("Func In D"); } } class E : D // 注意E是从D类继承,所以D是父类,E是子类 { } class F : A { private new void Func() //注意new关键字前有private修饰符,故该隐藏只在F类内有效 { Console.WriteLine("Func In F"); } public void Func2() { Func(); //在F类内隐藏了基类的Func方法,故此处调用的private new void Func() } } static void Main(string[] args) { A a; // 定义一个a这个A类的对象.这个A就是a的申明类 A b; // 定义一个b这个A类的对象.这个A就是b的申明类 A c; // 定义一个c这个A类的对象.这个A就是c的申明类 A d; // 定义一个d这个A类的对象.这个A就是d的申明类 A e; // 定义一个e这个A类的对象.这个A就是e的申明类 A f; // 定义一个f这个A类的对象.这个A就是f的申明类 a = new A(); // 实例化a对象,A是a的实例类 b = new B(); // 实例化b对象,B是b的实例类 c = new C(); // 实例化c对象,C是c的实例类 d = new D(); // 实例化d对象,D是d的实例类 e = new E(); // 实例化e对象,E是e的实例类 f = new F(); // 实例化f对象,F是f的实例类 Console.WriteLine("a.Func();"); a.Func(); // 执行a.Func:1.先检查申明类A 2.检查到是虚拟方法 3.转去检查实例类A,就为本身 4.执行实例类A中的方法 5.输出结果 Func In A Console.WriteLine("b.Func();"); b.Func(); // 执行b.Func:1.先检查申明类A 2.检查到是虚拟方法 3.转去检查实例类B,有重载的 4.执行实例类B中的方法 5.输出结果 Func In B Console.WriteLine("c.Func();"); c.Func(); // 执行c.Func:1.先检查申明类A 2.检查到是虚拟方法 3.转去检查实例类C,无重载的 4.转去检查类C的父类B,有重载的 5.执行父类B中的Func方法 5.输出结果 Func In B Console.WriteLine("d.Func();"); d.Func(); // 执行d.Func:1.先检查申明类A 2.检查到是虚拟方法 3.转去检查实例类D,无重载的(这个地方要注意了,虽然D里有实现Func(),但没有使用override关键字,所以不会被认为是重载) 4.转去检查类D的父类A,就为本身 5.执行父类A中的Func方法 5.输出结果 Func In A Console.WriteLine("e.Func();"); e.Func(); // 执行e.Func:E继承D,E.Func没有重写父类中的方法,相当于执行父类D中的Func方法,输出结果 Func In A Console.WriteLine("f.Func();"); f.Func(); // 执行f.Func:F类中虽然隐藏了基类中的Func方法,但是有private修饰符,该隐藏只在F类范围内有效。执行f.Func相当于执行其基类中的Func方法,输出结果 Func In A D d1 = new D(); Console.WriteLine("d1.Func();"); d1.Func(); // 执行D类里的Func(),输出结果 Func In D E e1 = new E(); Console.WriteLine("e1.Func();"); e1.Func(); // 执行E类里的Func(),输出结果 Func In D F f1 = new F(); Console.WriteLine("f1.Func();"); f1.Func(); // 执行F类里的Func(),输出结果 Func In A Console.WriteLine("f1.Func2();"); f1.Func2(); // 执行F类里的Func2(),输出结果 Func In F Console.ReadLine(); }
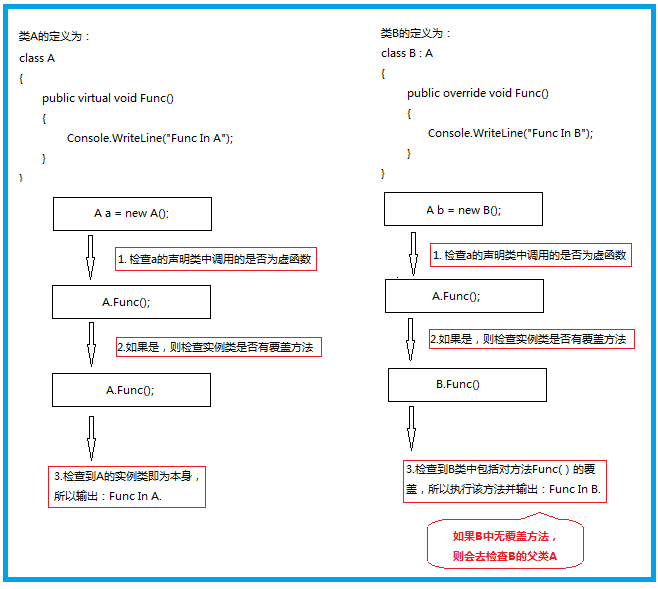
05. New和Override的用法:
New是新建一个新方法,对旧方法进行了屏蔽,而Override只是对父类中的方法进行了覆盖,具体详细用法参见4. Virtual用法示例;
06. foreach用法:
foreach遍历访问的对象需要实现IEnumerable接口或声明GetEnumerator方法的类型;
MSDN上的例子:

using System; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace CSP { public class Person { public string firstName; public string lastName; public Person(string fName, string lName) { this.firstName = fName; this.lastName = lName; } } public class People : IEnumerable { private Person[] _people; public People(Person[] pArray) { _people = new Person[pArray.Length]; for (int i = 0; i < pArray.Length; i++) { _people[i] = pArray[i]; } } // Implementation for the GetEnumerator method. IEnumerator IEnumerable.GetEnumerator() { return (IEnumerator)GetEnumerator(); } public PeopleEnum GetEnumerator() { return new PeopleEnum(_people); } } public class PeopleEnum : IEnumerator { public Person[] _people; int position = -1; public PeopleEnum(Person[] list) { _people = list; } public bool MoveNext() { position++; return (position < _people.Length); } public void Reset() { position = -1; } object IEnumerator.Current { get { return Current; } } public Person Current { get { try { return _people[position]; } catch (IndexOutOfRangeException) { throw new InvalidOperationException(); } } } } class App { static void Main() { Person[] peopleArray = new Person[3] { new Person("John", "Smith"), new Person("Jim", "Johnson"), new Person("Sue", "Rabon"), }; People peopleList = new People(peopleArray); foreach (Person p in peopleList) Console.WriteLine(p.firstName + " " + p.lastName); Console.ReadLine(); } } }
下面例子是对上面的改动,只保留了对GetEnumerator()方法的实现,移除了对IEnumerable接口和IEnumerator接口的继承,执行结果同上例一样:

using System; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace CSP { public class Person { public string firstName; public string lastName; public Person(string fName, string lName) { this.firstName = fName; this.lastName = lName; } } public class People { private Person[] _people; public People(Person[] pArray) { _people = new Person[pArray.Length]; for (int i = 0; i < pArray.Length; i++) { _people[i] = pArray[i]; } } public PeopleEnum GetEnumerator() { return new PeopleEnum(_people); } } public class PeopleEnum { public Person[] _people; int position = -1; public PeopleEnum(Person[] list) { _people = list; } public bool MoveNext() { position++; return (position < _people.Length); } public Person Current { get { try { return _people[position]; } catch (IndexOutOfRangeException) { throw new InvalidOperationException(); } } } } class App { static void Main() { Person[] peopleArray = new Person[3] { new Person("John", "Smith"), new Person("Jim", "Johnson"), new Person("Sue", "Rabon"), }; People peopleList = new People(peopleArray); foreach (Person p in peopleList) Console.WriteLine(p.firstName + " " + p.lastName); Console.ReadLine(); } } }
PS.
A.实现实现IEnumerable接口的同时就必须实现IEnumerator接口;
B.不一定要实现IEnumerable接口,但一定要实现GetEnumrator方法。
对于上述的功能,可以也尝试使用语法糖(便捷写法)C# yield来进行实现;
07. 静态构造函数
静态构造函数,也称静态代码块,主要用于初始化静态变量,示例如下:

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace CSP { public class StaticBlock { public string Title; static StaticBlock() { Console.WriteLine("Here is the static block,only can be called for 1 time!"); } public StaticBlock(string Title) { this.Title = Title; } } class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { StaticBlock sb_morning = new StaticBlock("Good morning!"); Console.WriteLine(sb_morning.Title); StaticBlock sb_afternoon = new StaticBlock("Good afternoon!"); Console.WriteLine(sb_afternoon.Title); Console.ReadLine(); } } }
静态构造函数具有如下特点(来自网络):
A.静态构造函数既无访问修饰符亦无参数;
B.如果没有编写静态构造函数,而这时类中包含带有初始值设定的静态字段,那么编译器会自动生成默认的静态构造函数。
C.在创建第一个类实例或任何静态成员被引用时,.NET将自动调用静态构造函数来初始化类,即无法直接调用与控制静态构造函数。
D.如果类中包含用来开始执行的 Main 方法,则该类的静态构造函数将在调用 Main 方法之前执行。
E.如果类中的静态字段带有初始化,则静态字段的初始化语句将在静态构造函数之前运行。
F.一个类只能有一个静态构造函数,不可以被继承且最多只运行一次。
08. 【反射】typeof/GetType
typeof:获取类运行时的类型及方法列表,参数只能为类名,用法typeof(类名);
GetType:获取类运行时的类型及方法列表,由对象调用,用法:obj.GetType();
09. where T : class
主要用来对接口进行限制,如下所示,限制接口IDataComponentBase<T>中的T必须为一个引用类型,如类,接口,数组;
public interface IDataComponentBase<T> where T : class
10. Guid对象赋值:
Guid gd = new Guid("3a4f38a3-e064-e611-80d6-080027c84e1f");
11. Dispose():
在使用using方法结束时会自动调用Dispose(),以便显示释放非托管资源(前提是该当前类必须实现接口:IDisposable);
12. 保留两位小数:
Decimal OVNum,NCNum;
... ...
Decimal TotNum = OVNum + NCNum;
Decimal d = NCNum * 100 / TotNum;
e.Result = Decimal.Round(d, 2);
13. 利用List自带的Sort进行排序:

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace CA { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { List<Light> lts = new List<Light>(); Light lt0 = new Light(); lt0.LTypeName = "Filament"; lt0.W = 12; Light lt1 = new Light(); lt1.LTypeName = "Common"; lt1.W = 25; Light lt2 = new Light(); lt2.LTypeName = "Efficient"; lt2.W = 50; lts.Add(lt0); lts.Add(lt1); lts.Add(lt2); Console.WriteLine("Before sort:"); foreach (Light l in lts) { Console.WriteLine(l.LTypeName+":"+l.W); } //A~Z //lts.Sort((x, y) => x.LTypeName.CompareTo(y.LTypeName)); //Z~A lts.Sort((x, y) => -x.LTypeName.CompareTo(y.LTypeName)); Console.WriteLine("After sort:"); foreach (Light l in lts) { Console.WriteLine(l.LTypeName + ":" + l.W); } Console.ReadLine(); } } public class Light { public string LTypeName { get; set; } public int W { get; set; } } }
14. 数组,ArrayList,List的区别:
数组的优点是可以存储多个维度的记录,且连续存放,缺点是需要在定义时指定数组的长度,且定义好后不能扩展;
ArrayList在定义时不需要指定长度也不需要定义存入的数据的数据类型,可以自由扩展。所以ArrayList可以存放不同类型的数据(以object存入,要进行装箱操作)到ArrayList,所以ArrayList为非类型安全的;
使用如下所示:
ArrayList al = new ArrayList();
al.Add(100);
al.Add("Hello");
List与ArrayList一样,在定义时不需要指定长度,可以自由扩展。同时,在声明List时,需要定义存入的数据的数据类型,实现了类型安全;
ArrayList的命名空间:System.Collections.ArrayList
List的命名空间:System.Collections.Generic.List
15. const/readonly
关于C#还有更多内容需要研究,希望自己能再接再厉,继续总结!
