在上一篇文章 从零搭建springboot+mybatis逆向工程 中介绍了如何在IDEA+springboot下搭建mybatis逆向工程以及一个简单的接口。本文主要总结一下mapper接口中方法的使用,和个人的一些理解。
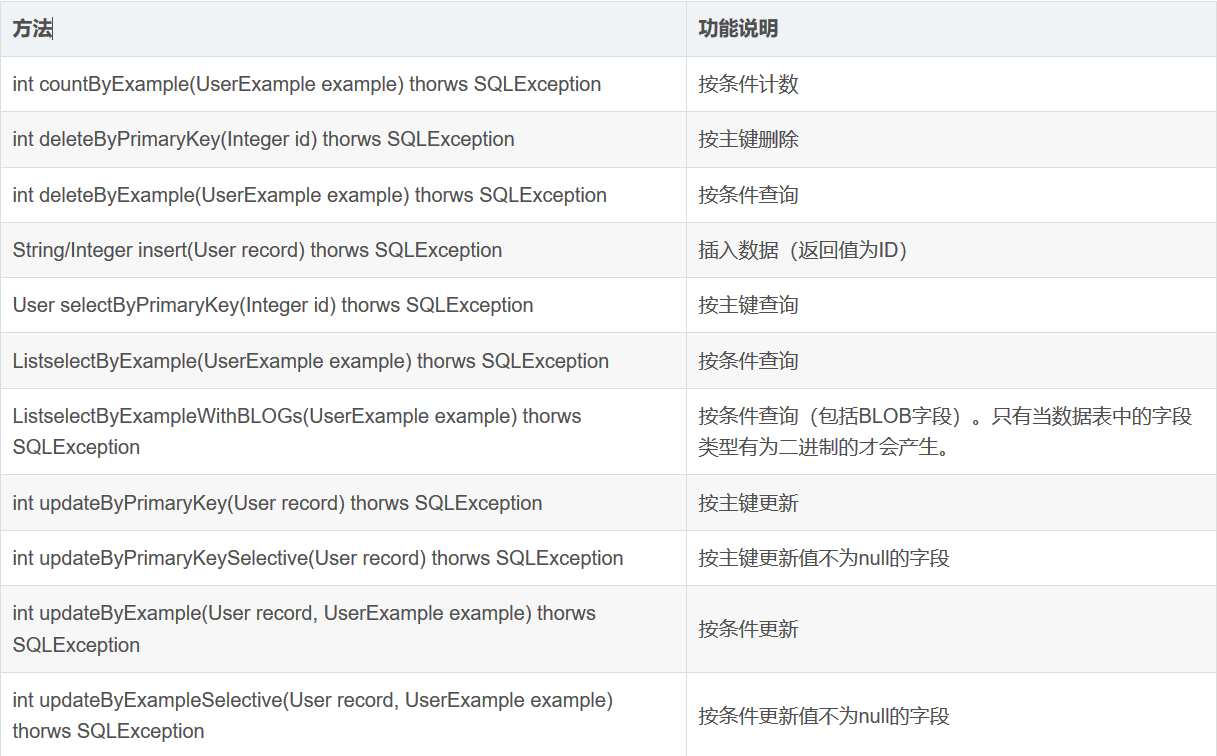
一、mapper接口中的方法解析
mapper接口中的函数及方法
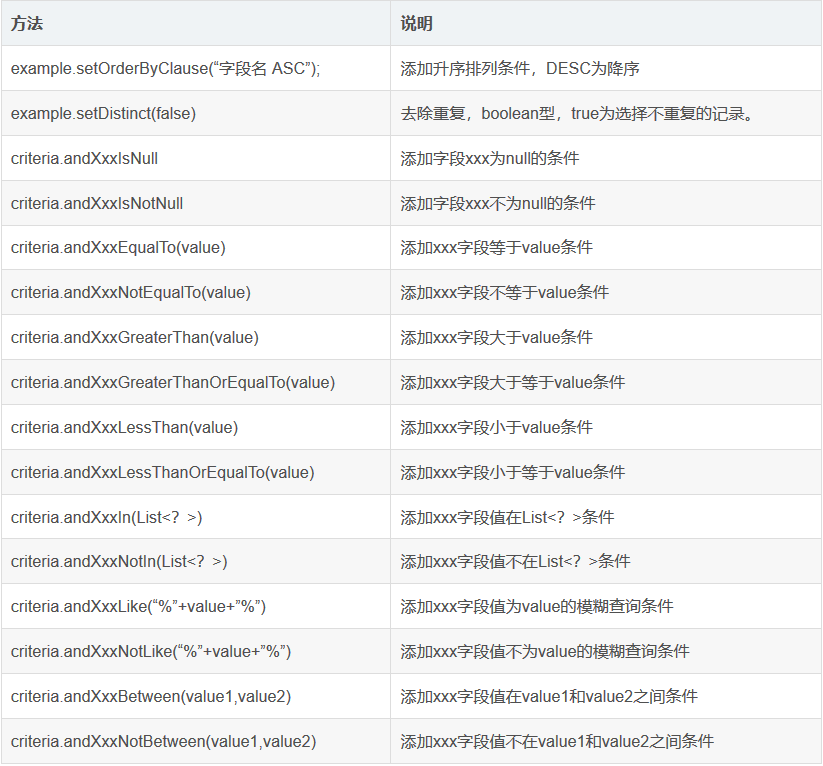
二、example实例解析
mybatis的逆向工程中会生成实例及实例对应的example,example用于添加条件,相当where后面的部分
xxxExample example = new xxxExample();
Criteria criteria = new Example().createCriteria();
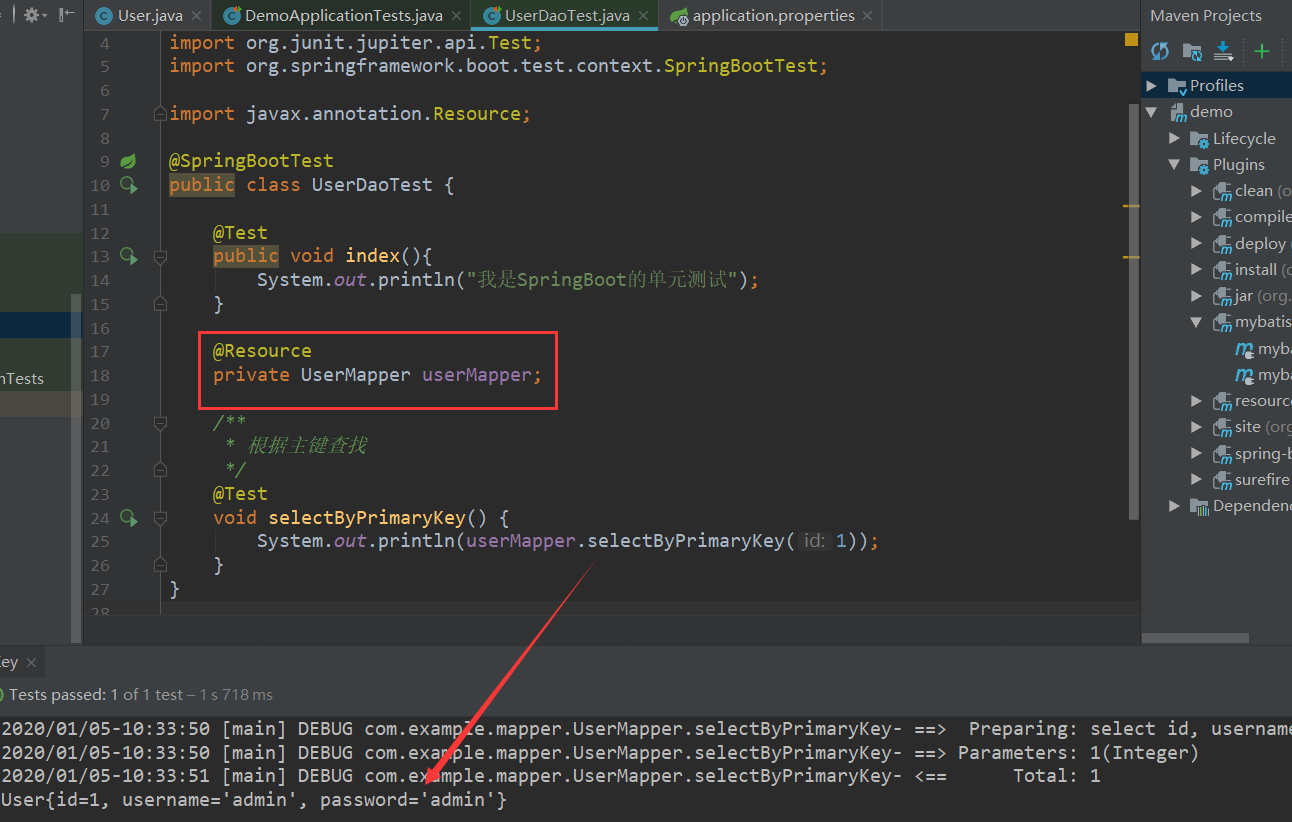
三、单元测试中使用
创建单元测试类,在springboot中十分方便

1、selectByPrimaryKey
先注入userMapper,然后再测试方法
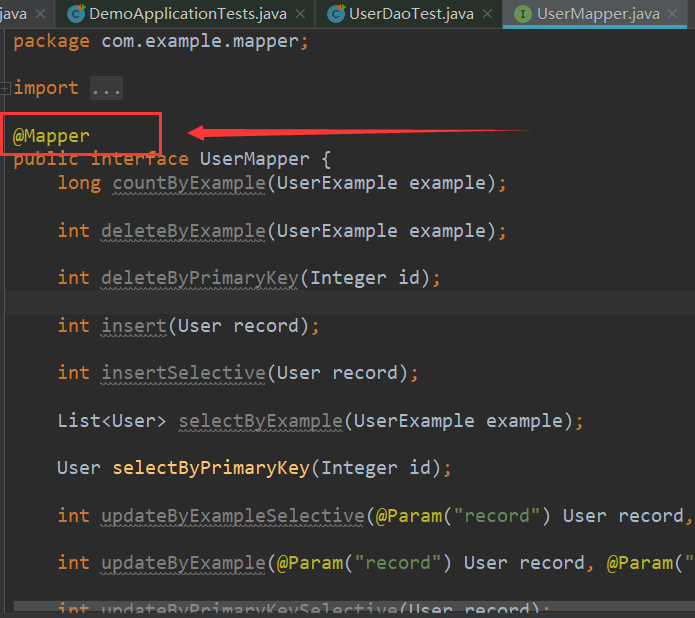
不要忘了在UserMapper接口上加上@Mapper注解,不然会报错
package com.example.dao;
import com.example.mapper.UserMapper;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@SpringBootTest
public class UserDaoTest {
@Test
public void index(){
System.out.println("我是SpringBoot的单元测试");
}
@Resource
private UserMapper userMapper;
/**
* 根据主键查找
*/
@Test
void selectByPrimaryKey() {
System.out.println(userMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(1));
}
}
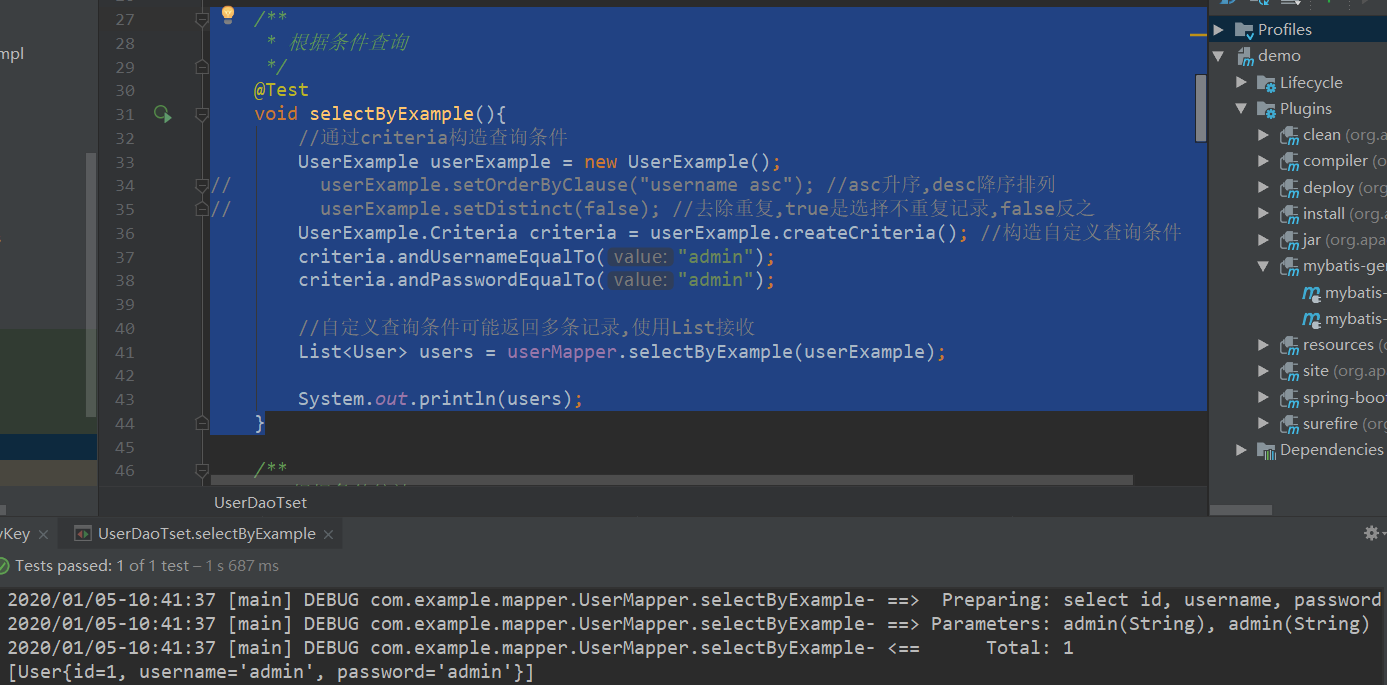
2、selectByExample
/**
* 根据条件查询
*/
@Test
void selectByExample(){
//通过criteria构造查询条件
UserExample userExample = new UserExample();
// userExample.setOrderByClause("username asc"); //asc升序,desc降序排列
// userExample.setDistinct(false); //去除重复,true是选择不重复记录,false反之
UserExample.Criteria criteria = userExample.createCriteria(); //构造自定义查询条件
criteria.andUsernameEqualTo("admin");
criteria.andPasswordEqualTo("admin");
//自定义查询条件可能返回多条记录,使用List接收
List<User> users = userMapper.selectByExample(userExample);
System.out.println(users);
}
3、insert
/**
* 插入
*/
@Test
void insert(){
User user = new User();
// user.setId(null);
user.setUsername("张三");
// user.setPassword();
System.out.println(userMapper.insert(user));
}
4、insertSelective
@Test
void insertSelective(){
User user = new User();
user.setUsername("zhangsan");
System.out.println(userMapper.insertSelective(user));
}
5、deleteByPrimaryKey
@Test
void deleteByPrimaryKey(){
System.out.println(userMapper.deleteByPrimaryKey(2));
}
6、deleteByExample
@Test
void deleteByExample(){
//通过criteria构造查询条件
UserExample userExample = new UserExample();
// userExample.setOrderByClause("username asc"); //asc升序,desc降序排列
// userExample.setDistinct(false); //去除重复,true是选择不重复记录,false反之
UserExample.Criteria criteria = userExample.createCriteria(); //构造自定义查询条件
criteria.andIdBetween(5,13);
//自定义查询条件可能返回多条记录,使用List接收
userMapper.deleteByExample(userExample);
System.out.println();
}
7、updateByPrimaryKey
@Test
void updateByPrimaryKey(){
User user = new User();
user.setId(4);
// user.setUsername("lisi");
userMapper.updateByPrimaryKey(user);
}
8、updateByPrimaryKeySelective
@Test
void updateByPrimaryKeySelective(){
User user = new User();
user.setId(4);
user.setUsername("lisi");
userMapper.updateByPrimaryKeySelective(user);
}
9、updateByExample
@Test
void updateByExample(){
//通过criteria构造查询条件
UserExample userExample = new UserExample();
// userExample.setOrderByClause("username asc"); //asc升序,desc降序排列
// userExample.setDistinct(false); //去除重复,true是选择不重复记录,false反之
UserExample.Criteria criteria = userExample.createCriteria(); //构造自定义查询条件
criteria.andIdEqualTo(3);
User user = new User();
user.setId(3);
user.setUsername("李四2");
// user.setPassword("123456");
userMapper.updateByExample(user,userExample);
}
10、updateByExampleSelective
@Test
void updateByExampleSelective(){
//通过criteria构造查询条件
UserExample userExample = new UserExample();
// userExample.setOrderByClause("username asc"); //asc升序,desc降序排列
// userExample.setDistinct(false); //去除重复,true是选择不重复记录,false反之
UserExample.Criteria criteria = userExample.createCriteria(); //构造自定义查询条件
criteria.andPasswordEqualTo("123456");
User user = new User();
user.setUsername("李四");
// user.setPassword("123456");
userMapper.updateByExampleSelective(user,userExample);
}
四、Example与Selective
1、Example
相当于WHERE,将一些限制条件拼接到SQL语句后面,具体的参照上面所说。这里举一个简单的例子:这里相当于一个登录验证的功能,通过用户名和密码来验证用户
//通过criteria构造查询条件
UserExample userExample = new UserExample();
// userExample.setOrderByClause("username asc"); //asc升序,desc降序排列
// userExample.setDistinct(false); //去除重复,true是选择不重复记录,false反之
UserExample.Criteria criteria = userExample.createCriteria(); //构造自定义查询条件
criteria.andUsernameEqualTo("admin");
criteria.andPasswordEqualTo("admin");
//自定义查询条件可能返回多条记录,使用List接收
List<User> users = userMapper.selectByExample(userExample);
System.out.println(users);
SQL语句如下

查询结果如下

2、Selective
Selective会对为空的字段进行屏蔽
以更新为例
<update id="updateByPrimaryKeySelective" parameterType="com.example.pojo.User">
update t_user
<set>
<if test="username != null">
username = #{username,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="password != null">
password = #{password,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
</set>
where id = #{id,jdbcType=INTEGER}
</update>
<update id="updateByPrimaryKey" parameterType="com.example.pojo.User">
update t_user
set username = #{username,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
password = #{password,jdbcType=VARCHAR}
where id = #{id,jdbcType=INTEGER}
</update>
@Test
void updateByPrimaryKey(){
User user = new User();
user.setId(4);
/**
* updateByPrimaryKey会将主键为4的那条记录更新为除了主键其他字段全为空的一条记录
*/
userMapper.updateByPrimaryKey(user);
}
@Test
void updateByPrimaryKeySelective(){
User user = new User();
user.setId(3);
user.setUsername("lisi");
/**
* updateByPrimaryKeySelective会将主键为3那条记录的username字段更新为“lisi”,其他字段不变
*/
userMapper.updateByPrimaryKeySelective(user);
}