| 这个作业属于课程 | 软件工程 |
|---|---|
| 这个作业的要求在哪里 | 结对项目 |
| 这个作业的目标是 | 实现一个自动生成小学四则运算题目的命令行程序 |
| 成员 | 3118005408 方俊涛 、3118005409 冯宇航 |
@
PSP
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 30 | 20 |
| · Estimate | · 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 30 | 20 |
| Development | 开发 | 470 | 455 |
| · Analysis | · 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 150 | 120 |
| · Design Spec | · 生成设计文档 | 30 | 20 |
| · Design Review | · 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) | 20 | 15 |
| · Coding Standard | · 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 20 | 10 |
| · Design | · 具体设计 | 30 | 20 |
| · Coding | · 具体编码 | 150 | 130 |
| · Code Review | · 代码复审 | 30 | 20 |
| ·Test | · 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 40 | 120 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 75 | 80 |
| · Test Report | · 测试报告 | 25 | 50 |
| · Size Measurement | · 计算工作量 | 20 | 10 |
| · Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | · 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 30 | 20 |
| 合计 | 575 | 555 |
效能分析
花费时间:30min
egg :python main.py -r 50 -n 1000
改进前:
通过pycharm自带的效能分析工具来看,我们的程序在creQuestion()上花费的时间是比较多的,原因是该函数在实现生成表达式时,调用了self.isRepeat(expressionList, expression) 进行查重检测,此步奏涉及到大量的遍历二叉树


def creQuestion(self):
"""
表达式生成主函数
"""
expNum = self.expressionNum
expressionList = []
i = 0
while i < expNum:
random_num_operation = random.randint(1,self.operCount) #运算符的数目
is_need_parenteses = random.randint(0, 1) #是否需要加括号
number_of_oprand = random_num_operation + 1 # 操作数比操作符的数目多1
exp = []
for j in range(random_num_operation + number_of_oprand):
if j % 2 == 0:
# 随机生成操作数(含分数)
exp.append(self.getOperNum()['operStr'])
if j > 1 and exp[j - 1] == '÷' and exp[j] == '0':
while True:
exp[j - 1] = self.generateOperation()
if exp[j - 1] == '÷':
continue
else:
break
else:
# 生成运算符
exp.append(self.generateOperation())
if j > 3:
if exp[j-2] == '÷' : #为了子表达式为真分数,÷左右又括号除外
if exp[j-1] > exp[j-3]:
t = exp[j-1]
exp[j - 1] = exp[j-3]
exp[j - 3] = t
elif exp[j-2] == '-' :
if exp[j-1] < exp[j-3]:
t = exp[j-1]
exp[j - 1] = exp[j-3]
exp[j - 3] = t
# 判断是否要括号
if is_need_parenteses and number_of_oprand != 2:
expression = " ".join(self.generateParentheses(exp, number_of_oprand))
else:
expression = " ".join(exp)
#判断是否有重复
# if self.expressionNum <= 500:
if 1 :
if self.isRepeat(expressionList, expression) :
continue
else:
result = self.calculate(expression)
if result == "False" :
pass
else:
expressionList.append(expression)
#('第 %d 道题' % int(i + 1))
#print(expression)
i = i + 1
else:
result = self.calculate(expression)
if result == "False":
pass
else:
expressionList.append(expression)
# ('第 %d 道题' % int(i + 1))
# print(expression)
i = i + 1
return expressionList
改进后:
出于软件工程的实用性和需求分析,当需要生成的题目数量超过500时,由于题量较多,时间更显得重要,故判断题量较多时可不查重,改进后时间大大缩短
通过pycharm自带的效能分析工具来看,我们改进后的程序在expression_result()上花费的时间是比较多的,原因在于为了计算答案,多次调用suffixExpression进行中缀表达式转后缀表达式并进行计算。思考无果,暂时没有好算法进行替换
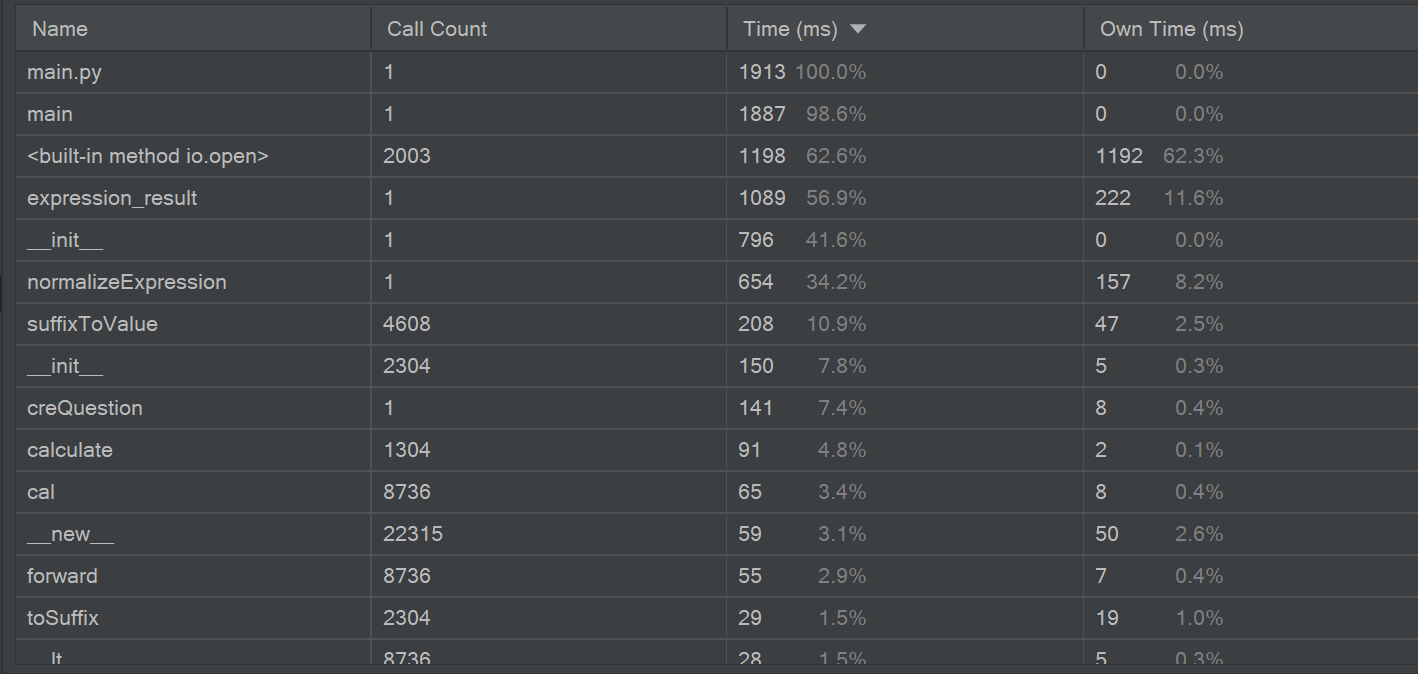
时间缩短为原来的1/37
def expression_result(self,exp_list):
"""
求表达式的结果
:param exp_list: 表达式列表
:return: None
"""
self.exp_list =exp_list
if os.path.exists('Answer.txt'): # 清空上一次的答案
with open('Answer.txt', 'r+') as file:
file.truncate(0)
for i, exp in enumerate(self.exp_list):
order_str = str(i + 1)
suffixExpression = SuffixExpression(exp)
#print("------suffixExpression:{}---------".format(str(suffixExpression.suffixToValue()) ))
exp_value = str(suffixExpression.suffixToValue()) + '
'
result = "Answer"+order_str + ': ' + exp_value
with open('Answer.txt', 'a+', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(result)
设计实现过程以及重要代码说明
本次设计程序我们采取了面向对象的方法进行编程,对于整个程序进行分析,我们以生成题目、计算答案、校对答案三个功能把它分为了三个模块构造了四个类,其中BinaryTree类主要服务于Product类实现生成题目的功能
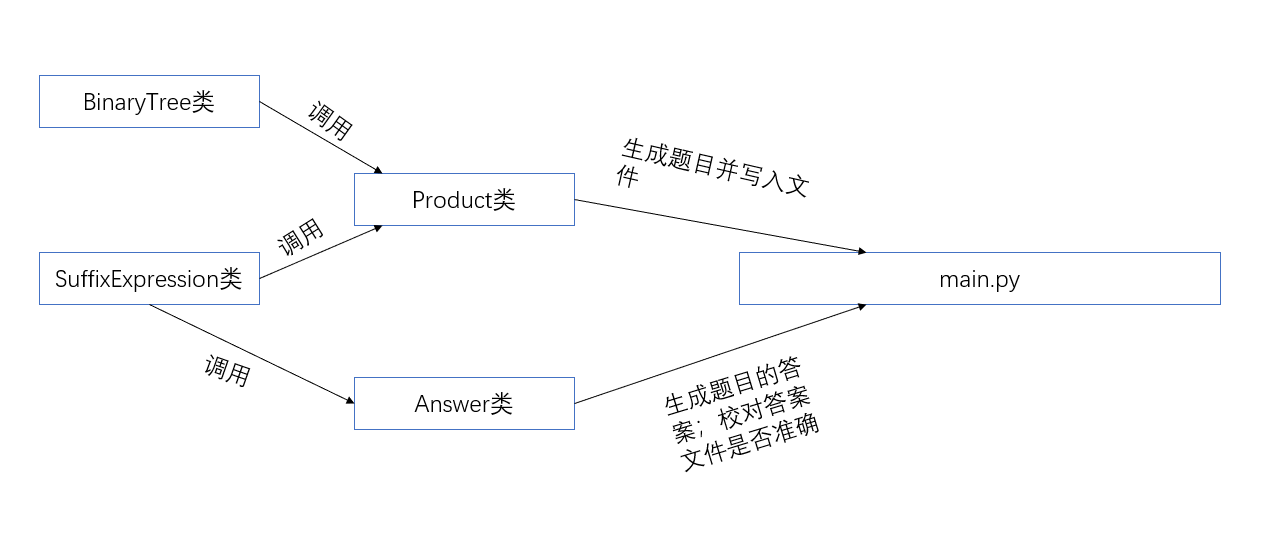
第一个类: BinaryTree类
该类有两个功能:生成二叉树和检查两颗二叉树是否相同
生成二叉树: 是将传入的后缀表达式列表用二叉树进行存储
检查两颗二叉树是否相同:实现的方法是基于递归的方法进行遍历结点
本类是为了Product类的def isRepeat(self, express_set, expression)函数服务的,在Product类为了避免生成重复的表达式,采用了基于二叉树的形式进行查重!
第二个类: SuffixExpression类
该类的功能如下:
* 将中缀表达式转化为后缀表达式(def toSuffix(self))
* 计算后缀表达式的值( def suffixToValue(self):)
其中将中缀表达式转化为后缀表达式的实现:
def toSuffix(self):
"""
中缀表达式转为后缀表达式
:self.exp : 中缀表达式列表
:return: result列表
"""
if not self.exp:
return []
ops_rule = {
'+': 1,
'-': 1,
'×': 2,
'÷': 2,
}
suffix_stack = [] # 后缀表达式结果
ops_stack = [] # 操作符栈
infix = self.exp.split(' ') # 将表达式分割得到单词
# print(infix)
for item in infix:
if item in ['+', '-', '×', '÷']: # 遇到运算符
while len(ops_stack) >= 0:
if len(ops_stack) == 0:
ops_stack.append(item)
break
op = ops_stack.pop()
if op == '(' or ops_rule[item] > ops_rule[op]:
ops_stack.append(op)
ops_stack.append(item)
break
else:
suffix_stack.append(op)
elif item == '(': # 左括号直接入栈
ops_stack.append(item)
elif item == ')': # 右括号
while len(ops_stack) > 0:
op = ops_stack.pop()
if op == "(": # 一直搜索到出现“(”为止
break
else:
suffix_stack.append(op)
else:
suffix_stack.append(item) # 数值直接入栈
while len(ops_stack) > 0:
suffix_stack.append(ops_stack.pop())
self.re =suffix_stack
return suffix_stack
该代码的思路解释:
我们实现中缀表达式转化为后缀表达式的思路:
预处理: 由于题目要求数字与运算符之间要有空格隔开,所以转化过程中需先清除空格
遍历中缀表达式:
- 如果遇到操作数,我们就直接将其存入后缀表达式栈suffix_stack[]
- 如果遇到操作符,则我们将其放入到操作符栈ops_stack中,遇到左括号时我们也将其放入操作符栈ops_stack中
- 如果遇到一个右括号,则将操作符栈ops_stack元素弹出,将弹出的操作符存入后缀表达式栈suffix_stack直到遇到左括号为止。注意,左括号只弹出并不存入后缀表达式栈suffix_stack。
- 如果遇到任何其他的操作符,如(“+”, “*”,“(”)等,从操作符栈ops_stack中弹出元素直到遇到发现更低优先级的元素(或者栈为空)为止。弹出完这些元素后,才将遇到的操作符压入到操作符栈ops_stack中。有一点需要注意,只有在遇到" ) "的情况下我们才弹出" ( ",其他情况我们都不会弹出" ( "。
- 如果我们读到了输入的中缀表达式的末尾,则将ops_stack栈中所有元素依次弹出。
第三个类:Product类
功能是生成要求的四则运算式子。
对于实现生成式子功能,我们把式子的各个要素分别构建方法进行生成,式子可能包含的要素分别为:整数、分数、括号、运算符。
其中分数的生成是较为复杂的,因为题目要求生成的都是真分数,所以在生成分数后我们有构建了一个方法把假分数转换为带分数
def DecToStr(self,operArray):
#分数转化为带分数字符串
operNum1 = operArray[0]
operNum2 = operArray[1]
if operNum2 == 1:
return operNum1
if(operNum1 > operNum2):
temp = int(operNum1/operNum2)
operNum1 -= (temp*operNum2)
return str(temp) + "'" + str(operNum1) + "/" + str(operNum2)
else:
return str(operNum1) + "/" + str(operNum2)
此外,我们的函数isRepeat(self, express_set, expression)实现了查重,避免生成运算本质相同的式子(egg: 3+2+4 与4+(3+2),像这样就是重复的一种情形 ),不过此算法的时间复杂度较大。
def isRepeat(self, express_set, expression):
"""
判断重复方法
:param
express_set: 表达式集合
expression: 生成的表达式
:return: True or False
"""
suffixExpression = SuffixExpression(expression)
target_exp_suffix = suffixExpression.re # 后缀表达式列表
binaryTree = BinaryTree()
target_exp_binary_tree = binaryTree.generateBinaryTree(target_exp_suffix)
for item in express_set:
suffixExpression2 = SuffixExpression(item)
source_exp_suffix = suffixExpression2.re
source_exp_binary_tree = binaryTree.generateBinaryTree(source_exp_suffix)
if binaryTree.treeIsSame(target_exp_binary_tree) == binaryTree.treeIsSame(source_exp_binary_tree):
return True
return False
第四个类:Answer类
功能是:
- 调用SuffixExpression类进行计算得出答案文档
- 校对提交的答案
由于需要对两个文档的答案进行校对,所以也有可能出现文档输入不正确的结果,所以设置了两个异常处理,防止打开文件出现问题导致程序出错
def check_answer(exercisefile, answerfile):
"""
校对答案
:param
exercisefile: 练习题文件
answerfile: 答案文件
:return: None
"""
wrong_num = 0
correct_num = 0
exercise_answer = []
correct_list = [] # 正确题目序号
wrong_list = [] # 错误题目序号
try:
with open(exercisefile, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
for line in f:
# 匹配出正则表达式
exp_str = re.findall(r'd+: (.*) =
', line)
if exp_str:
exp = exp_str[0]
else:
continue
p = SuffixExpression(exp)
exp_value = str(p.suffixToValue())
exercise_answer.append(exp_value)
except IOError:
print('please check if the path is correct')
# 判断表达式列表是否为空
try:
with open(answerfile, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
for i, line in enumerate(f):
ans_str = re.findall(r'd+: (.*)
', line)
# 容错
if ans_str:
ans = ans_str[0]
else:
continue
# 判断是否正确
if ans == exercise_answer[i]:
correct_num += 1
correct_list.append(i + 1)
else:
wrong_num += 1
wrong_list.append(i + 1)
with open('Grade.txt', 'w+', encoding='utf-8') as f:
correct_str = 'Correct: ' + str(correct_num) + ' ' + str(correct_list) + '
'
wrong_str = 'Wrong: ' + str(wrong_num) + ' ' + str(wrong_list)
f.write(correct_str)
f.write(wrong_str)
except IOError:
print('please check if the path is correct')
在读取文件时,采用正则表达式获取所需要的信息:
ans_str = re.findall(r'd+: (.*)
', line)
exp_str = re.findall(r'd+: (.*) =
', line)
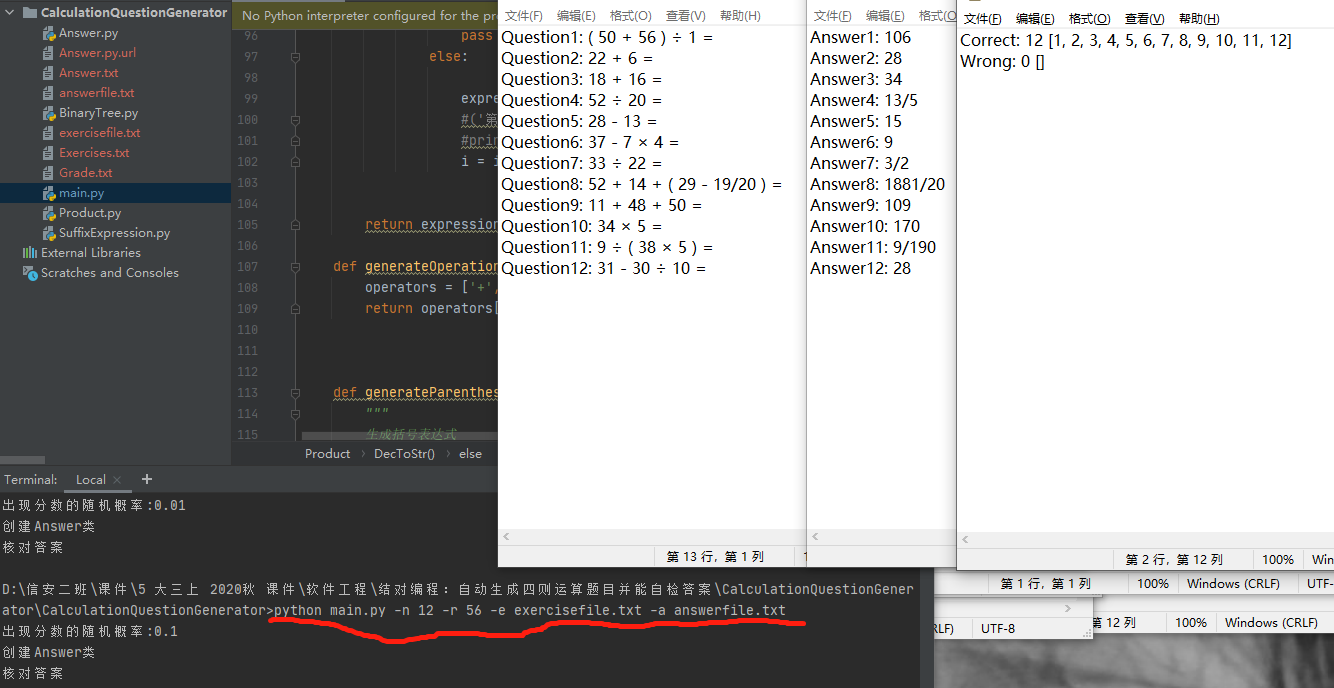
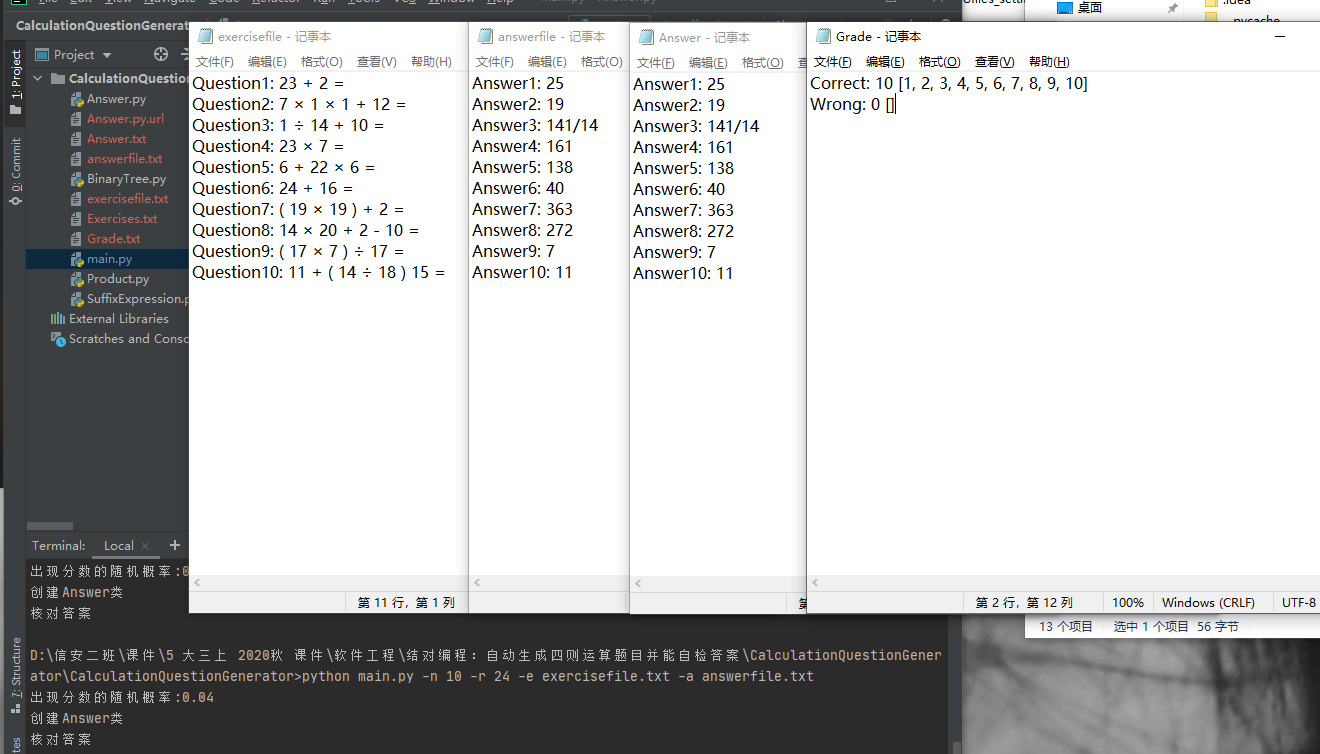
测试运行
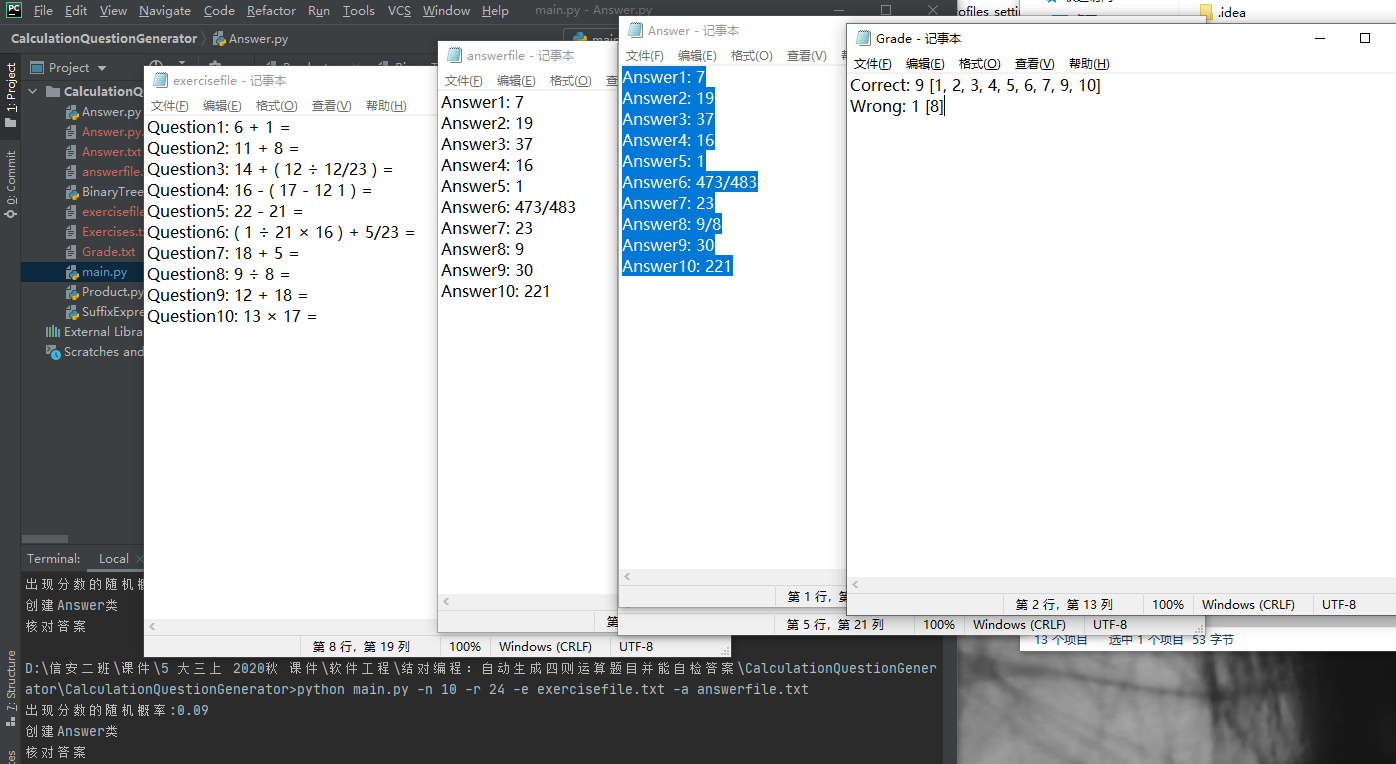
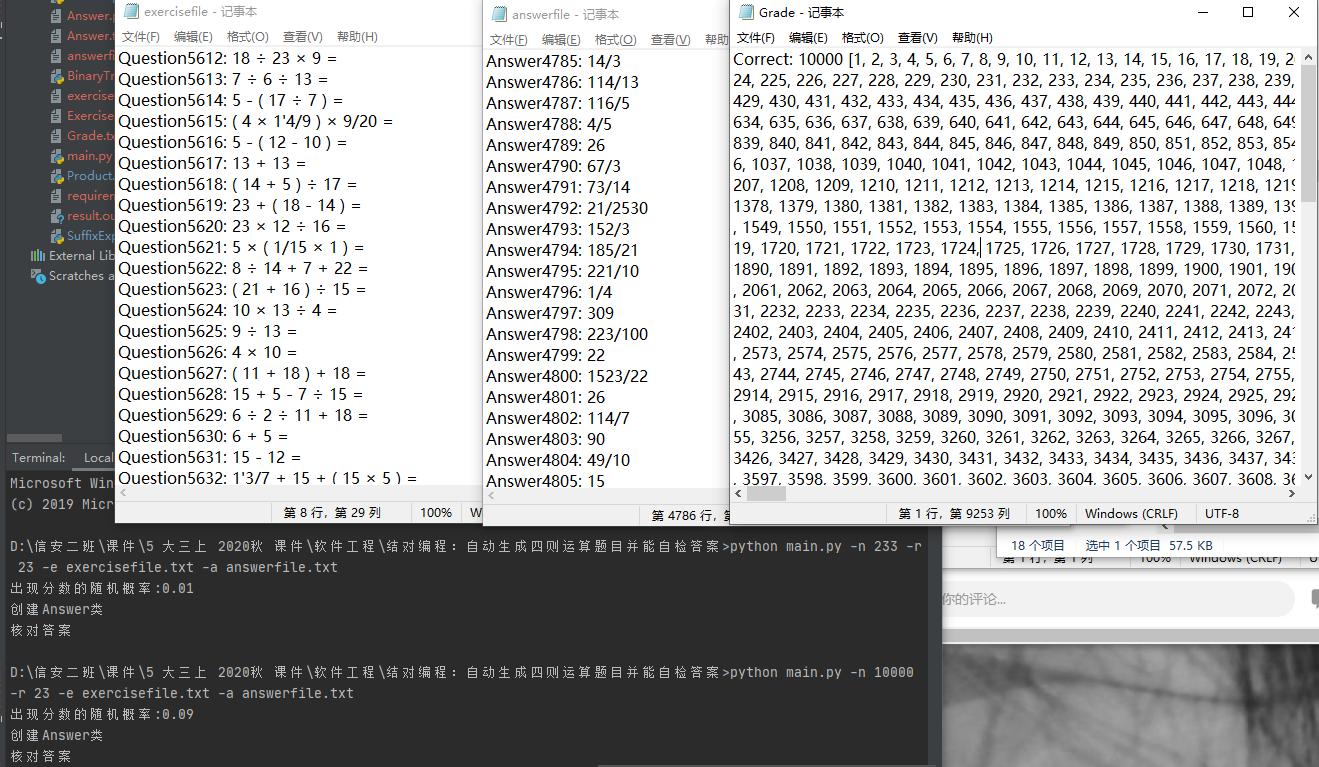
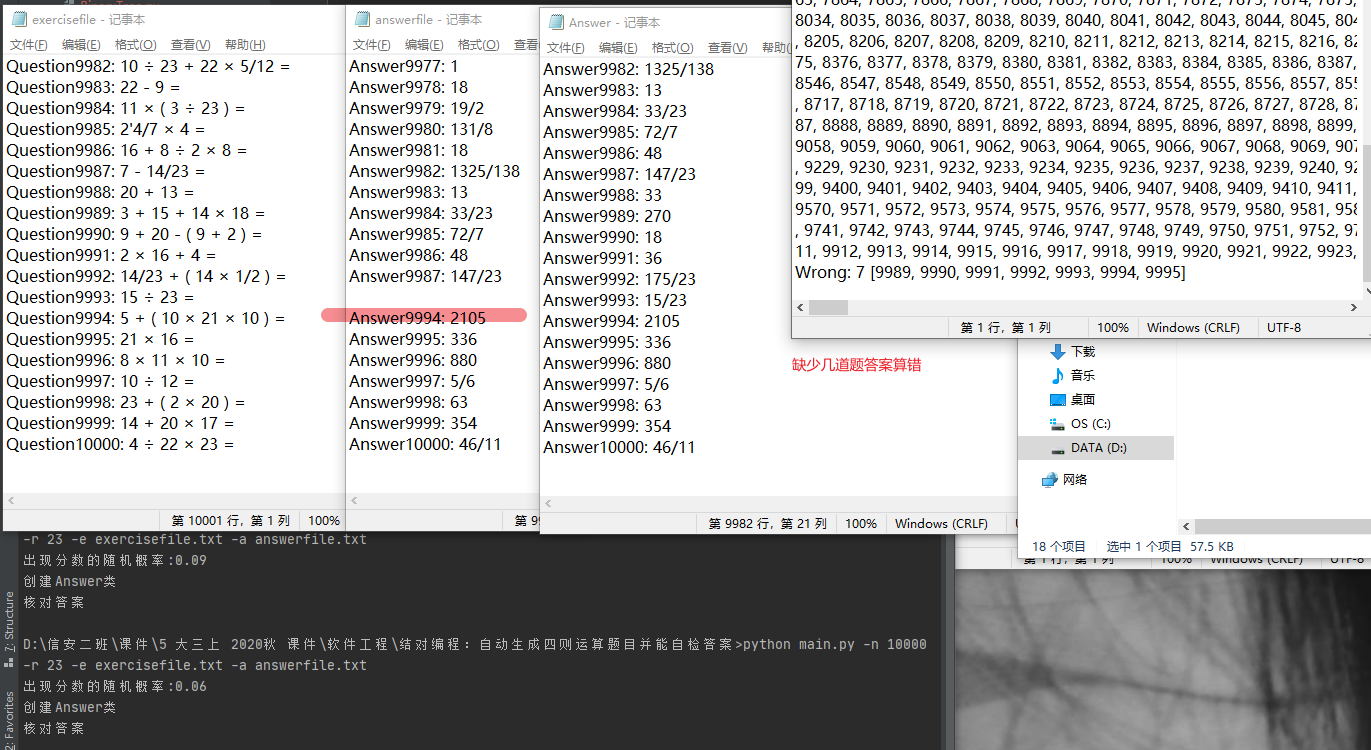

项目小结
冯宇航
对于结对项目的实操是给我们团队编程的一次训练,团队合作可能成员实力有强有弱,这时候能力较强的可能要付出多一点教导能力较弱的成员,两人一个学习一个复习,共同进步。
方俊涛
本次结对编程利用python采用了面向对象的思想,进行分模块分类实现。使用到的数据结构有:二叉树,列表,栈。用到的技术有中缀表达式转化为后缀表达式,二叉树判定重复等等。合作方面:开发前二人进行较多的讨论,通过事先调研、二人讨论确定本次开发所需要的技术,并 确定各自任务和合作内容。两人合作可以发现各自无法发现的bug,并互相促进更进进度。结对编程重要的还是交流与互助!