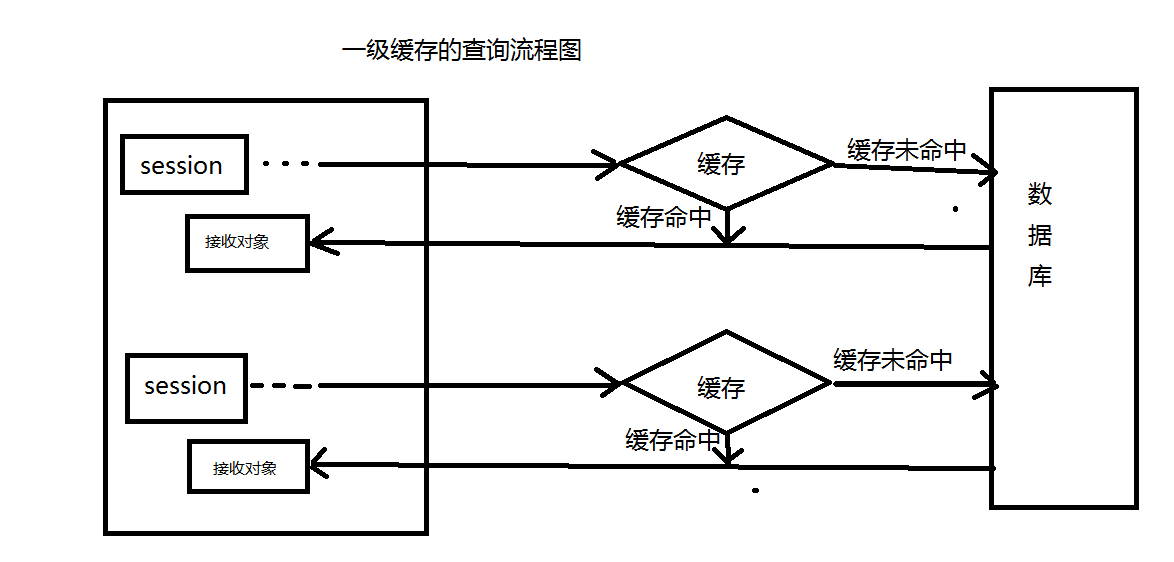
首先我们应该弄清什么是hibernate缓存:hibernate缓存是指为了降低应用程序对物理数据源的访问频次,从而提高应用程序的运行性能的一种策略。我们要将这个跟计算机内存或者cpu的缓存区分开。
一、hibernate查询的几种方式
既然是基于查询分析hibernate一级缓存,我们就来分析分析hibernate查询方式
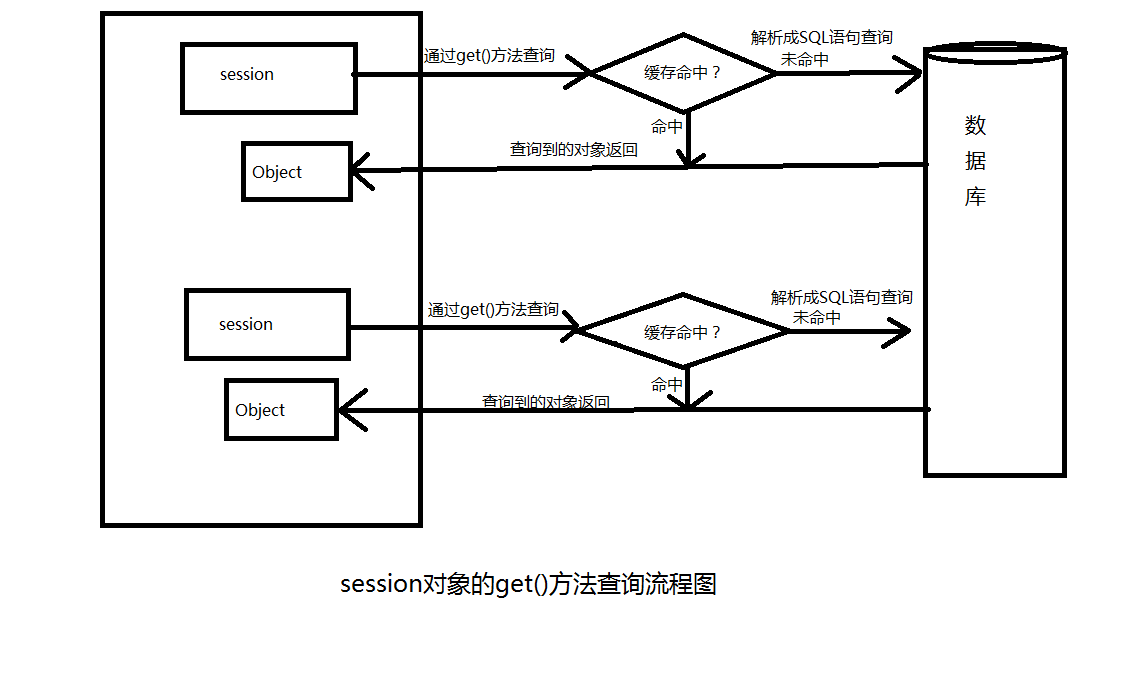
1、通过session对象的get()方法
我们通过查看hibernate的api文档找到了session接口,并重点看了get()方法,我们主要使用一下两种get()方法:![]()
通过传入由实体类获得的Class类对象(姑且叫做类类型)和该类的唯一标识符两个参数,返回一个Object类型的查询对象。
![]()
通过传入实体类名和该类对象的唯一标识符两个参数,返回一个Object类型的查询对象。
代码示例:
1 package com.third;
2
3 import java.util.List;
4
5 import org.hibernate.Query;
6 import org.hibernate.Session;
7 import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
8 import org.hibernate.Transaction;
9 import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
10 import org.hibernate.service.ServiceRegistry;
11 import org.hibernate.service.ServiceRegistryBuilder;
12 import org.junit.After;
13 import org.junit.Before;
14 import org.junit.Test;
15
16 import com.third.Dao2.Students2;
17 import com.third.Dao2.Students2PartInfo;
18
19 public class Test3 {
20 private static SessionFactory sessionFactory;
21 private static Session session;
22 private static Transaction transaction;
23 @Before
24 public void init(){
25 //先获取配置对象,匹配hibernate.cfg.xml文件
26 Configuration config=new Configuration().configure();
27 //获取注册服务对象(该对象中包含hibernate.cfg.xml中的<properties>和<maping>信息
28 ServiceRegistry serviceRegistry=new ServiceRegistryBuilder().applySettings(config.getProperties()).buildServiceRegistry();
29 //获取sessionFactory对象,通过sessionFactory对象读取hibernate.cfg.xml文档信息,并通过<mapping>标签加载hbm.xml文件信息
30 sessionFactory=config.buildSessionFactory(serviceRegistry);
31 }
32
33 @Test
34 public void test3(){
35 //通过sessionFactory对象获取session对象
36 session=sessionFactory.openSession();
37 //通过session对象开启事务,并且返回事务(transaction)对象
38 transaction=session.beginTransaction();
39
40 //第一个session对象通过get()方法第一次查询相同记录
41 Students2 stu1=(Students2) session.get(Students2.class, 1);
42 //第一个session对象通过get()函数第二次查询相同记录
43 Students2 stu2=(Students2) session.get(Students2.class, 1);
44 System.out.println("学号:"+stu1.getSid()
45 +" 姓别:"+stu1.getSgender()+" 姓名:"+stu1.getSname());
46 System.out.println("学号:"+stu2.getSid()
47 +" 姓别:"+stu2.getSgender()+" 姓名:"+stu2.getSname());
48
49 //重新获得一个session对象,再一次执行session对象的get()方法查询相同记录
50 Session session1=sessionFactory.openSession();
51 Students2 stu3=(Students2) session1.get(Students2.class, 1);
52 System.out.println("学号:"+stu3.getSid()
53 +" 姓别:"+stu3.getSgender()+" 姓名:"+stu3.getSname());
54
55
56 }
57
58 @After
59 public void destory(){
60 transaction.commit();
61 //关闭开启的资源
62 if(session!=null){
63 session.close();
64 }
65 if(sessionFactory!=null){
66 sessionFactory.close();
67 }
68 }
69 }
运行结果:
Hibernate:
select
students2x0_.SID as SID1_1_0_,
students2x0_.SNAME as SNAME2_1_0_,
students2x0_.SGENDER as SGENDER3_1_0_
from
STUDENTS2 students2x0_
where
students2x0_.SID=?
学号:1 姓别:女 姓名:小美
学号:1 姓别:女 姓名:小美
Hibernate:
select
students2x0_.SID as SID1_1_0_,
students2x0_.SNAME as SNAME2_1_0_,
students2x0_.SGENDER as SGENDER3_1_0_
from
STUDENTS2 students2x0_
where
students2x0_.SID=?
学号:1 姓别:女 姓名:小美
分析:在同一个session对象的条件下查询同一表格记录,hibernate解析的SQL语句只会执行一次,重新获得一个session对象后,再去查询相同的表格记录时,hibernate解析而成的SQL语句会在执行一次。
我们不难得出:在同一个session对象的情况下,使用get()方法查询相同的对象会使用到缓存(一级缓存),不同的session对象在查询相同对象正常情况下是不会使用缓存。
2、通过session的load()方法
我们通过查看hibernate的api文档找到了session接口,并重点看了load()方法,我们主要使用一下两种load()方法:

通过传入由实体类获得的Class类对象(姑且叫做类类型)和该类的唯一标识符两个参数,返回一个Object类型的查询对象。

通过传入实体类名和该类对象的唯一标识符两个参数,返回一个Object类型的查询对象。
代码示例:
1 package com.third;
2
3 import java.util.List;
4
5 import org.hibernate.Query;
6 import org.hibernate.Session;
7 import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
8 import org.hibernate.Transaction;
9 import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
10 import org.hibernate.service.ServiceRegistry;
11 import org.hibernate.service.ServiceRegistryBuilder;
12 import org.junit.After;
13 import org.junit.Before;
14 import org.junit.Test;
15
16 import com.third.Dao2.Students2;
17 import com.third.Dao2.Students2PartInfo;
18
19 public class Test3 {
20 private static SessionFactory sessionFactory;
21 private static Session session;
22 private static Transaction transaction;
23 @Before
24 public void init(){
25 //先获取配置对象,匹配hibernate.cfg.xml文件
26 Configuration config=new Configuration().configure();
27 //获取注册服务对象(该对象中包含hibernate.cfg.xml中的<properties>和<maping>信息
28 ServiceRegistry serviceRegistry=new ServiceRegistryBuilder().applySettings(config.getProperties()).buildServiceRegistry();
29 //获取sessionFactory对象,通过sessionFactory对象读取hibernate.cfg.xml文档信息,并通过<mapping>标签加载hbm.xml文件信息
30 sessionFactory=config.buildSessionFactory(serviceRegistry);
31 }
32
33 @Test
34 public void test3(){
35 //通过sessionFactory对象获取session对象
36 session=sessionFactory.openSession();
37 //通过session对象开启事务,并且返回事务(transaction)对象
38 transaction=session.beginTransaction();
39
40 //第一个session对象通过get()方法第一次查询相同记录
41 Students2 stu1=(Students2) session.load(Students2.class, 1);
42 //第一个session对象通过get()函数第二次查询相同记录
43 Students2 stu2=(Students2) session.load(Students2.class, 1);
44 System.out.println("学号:"+stu1.getSid()
45 +" 姓别:"+stu1.getSgender()+" 姓名:"+stu1.getSname());
46 System.out.println("学号:"+stu2.getSid()
47 +" 姓别:"+stu2.getSgender()+" 姓名:"+stu2.getSname());
48
49 //重新获得一个session对象,再一次执行session对象的get()方法查询相同记录
50 Session session1=sessionFactory.openSession();
51 Students2 stu3=(Students2) session1.load(Students2.class, 1);
52 System.out.println("学号:"+stu3.getSid()
53 +" 姓别:"+stu3.getSgender()+" 姓名:"+stu3.getSname());
54
55 }
56
57 @After
58 public void destory(){
59 transaction.commit();
60 //关闭开启的资源
61 if(session!=null){
62 session.close();
63 }
64 if(sessionFactory!=null){
65 sessionFactory.close();
66 }
67 }
68 }
运行结果:
Hibernate:
select
students2x0_.SID as SID1_1_0_,
students2x0_.SNAME as SNAME2_1_0_,
students2x0_.SGENDER as SGENDER3_1_0_
from
STUDENTS2 students2x0_
where
students2x0_.SID=?
学号:1 姓别:女 姓名:小美
学号:1 姓别:女 姓名:小美
Hibernate:
select
students2x0_.SID as SID1_1_0_,
students2x0_.SNAME as SNAME2_1_0_,
students2x0_.SGENDER as SGENDER3_1_0_
from
STUDENTS2 students2x0_
where
students2x0_.SID=?
学号:1 姓别:女 姓名:小美
分析:在同一个session对象的条件下查询同一表格记录,hibernate解析的SQL语句只会执行一次,重新获得一个session对象后,再去查询相同的表格记录时,hibernate解析而成的SQL语句会在执行一次。
我们不难得出:在同一个session对象的情况下,使用load()方法查询相同的对象会使用到缓存(一级缓存),不同的session对象在查询相同对象正常情况下是不会使用缓存。
我们可以总结得到,load()函数的查询流程和get()函数的查询流程基本相同。
3、通过session对象的createQuery(String HQL)方法
我们通过查看hibernate的api文档找到了session接口,找到createQuery(String HQL)方法,该方法的返回值类型是一个Query(查询),于是,我们找到Query接口,我们找到了两个方法,是将查询结果返回的。
![]()
以List的方式返回查询结果

以迭代器的方式返回查询结果
(1)以List的方式返回查询结果
1)有select子句
1 package com.third;
2
3 import java.util.List;
4
5 import org.hibernate.Query;
6 import org.hibernate.Session;
7 import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
8 import org.hibernate.Transaction;
9 import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
10 import org.hibernate.service.ServiceRegistry;
11 import org.hibernate.service.ServiceRegistryBuilder;
12 import org.junit.After;
13 import org.junit.Before;
14 import org.junit.Test;
15
16 import com.third.Dao2.Students2;
17 import com.third.Dao2.Students2PartInfo;
18
19 public class Test3 {
20 private static SessionFactory sessionFactory;
21 private static Session session;
22 private static Transaction transaction;
23 @Before
24 public void init(){
25 //先获取配置对象,匹配hibernate.cfg.xml文件
26 Configuration config=new Configuration().configure();
27 //获取注册服务对象(该对象中包含hibernate.cfg.xml中的<properties>和<maping>信息
28 ServiceRegistry serviceRegistry=new ServiceRegistryBuilder().applySettings(config.getProperties()).buildServiceRegistry();
29 //获取sessionFactory对象,通过sessionFactory对象读取hibernate.cfg.xml文档信息,并通过<mapping>标签加载hbm.xml文件信息
30 sessionFactory=config.buildSessionFactory(serviceRegistry);
31 }
32
33 @Test
34 public void test3(){
35 //通过sessionFactory对象获取session对象
36 session=sessionFactory.openSession();
37 //通过session对象开启事务,并且返回事务(transaction)对象
38 transaction=session.beginTransaction();
39
40 //创建HQL语句用于后面的查询需要
41 //查询所有记录的sid和sname信息(hql语句)
42 String hql=" select sid,sname,sgender from Students2";
43
44 //创建多条记录查询对象query1
45 Query query=session.createQuery(hql);
46
47 /*
48 * 相同session对象,相同query对象,查询相同的对象
49 */
50 List<Object[]> list=query.list();
51 for (Object[] objects : list) {
52 System.out.println("学号:"+objects[0]+" 姓名:"+objects[1]+" 性别:"+objects[2]);
53 }
54
55 List<Object[]> list1=query.list();
56 for (Object[] objects : list1) {
57 System.out.println("学号:"+objects[0]+" 姓名:"+objects[1]+" 性别:"+objects[2]);
58 }
59 }
60
61 @After
62 public void destory(){
63 transaction.commit();
64 //关闭开启的资源
65 if(session!=null){
66 session.close();
67 }
68 if(sessionFactory!=null){
69 sessionFactory.close();
70 }
71 }
72 }
运行结果:
Hibernate:
select
students2x0_.SID as col_0_0_,
students2x0_.SNAME as col_1_0_,
students2x0_.SGENDER as col_2_0_
from
STUDENTS2 students2x0_
学号:1 姓名:小美 性别:女
学号:2 姓名:小泽 性别:男
学号:3 姓名:小敏 性别:女
Hibernate:
select
students2x0_.SID as col_0_0_,
students2x0_.SNAME as col_1_0_,
students2x0_.SGENDER as col_2_0_
from
STUDENTS2 students2x0_
学号:1 姓名:小美 性别:女
学号:2 姓名:小泽 性别:男
学号:3 姓名:小敏 性别:女
2)没有select子句
1 package com.third;
2
3 import java.awt.event.FocusEvent;
4 import java.util.Iterator;
5 import java.util.List;
6
7 import org.hibernate.Query;
8 import org.hibernate.Session;
9 import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
10 import org.hibernate.Transaction;
11 import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
12 import org.hibernate.service.ServiceRegistry;
13 import org.hibernate.service.ServiceRegistryBuilder;
14 import org.junit.After;
15 import org.junit.Before;
16 import org.junit.Test;
17
18 import com.third.Dao2.Students2;
19 import com.third.Dao2.Students2PartInfo;
20
21 public class Test3 {
22 private static SessionFactory sessionFactory;
23 private static Session session;
24 private static Transaction transaction;
25 @Before
26 public void init(){
27 //先获取配置对象,匹配hibernate.cfg.xml文件
28 Configuration config=new Configuration().configure();
29 //获取注册服务对象(该对象中包含hibernate.cfg.xml中的<properties>和<maping>信息
30 ServiceRegistry serviceRegistry=new ServiceRegistryBuilder().applySettings(config.getProperties()).buildServiceRegistry();
31 //获取sessionFactory对象,通过sessionFactory对象读取hibernate.cfg.xml文档信息,并通过<mapping>标签加载hbm.xml文件信息
32 sessionFactory=config.buildSessionFactory(serviceRegistry);
33 }
34
35 @Test
36 public void test3(){
37 //通过sessionFactory对象获取session对象
38 session=sessionFactory.openSession();
39 //通过session对象开启事务,并且返回事务(transaction)对象
40 transaction=session.beginTransaction();
41
42 String hql="from Students2";
43 Query query=session.createQuery(hql);
44 List<Students2> stu=query.list();
45 for (Students2 stu1 : stu) {
46 System.out.println("学号:"+stu1.getSid()+" 姓名:"+stu1.getSname()+" 性别:"+stu1.getSgender());
47 }
48 List<Students2> stu2=query.list();
49 for (Students2 stu3 : stu2) {
50 System.out.println("学号:"+stu3.getSid()+" 姓名:"+stu3.getSname()+" 性别:"+stu3.getSgender());
51 }
52
53
54 }
55
56 @After
57 public void destory(){
58 transaction.commit();
59 //关闭开启的资源
60 if(session!=null){
61 session.close();
62 }
63 if(sessionFactory!=null){
64 sessionFactory.close();
65 }
66 }
67 }
运行结果:
Hibernate:
select
students2x0_.SID as SID1_1_,
students2x0_.SNAME as SNAME2_1_,
students2x0_.SGENDER as SGENDER3_1_
from
STUDENTS2 students2x0_
学号:1 姓名:小美 性别:女
学号:2 姓名:小泽 性别:男
学号:3 姓名:小敏 性别:女
Hibernate:
select
students2x0_.SID as SID1_1_,
students2x0_.SNAME as SNAME2_1_,
students2x0_.SGENDER as SGENDER3_1_
from
STUDENTS2 students2x0_
学号:1 姓名:小美 性别:女
学号:2 姓名:小泽 性别:男
学号:3 姓名:小敏 性别:女
分析:相同session,甚至相同query对象情况下,查询相同的对象,hibernate解析的SQL语句在数据库执行了两次。
很明显能看出:session.createQuery(hql).list()方法,不会使用缓存。

(2)以迭代的方式返回查询结果
代码示例:
1 package com.third;
2
3 import java.util.Iterator;
4 import java.util.List;
5
6 import org.hibernate.Query;
7 import org.hibernate.Session;
8 import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
9 import org.hibernate.Transaction;
10 import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
11 import org.hibernate.service.ServiceRegistry;
12 import org.hibernate.service.ServiceRegistryBuilder;
13 import org.junit.After;
14 import org.junit.Before;
15 import org.junit.Test;
16
17 import com.third.Dao2.Students2;
18 import com.third.Dao2.Students2PartInfo;
19
20 public class Test3 {
21 private static SessionFactory sessionFactory;
22 private static Session session;
23 private static Transaction transaction;
24 @Before
25 public void init(){
26 //先获取配置对象,匹配hibernate.cfg.xml文件
27 Configuration config=new Configuration().configure();
28 //获取注册服务对象(该对象中包含hibernate.cfg.xml中的<properties>和<maping>信息
29 ServiceRegistry serviceRegistry=new ServiceRegistryBuilder().applySettings(config.getProperties()).buildServiceRegistry();
30 //获取sessionFactory对象,通过sessionFactory对象读取hibernate.cfg.xml文档信息,并通过<mapping>标签加载hbm.xml文件信息
31 sessionFactory=config.buildSessionFactory(serviceRegistry);
32 }
33
34 @Test
35 public void test3(){
36 //通过sessionFactory对象获取session对象
37 session=sessionFactory.openSession();
38 //通过session对象开启事务,并且返回事务(transaction)对象
39 transaction=session.beginTransaction();
40
41 /*
42 * 这里我们执行带有select子句的查询
43 */
44 //创建HQL语句用于后面的查询需要
45 //查询所有记录的sid和sname信息(hql语句)
46 String hql=" select sid,sname,sgender from Students2";
47
48 //创建多条记录查询对象query1
49 Query query=session.createQuery(hql);
50 System.out.println("*************带有select子句的查询*********************");
51 Iterator it=query.iterate();
52 while(it.hasNext()){
53 Object[] obj=(Object[])it.next();
54 System.out.println("学号:"+obj[0]+" 姓名:"+obj[1]+" 性别:"+obj[2]);
55 }
56 //在同一session同一query1对象下查询相同的对象
57 System.out.println("同一个session并且同一个query对象下查询相同对象:");
58 Iterator it2=query.iterate();
59 while(it2.hasNext()){
60 Object[] obj=(Object[])it2.next();
61 System.out.println("学号:"+obj[0]+" 姓名:"+obj[1]+" 性别:"+obj[2]);
62 }
63 System.out.println("**************不带select子句的查询**********************");
64 /*
65 * 这里我们执行不带有select子句的查询
66 */
67 Session session1=sessionFactory.openSession();
68 String hql1="from Students2";
69 Query query1=session.createQuery(hql1);
70 Iterator<Students2> it1=query1.iterate();
71 while(it1.hasNext()){
72 Students2 stu=it1.next();
73 System.out.println("学号:"+stu.getSid()
74 +" 姓别:"+stu.getSgender()+" 姓名:"+stu.getSname());
75 }
76 //在同一session同一query1对象下查询相同的对象
77 System.out.println("在同一session同一query1对象下查询相同的对象:");
78 Iterator<Students2> it3=query1.iterate();
79 while(it3.hasNext()){
80 Students2 stu=it3.next();
81 System.out.println("学号:"+stu.getSid()
82 +" 姓别:"+stu.getSgender()+" 姓名:"+stu.getSname());
83 }
84 //在同一个session但是不是一个query对象下查询相同对象
85 System.out.println("在同一个session但是不是一个query对象下查询相同对象:");
86 Query query2=session.createQuery(hql1);
87 Iterator<Students2> it4=query2.iterate();
88 while(it4.hasNext()){
89 Students2 stu=it4.next();
90 System.out.println("学号:"+stu.getSid()
91 +" 姓别:"+stu.getSgender()+" 姓名:"+stu.getSname());
92 }
93 //在不同的session中,查询相同的对象
94 System.out.println("在不同的session中,查询相同的对象:");
95 Session session2=sessionFactory.openSession();
96 String hql2="from Students2";
97 Query query3=session2.createQuery(hql1);
98 Iterator<Students2> it5=query3.iterate();
99 while(it5.hasNext()){
100 Students2 stu=it5.next();
101 System.out.println("学号:"+stu.getSid()
102 +" 姓别:"+stu.getSgender()+" 姓名:"+stu.getSname());
103 }
104 }
105
106 @After
107 public void destory(){
108 transaction.commit();
109 //关闭开启的资源
110 if(session!=null){
111 session.close();
112 }
113 if(sessionFactory!=null){
114 sessionFactory.close();
115 }
116 }
117 }
运行结果:
*************带有select子句的查询*********************
Hibernate:
select
students2x0_.SID as col_0_0_,
students2x0_.SNAME as col_1_0_,
students2x0_.SGENDER as col_2_0_
from
STUDENTS2 students2x0_
学号:1 姓名:小美 性别:女
学号:2 姓名:小泽 性别:男
学号:3 姓名:小敏 性别:女
同一个session并且同一个query对象下查询相同对象:
Hibernate:
select
students2x0_.SID as col_0_0_,
students2x0_.SNAME as col_1_0_,
students2x0_.SGENDER as col_2_0_
from
STUDENTS2 students2x0_
学号:1 姓名:小美 性别:女
学号:2 姓名:小泽 性别:男
学号:3 姓名:小敏 性别:女
**************不带select子句的查询**********************
Hibernate:
select
students2x0_.SID as col_0_0_
from
STUDENTS2 students2x0_
Hibernate:
select
students2x0_.SID as SID1_1_0_,
students2x0_.SNAME as SNAME2_1_0_,
students2x0_.SGENDER as SGENDER3_1_0_
from
STUDENTS2 students2x0_
where
students2x0_.SID=?
学号:1 姓别:女 姓名:小美
Hibernate:
select
students2x0_.SID as SID1_1_0_,
students2x0_.SNAME as SNAME2_1_0_,
students2x0_.SGENDER as SGENDER3_1_0_
from
STUDENTS2 students2x0_
where
students2x0_.SID=?
学号:2 姓别:男 姓名:小泽
Hibernate:
select
students2x0_.SID as SID1_1_0_,
students2x0_.SNAME as SNAME2_1_0_,
students2x0_.SGENDER as SGENDER3_1_0_
from
STUDENTS2 students2x0_
where
students2x0_.SID=?
学号:3 姓别:女 姓名:小敏
在同一session同一query1对象下查询相同的对象:
Hibernate:
select
students2x0_.SID as col_0_0_
from
STUDENTS2 students2x0_
学号:1 姓别:女 姓名:小美
学号:2 姓别:男 姓名:小泽
学号:3 姓别:女 姓名:小敏
在同一个session但是不是一个query对象下查询相同对象:
Hibernate:
select
students2x0_.SID as col_0_0_
from
STUDENTS2 students2x0_
学号:1 姓别:女 姓名:小美
学号:2 姓别:男 姓名:小泽
学号:3 姓别:女 姓名:小敏
在不同的session中,查询相同的对象:
Hibernate:
select
students2x0_.SID as col_0_0_
from
STUDENTS2 students2x0_
Hibernate:
select
students2x0_.SID as SID1_1_0_,
students2x0_.SNAME as SNAME2_1_0_,
students2x0_.SGENDER as SGENDER3_1_0_
from
STUDENTS2 students2x0_
where
students2x0_.SID=?
学号:1 姓别:女 姓名:小美
Hibernate:
select
students2x0_.SID as SID1_1_0_,
students2x0_.SNAME as SNAME2_1_0_,
students2x0_.SGENDER as SGENDER3_1_0_
from
STUDENTS2 students2x0_
where
students2x0_.SID=?
学号:2 姓别:男 姓名:小泽
Hibernate:
select
students2x0_.SID as SID1_1_0_,
students2x0_.SNAME as SNAME2_1_0_,
students2x0_.SGENDER as SGENDER3_1_0_
from
STUDENTS2 students2x0_
where
students2x0_.SID=?
学号:3 姓别:女 姓名:小敏
分析:以迭代器方式返回的查询,执行我们分成使用select子句和没有使用select子句的查询:
1)使用了select子句的查询,是不会使用缓存的
2)不使用select子句的查询,情况可以分为在同一个session下和不同的session下查询相同的对象。在同一个session下,第一次查询缓存中不存在的对象时,会先到数据库中查询要查对象的主键,然后依靠主键使用where子句限定主键,然后一一按照主键到数据库中执行SQL语句查询对象;再次查询相同对象时,会现在缓存中查询对象的编号,找到相同编号的返回,找不到的,再到数据库去按照编号查找。在不同session下,缓存一般不能使用。

二、一级缓存相关介绍
1、hibernate一级缓存也称为“会话级缓存”、“session缓存”。
2、一级缓存的生命周期和session相同,session销毁,缓存也销毁。
3、一级缓存数据的使用范围,或者说是作用域为当前会话。
4、hibernate一级缓存的API
一级缓存无法取消,用两个方法管理。
evict():用于将某个对象从session中的一级缓存中清除。
clear():用于将一级缓存中的对象全部清除。
1 package com.third;
2
3 import org.hibernate.Session;
4 import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
5 import org.hibernate.Transaction;
6 import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
7 import org.hibernate.service.ServiceRegistry;
8 import org.hibernate.service.ServiceRegistryBuilder;
9 import org.junit.After;
10 import org.junit.Before;
11 import org.junit.Test;
12
13 import com.third.Dao2.Students2;
14
15 public class Test3 {
16 private static SessionFactory sessionFactory;
17 private static Session session;
18 private static Transaction transaction;
19 @Before
20 public void init(){
21 //先获取配置对象,匹配hibernate.cfg.xml文件
22 Configuration config=new Configuration().configure();
23 //获取注册服务对象(该对象中包含hibernate.cfg.xml中的<properties>和<maping>信息
24 ServiceRegistry serviceRegistry=new ServiceRegistryBuilder().applySettings(config.getProperties()).buildServiceRegistry();
25 //获取sessionFactory对象,通过sessionFactory对象读取hibernate.cfg.xml文档信息,并通过<mapping>标签加载hbm.xml文件信息
26 sessionFactory=config.buildSessionFactory(serviceRegistry);
27 }
28
29 @Test
30 public void test3(){
31 //通过sessionFactory对象获取session对象
32 session=sessionFactory.openSession();
33 //通过session对象开启事务,并且返回事务(transaction)对象
34 transaction=session.beginTransaction();
35
36 Students2 stu1=(Students2) session.get(Students2.class, 1);
37 Students2 stu2=(Students2) session.get(Students2.class, 2);
38 Students2 stu3=(Students2) session.get(Students2.class, 3);
39
40 System.out.println("第一遍查询:");
41 System.out.println("学号:"+stu1.getSid()+" 姓名:"+stu1.getSname()+" 性别:"+stu1.getSgender());
42 System.out.println("学号:"+stu2.getSid()+" 姓名:"+stu2.getSname()+" 性别:"+stu2.getSgender());
43 System.out.println("学号:"+stu3.getSid()+" 姓名:"+stu3.getSname()+" 性别:"+stu3.getSgender());
44
45 //先使用evict()方法,然后在查询相同session下之前查过的对象
46 System.out.println("先使用evict()方法,然后在查询相同session下之前查过的对象:");
47 session.evict(stu1);
48 Students2 stu4=(Students2) session.get(Students2.class, 1);
49 System.out.println("学号:"+stu4.getSid()+" 姓名:"+stu4.getSname()+" 性别:"+stu4.getSgender());
50
51 //使用clear()方法,然后再查询相同session下之前查过的对象。
52 System.out.println("使用clear()方法,然后再查询相同session下之前查过的对象:");
session.clear();
53 Students2 stu5=(Students2) session.get(Students2.class, 1);
54 Students2 stu6=(Students2) session.get(Students2.class, 2);
55 Students2 stu7=(Students2) session.get(Students2.class, 3);
56
57 System.out.println("学号:"+stu5.getSid()+" 姓名:"+stu5.getSname()+" 性别:"+stu5.getSgender());
58 System.out.println("学号:"+stu6.getSid()+" 姓名:"+stu6.getSname()+" 性别:"+stu6.getSgender());
59 System.out.println("学号:"+stu7.getSid()+" 姓名:"+stu7.getSname()+" 性别:"+stu7.getSgender());
60 }
61
62 @After
63 public void destory(){
64 transaction.commit();
65 //关闭开启的资源
66 if(session!=null){
67 session.close();
68 }
69 if(sessionFactory!=null){
70 sessionFactory.close();
71 }
72 }
73 }
运行结果:
Hibernate:
select
students2x0_.SID as SID1_1_0_,
students2x0_.SNAME as SNAME2_1_0_,
students2x0_.SGENDER as SGENDER3_1_0_
from
STUDENTS2 students2x0_
where
students2x0_.SID=?
Hibernate:
select
students2x0_.SID as SID1_1_0_,
students2x0_.SNAME as SNAME2_1_0_,
students2x0_.SGENDER as SGENDER3_1_0_
from
STUDENTS2 students2x0_
where
students2x0_.SID=?
Hibernate:
select
students2x0_.SID as SID1_1_0_,
students2x0_.SNAME as SNAME2_1_0_,
students2x0_.SGENDER as SGENDER3_1_0_
from
STUDENTS2 students2x0_
where
students2x0_.SID=?
第一遍查询:
学号:1 姓名:小美 性别:女
学号:2 姓名:小泽 性别:男
学号:3 姓名:小敏 性别:女
先使用evict()方法,然后在查询相同session下之前查过的对象:
Hibernate:
select
students2x0_.SID as SID1_1_0_,
students2x0_.SNAME as SNAME2_1_0_,
students2x0_.SGENDER as SGENDER3_1_0_
from
STUDENTS2 students2x0_
where
students2x0_.SID=?
学号:1 姓名:小美 性别:女
使用clear()方法,然后再查询相同session下之前查过的对象:
Hibernate:
select
students2x0_.SID as SID1_1_0_,
students2x0_.SNAME as SNAME2_1_0_,
students2x0_.SGENDER as SGENDER3_1_0_
from
STUDENTS2 students2x0_
where
students2x0_.SID=?
Hibernate:
select
students2x0_.SID as SID1_1_0_,
students2x0_.SNAME as SNAME2_1_0_,
students2x0_.SGENDER as SGENDER3_1_0_
from
STUDENTS2 students2x0_
where
students2x0_.SID=?
Hibernate:
select
students2x0_.SID as SID1_1_0_,
students2x0_.SNAME as SNAME2_1_0_,
students2x0_.SGENDER as SGENDER3_1_0_
from
STUDENTS2 students2x0_
where
students2x0_.SID=?
学号:1 姓名:小美 性别:女
学号:2 姓名:小泽 性别:男
学号:3 姓名:小敏 性别:女
三、总结:
(1)一级缓存的数据的作用范围为一个session,缓存会随着session的销毁而销毁。
(2)其中通过get()、load()、和以Iterator(迭代器)方式返回无select子句查询都会使用到缓存,但是通过以list方式和Iterator(迭代器)方式返回的有select子句的查询不会使用缓存。
(3)其中以Iterator(迭代器)方式返回的hibernate查询都是先从数据库中查询对象的编号,然后到缓存中查找匹配的编号,找到了直接返回,找不到通过where子句限定以编号去数据库中查找,然后返回。
一级缓存查询的流程图: