一、补充
@classmethod
整个方法中没有用到对象命名空间中的名字,且用到了类的命名空间中的名字(普通方法和属性property除外)
类方法的默认参数:cls 调用这个发方法的类
类方法的调用方式:通过类名调用
通过类名调用的本质是方法
@statimethod
将一个普通函数放到类中来就给这个函数加一个@staticmethod装饰器
这个函数就不需要传默认的参数:self,cls
静态方法的调用方式:通过类名调用
通过类名调用本质是函数
from types import MethodType,FunctionType 配合isinstance使用,判断是方法还是函数
通过类名调用,@classmethod的是方法,@statimethod的是函数
from types import FunctionType,MethodType
class Foo:
@classmethod
def func1(cls):pass
@staticmethod
def func2():pass
print('Foo.func1-Function:',isinstance(Foo.func1,FunctionType)) # 判断类方法是否函数
print('Foo.func1-Method:',isinstance(Foo.func1,MethodType)) # 判断类方法是否方法
print('----------------------------------------')
print('Foo.func2-Function:',isinstance(Foo.func2,FunctionType)) # 判断静态方法是否函数
print('Foo.func2-Method:',isinstance(Foo.func2,MethodType)) # 判断静态方法是否方法
'''
Foo.func1-Function: False
Foo.func1-Method: True
----------------------------------------
Foo.func2-Function: True
Foo.func2-Method: False
'''
通过对象调用,@classmethod的是方法,@statimethod的是函数
from types import FunctionType,MethodType
class Foo:
@classmethod
def func1(cls):pass
@staticmethod
def func2():pass
f = Foo()
print('Foo.func1-Function:',isinstance(f.func1,FunctionType)) # 判断对象类方法是否函数
print('Foo.func1-Method:',isinstance(f.func1,MethodType)) # 判断对象类方法是否方法
print('----------------------------------------')
print('Foo.func2-Function:',isinstance(f.func2,FunctionType)) # 判断对象静态方法是否函数
print('Foo.func2-Method:',isinstance(f.func2,MethodType)) # 判断对象静态方法是否方法
'''
Foo.func1-Function: False
Foo.func1-Method: True
----------------------------------------
Foo.func2-Function: True
Foo.func2-Method: False
'''
类可以被调用,对象不能被调用
def func(args):
if callable(args):
print(args())
else:
print('not callable:',args)
class Foo:pass
f = Foo()
func(Foo) # 类 <__main__.Foo object at 0x0000016AE645C278>
func(f) # 对象 not callable: <__main__.Foo object at 0x0000016AE645C320>
总结:
需要明确传递参数的是function(函数),不需要明确传递参数的是method(方法)。类直接调用是function(函数),类的实例调用的是method(方法)
类方法:类调用和对象调用都是method(方法)
静态方法:类调用和对象调用都是function(函数)
# 判断函数、方法、对象
from types import MethodType,FunctionType
def func(*args):
function_count = 0
method_count = 0
foo_obj = 0
for item in args:
if isinstance(item,FunctionType):function_count += 1
elif isinstance(item,MethodType):method_count += 1
elif isinstance(item,Foo):foo_obj += 1
return {'function_count': function_count, 'method_count': method_count, 'foo_obj': foo_obj}
def func1():pass
class Foo:
def method1(self):pass
f1 = Foo()
ret = func(func1,f1.method1,Foo.method1,Foo(),func,f1)
print(ret)
'''
{'function_count': 3, 'method_count': 1, 'foo_obj': 2}
'''
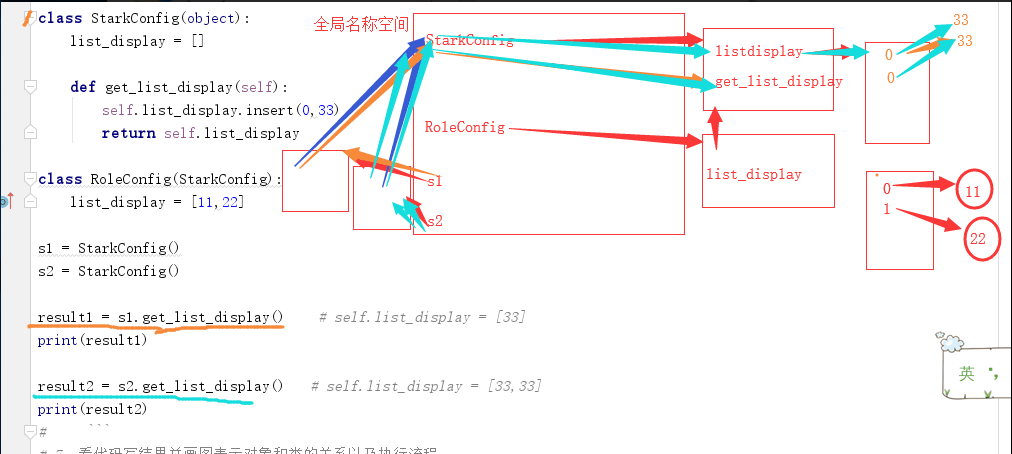
类、对象内存机制的解析
二、反射
反射作用:使用字符串数据类型的变量名来获取这个变量的值
使用反射的三个场景:
① input
② 文件:从文件中读出的字符串,想转化成变量的名字
③ 网络:将网络传输的字符串转化成变量的名字,函数名是变量,类名也是变量,直接执行变量
反射变量的方式:
① 反射类中的变量(反射静态变量,类方法,静态方法)
② 反射对象中的变量(反射对象中的对象属性,普通方法)
③ 反射模块中的变量
④ 反射本文件中的变量
反射使用的常用函数:
① hasattr() 用于判断对象是否包含对应的属性
② getattr() 获取对象object的属性或者方法,如果存在打印出来,如果不存在,打印出默认值,默认值可选。
需要注意的是,如果是返回的对象的方法,返回的是方法的内存地址,如果需要运行这个方法,
可以在后面添加一对括号。
getattr(变量名:命名空间,字符串:属于一个命名类的变量名)
③ setattr() 给对象的属性赋值,若属性不存在,先创建再赋值
setattr() 接收三个参数,命名空间,‘变量名’,变量值
④ delattr() 删除 object对象 中的 name属性
三、反射类中的变量
① 反射静态变量
class A:
city = 'Shenzhen'
if hasattr(A,'city'): # 判断类中是否存在该变量名,变量名字符串格式,相当于 A.city in A
ret = getattr(A,'city') # getattr(类名,变量名的字符串格式),相当于 ret = A.city
print(ret) # Shenzhen
② 反射类方法
class B:
@classmethod
def func(cls): # 类方法
return 666
if hasattr(B,'func'): # 判断类中是否存在该变量名,变量名字符串格式,相当于B.func in B
ret = getattr(B,'func') # getattr(类名,变量名的字符串格式),相当于 ret = B.func
print(ret) # <bound method B.func of <class '__main__.B'>>
print(ret()) # 执行B.func() 666
③ 反射静态方法
class C:
@staticmethod
def func(): # 静态方法
return 333
if hasattr(C,'func'): # 判断类中是否存在该变量名,变量名字符串格式,相当于C.func in C
ret = getattr(C,'func') # getattr(类名,变量名的字符串格式),相当于 ret = C.func
print(ret) # <function C.func at 0x000001D058918BF8>
print(ret()) # 执行C.func() 333
四、反射对象中的变量
① 反射对象属性
class A:
name = 'gg'
def __init__(self,city):
self.city = city # 对象属性
a = A('广州')
if hasattr(a,'city'):
ret = getattr(a,'city') # 相当于 ret = a.city
print(ret) # 广州
print(a.city) # 广州
② 反射普通方法
class B:
def func(self):
print(666)
b = B()
if hasattr(b,'func'):
ret = getattr(b,'func') # 相当于 ret = b.func
print(ret) # <bound method B.func of <__main__.B object at 0x00000242F27DC5F8>>
ret() # 666
b.func() # 666
五、反射模块中的变量
import os
getattr(os,'rename')('a.txt','b.txt') # 相当于 os.rename('a.txt','b.txt')
# os.rename('a.txt','b.txt')
六、反射本文件中的变量
import sys
city = '北京'
print(sys.modules['__main__']) # 本文件的命名空间
print(sys.modules['__main__'].city) # 相当与 print(city)
print(sys.modules[__name__]) # 本文件的命名空间(默认使用此方式)
# __name__ == '__main__'
ret = getattr(sys.modules[__name__],'city') # 相当于 ret = city , 相当于 sys.modules['__main__'].city
ret = getattr(sys.modules[__name__],'city') # 相当于本文件中的city变量
print(ret)
七、setattr() 和 delattr()
setattr(object, name, value)
object -- 对象。
name -- 字符串,对象属性。
value -- 属性值。
class A:pass
setattr(A,'city','广州') # 相当于 A.city = '广州'
print(A.__dict__)
print(A.city) # 广州
delattr(object, name)
object -- 对象。
name -- 必须是对象的属性。
class B:
city = '上海'
delattr(B,'city') # 相当于 del B.city
八、内置方法
内置方法:不是需要程序员定义,本身就存在在类中的方法就是内置方法
内置方法的形式: __名字__
名字——双下方法,魔术方法,内置方法
__init__ 类的初始化方法,不需要主动调用,而是在类的实例化的时候内部自动调用的
所有的双下方法,都不需要直接去调用,都是有另一种自动触发它的语法
__str__
__str__的方法,必须return str类型
①当打印一个对象的时候触发__str__,打印的是__方法的返回值
②当使用%s格式化的时候,触发__str__
③str强转数据类型的时候,触发__str__
class A:
def __init__(self,city,province):
self.city = city
self.province = province
def __str__(self):
return '%s在%s内' % (self.city,self.province)
a = A('广州市','广东省')
print(a)
print('%s' % a)
print(str(a))
'''
广州市在广东省内
广州市在广东省内
广州市在广东省内
'''
__repr__
__repr__的方法,必须return str类型
__repr__相当于__str__的备胎,有__str__的时候执行__str__,没有__str__的时候,执行__repr__
repr()内置函数对应的结果是__repr__的返回值
① 当使用repr()的时候触发__repr__
② 当使用%r格式化输出的时候触发__repr__
③ 当打印一个对象的时候触发__repr__,打印的是__方法的返回值
④ 当使用%s格式化的时候,触发__repr__
⑤ str强转数据类型的时候,触发__repr__
class A:
def __init__(self,city,province):
self.city = city
self.province = province
def __repr__(self):
return '%s在%s内' % (self.city,self.province)
a = A('深圳市','广东省')
print(a)
print('%s' % a)
print(str(a))
print(repr(a))
print('%r' % a)
'''
深圳市在广东省内
深圳市在广东省内
深圳市在广东省内
深圳市在广东省内
深圳市在广东省内
'''
继承关系中,__str__和__repr__的优先级:
结论:子类的__str__ >>> 父类的__str__ >>> 子类的__repr__ >>> 父类的__repr__