全排列在笔试面试中很热门,因为它难度适中,既可 以考察递归实现,又能进一步考察非递归的实现,便于区分出考生的水平。所以在百度和迅雷的校园招聘以及程序员和软件设计师的考试中都考到了,因此本文对全 排列作下总结帮助大家更好的学习和理解。对本文有任何补充之处,欢迎大家指出。
首先来看看题目是如何要求的(百度迅雷校招笔试题)。
一、字符串的排列
用C++写一个函数, 如 Foo(const char *str), 打印出 str 的全排列,
如 abc 的全排列: abc, acb, bca, dac, cab, cba
一、全排列的递归实现
为方便起见,用123来示例下。123的全 排列有123、132、213、231、312、321这六种。首先考虑213和321这二个数是如何得出的。显然这二个都是123中的1与后面两数交换 得到的。然后可以将123的第二个数和每三个数交换得到132。同理可以根据213和321来得231和312。因此可以知道——全排列就是从第一个数字 起每个数分别与它后面的数字交换。找到这个规律后,递归的代码就很容易写出来了:
- #include<iostream>
- using namespace std;
- #include<assert.h>
- void Permutation(char* pStr, char* pBegin)
- {
- assert(pStr && pBegin);
- if(*pBegin == '�')
- printf("%s ",pStr);
- else
- {
- for(char* pCh = pBegin; *pCh != '�'; pCh++)
- {
- swap(*pBegin,*pCh);
- Permutation(pStr, pBegin+1);
- swap(*pBegin,*pCh);
- }
- }
- }
- int main(void)
- {
- char str[] = "abc";
- Permutation(str,str);
- return 0;
- }
另外一种写法:
- //k表示当前选取到第几个数,m表示共有多少个数
- void Permutation(char* pStr,int k,int m)
- {
- assert(pStr);
- if(k == m)
- {
- static int num = 1; //局部静态变量,用来统计全排列的个数
- printf("第%d个排列 %s ",num++,pStr);
- }
- else
- {
- for(int i = k; i <= m; i++)
- {
- swap(*(pStr+k),*(pStr+i));
- Permutation(pStr, k + 1 , m);
- swap(*(pStr+k),*(pStr+i));
- }
- }
- }
- int main(void)
- {
- char str[] = "abc";
- Permutation(str , 0 , strlen(str)-1);
- return 0;
- }
如果字符串中有重复字符的话,上面的那个方法肯定不会符合要求的,因此现在要想办法来去掉重复的数列。
二、去掉重复的全排列的递归实现
由于全排列就是从第一个数字起每个数分别与它后面的数字交换。我们先尝试加个这样的判断——如果一个数与后面的数字相同那么这二个数就不交换了。如
122,第一个数与后面交换得212、221。然后122中第二数就不用与第三个数交换了,但对212,它第二个数与第三个数是不相同的,交换之后得到
221。与由122中第一个数与第三个数交换所得的221重复了。所以这个方法不行。
换种思维,对122,第一个数1与第二个数2交换得到212,然后考虑第一个数1与第三个数2交换,此时由于第三个数等于第二个数,所以第一个数不再与第三个数交换。再考虑212,它的第二个数与第三个数交换可以得到解决221。此时全排列生成完毕。
这样我们也得到了在全排列中去掉重复的规则——去重的全排列就是从第一个数字起每个数分别与它后面非重复出现的数字交换。下面给出完整代码:
- #include<iostream>
- using namespace std;
- #include<assert.h>
- //在[nBegin,nEnd)区间中是否有字符与下标为pEnd的字符相等
- bool IsSwap(char* pBegin , char* pEnd)
- {
- char *p;
- for(p = pBegin ; p < pEnd ; p++)
- {
- if(*p == *pEnd)
- return false;
- }
- return true;
- }
- void Permutation(char* pStr , char *pBegin)
- {
- assert(pStr);
- if(*pBegin == '�')
- {
- static int num = 1; //局部静态变量,用来统计全排列的个数
- printf("第%d个排列 %s ",num++,pStr);
- }
- else
- {
- for(char *pCh = pBegin; *pCh != '�'; pCh++) //第pBegin个数分别与它后面的数字交换就能得到新的排列
- {
- if(IsSwap(pBegin , pCh))
- {
- swap(*pBegin , *pCh);
- Permutation(pStr , pBegin + 1);
- swap(*pBegin , *pCh);
- }
- }
- }
- }
- int main(void)
- {
- char str[] = "baa";
- Permutation(str , str);
- return 0;
- }
OK,到现在我们已经能熟练写出递归的方法了,并且考虑了字符串中的重复数据可能引发的重复数列问题。那么如何使用非递归的方法来得到全排列了?
三、全排列的非递归实现
要考虑全排列的非递归实现,先来考虑如何计算字符串的下一个排列。如"1234"的下一个排列就是"1243"。只要对字符串反复求出下一个排列,全排列的也就迎刃而解了。
如何计算字符串的下一个排列了?来考虑"926520"这个字符串,我们从后向前找第一双相邻的递增数字,"20"、"52"都是非递增的,"26
"即满足要求,称前一个数字2为替换数,替换数的下标称为替换点,再从后面找一个比替换数大的最小数(这个数必然存在),0、2都不行,5可以,将5和2
交换得到"956220",然后再将替换点后的字符串"6220"颠倒即得到"950226"。
对于像“4321”这种已经是最“大”的排列,采用STL中的处理方法,将字符串整个颠倒得到最“小”的排列"1234"并返回false。
这样,只要一个循环再加上计算字符串下一个 排列的函数就可以轻松的实现非递归的全排列算法。按上面思路并参考STL中的实现源码,不难写成一份质量较高的代码。值得注意的是在循环前要对字符串排序 下,可以自己写快速排序的代码(请参阅《白话经典算法之六 快速排序 快速搞定》),也可以直接使用VC库中的快速排序函数(请参阅《使用VC库函数中的快速排序函数》)。下面列出完整代码:
- #include<iostream>
- #include<algorithm>
- #include<cstring>
- using namespace std;
- #include<assert.h>
- //反转区间
- void Reverse(char* pBegin , char* pEnd)
- {
- while(pBegin < pEnd)
- swap(*pBegin++ , *pEnd--);
- }
- //下一个排列
- bool Next_permutation(char a[])
- {
- assert(a);
- char *p , *q , *pFind;
- char *pEnd = a + strlen(a) - 1;
- if(a == pEnd)
- return false;
- p = pEnd;
- while(p != a)
- {
- q = p;
- p--;
- if(*p < *q) //找降序的相邻2数,前一个数即替换数
- {
- //从后向前找比替换点大的第一个数
- pFind = pEnd;
- while(*pFind < *p)
- --pFind;
- swap(*p , *pFind);
- //替换点后的数全部反转
- Reverse(q , pEnd);
- return true;
- }
- }
- Reverse(a , pEnd); //如果没有下一个排列,全部反转后返回false
- return false;
- }
- int cmp(const void *a,const void *b)
- {
- return int(*(char *)a - *(char *)b);
- }
- int main(void)
- {
- char str[] = "bac";
- int num = 1;
- qsort(str , strlen(str),sizeof(char),cmp);
- do
- {
- printf("第%d个排列 %s ",num++,str);
- }while(Next_permutation(str));
- return 0;
- }
至此我们已经运用了递归与非递归的方法解决了全排列问题,总结一下就是:
1、全排列就是从第一个数字起每个数分别与它后面的数字交换。
2、去重的全排列就是从第一个数字起每个数分别与它后面非重复出现的数字交换。
3、全排列的非递归就是由后向前找替换数和替换点,然后由后向前找第一个比替换数大的数与替换数交换,最后颠倒替换点后的所有数据。
二、字符串的组合
题目:输入一个字符串,输出该字符串中字符的所有组合。举个例子,如果输入abc,它的组合有a、b、c、ab、ac、bc、abc。
上面我们详细讨论了如何用递归的思路求字符串的排列。同样,本题也可以用递归的思路来求字符串的组合。
假设我们想在长度为n的字符串中求m个字符的组合。我们先从头扫描字符串的第一个字符。针对第一个字符,我们有两种选择:第一是把这个字符放到组合中去,
接下来我们需要在剩下的n-1个字符中选取m-1个字符;第二是不把这个字符放到组合中去,接下来我们需要在剩下的n-1个字符中选择m个字符。这两种选
择都很容易用递归实现。下面是这种思路的参考代码:
- #include<iostream>
- #include<vector>
- #include<cstring>
- using namespace std;
- #include<assert.h>
- void Combination(char *string ,int number,vector<char> &result);
- void Combination(char *string)
- {
- assert(string != NULL);
- vector<char> result;
- int i , length = strlen(string);
- for(i = 1 ; i <= length ; ++i)
- Combination(string , i ,result);
- }
- void Combination(char *string ,int number , vector<char> &result)
- {
- assert(string != NULL);
- if(number == 0)
- {
- static int num = 1;
- printf("第%d个组合 ",num++);
- vector<char>::iterator iter = result.begin();
- for( ; iter != result.end() ; ++iter)
- printf("%c",*iter);
- printf(" ");
- return ;
- }
- if(*string == '�')
- return ;
- result.push_back(*string);
- Combination(string + 1 , number - 1 , result);
- result.pop_back();
- Combination(string + 1 , number , result);
- }
- int main(void)
- {
- char str[] = "abc";
- Combination(str);
- return 0;
- }
由于组合可以是1个字符的组合,2个字符的字符……一直到n个字符的组合,因此在函数void Combination(char* string),我们需要一个for循环。另外,我们用一个vector来存放选择放进组合里的字符。
方法二:用位运算来实现求组合
- #include<iostream>
- using namespace std;
- int a[] = {1,3,5,4,6};
- char str[] = "abcde";
- void print_subset(int n , int s)
- {
- printf("{");
- for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; ++i)
- {
- if( s&(1<<i) ) // 判断s的二进制中哪些位为1,即代表取某一位
- printf("%c ",str[i]); //或者a[i]
- }
- printf("} ");
- }
- void subset(int n)
- {
- for(int i= 0 ; i < (1<<n) ; ++i)
- {
- print_subset(n,i);
- }
- }
- int main(void)
- {
- subset(5);
- return 0;
- }
字符串全排列扩展----八皇后问题
题目:在8×8的国际象棋上摆放八个皇后,使其不能相互攻击,即任意两个皇后不得处在同一行、同一列或者同一对角斜线上。下图中的每个黑色格子表示一个皇后,这就是一种符合条件的摆放方法。请求出总共有多少种摆法。
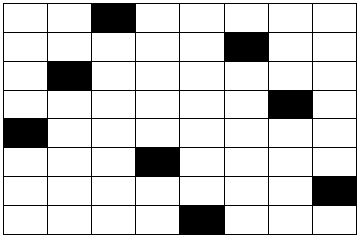
这就是有名的八皇后问题。解决这个问题通常需要用递归,而递归对编程能力的要求比较高。因此有不少面试官青睐这个题目,用来考察应聘者的分析复杂问题的能力以及编程的能力。
由于八个皇后的任意两个不能处在同一行,那么这肯定是每一个皇后占据一行。于是我们可以定义一个数组ColumnIndex[8],数组中第i个数字表示
位于第i行的皇后的列号。先把ColumnIndex的八个数字分别用0-7初始化,接下来我们要做的事情就是对数组ColumnIndex做全排列。由
于我们是用不同的数字初始化数组中的数字,因此任意两个皇后肯定不同列。我们只需要判断得到的每一个排列对应的八个皇后是不是在同一对角斜线上,也就是数
组的两个下标i和j,是不是i-j==ColumnIndex[i]-Column[j]或者j-i==ColumnIndex[i]-
ColumnIndex[j]。
关于排列的详细讨论,详见上面的讲解。
接下来就是写代码了。思路想清楚之后,编码并不是很难的事情。下面是一段参考代码:
- #include<iostream>
- using namespace std;
- int g_number = 0;
- void Permutation(int * , int , int );
- void Print(int * , int );
- void EightQueen( )
- {
- const int queens = 8;
- int ColumnIndex[queens];
- for(int i = 0 ; i < queens ; ++i)
- ColumnIndex[i] = i; //初始化
- Permutation(ColumnIndex , queens , 0);
- }
- bool Check(int ColumnIndex[] , int length)
- {
- int i,j;
- for(i = 0 ; i < length; ++i)
- {
- for(j = i + 1 ; j < length; ++j)
- {
- if( i - j == ColumnIndex[i] - ColumnIndex[j] || j - i == ColumnIndex[i] - ColumnIndex[j]) //在正、副对角线上
- return false;
- }
- }
- return true;
- }
- void Permutation(int ColumnIndex[] , int length , int index)
- {
- if(index == length)
- {
- if( Check(ColumnIndex , length) ) //检测棋盘当前的状态是否合法
- {
- ++g_number;
- Print(ColumnIndex , length);
- }
- }
- else
- {
- for(int i = index ; i < length; ++i) //全排列
- {
- swap(ColumnIndex[index] , ColumnIndex[i]);
- Permutation(ColumnIndex , length , index + 1);
- swap(ColumnIndex[index] , ColumnIndex[i]);
- }
- }
- }
- void Print(int ColumnIndex[] , int length)
- {
- printf("%d ",g_number);
- for(int i = 0 ; i < length; ++i)
- printf("%d ",ColumnIndex[i]);
- printf(" ");
- }
- int main(void)
- {
- EightQueen();
- return 0;
- }
转载:http://zhedahht.blog.163.co
题目:输入两个整数n和m,从数列1,2,3...n中随意取几个数,使其和等于m,要求列出所有的组合。
- #include <iostream>
- #include <list>
- using namespace std;
- list<int> list1;
- void find_factor(int sum,int n)
- {
- //递归出口
- if(n<=0||sum<=0)
- return;
- //输出找到的数
- if(sum==n)
- {
- list1.reverse();
- for(list<int>::iterator iter=list1.begin();iter!=list1.end();iter++)
- cout<<*iter<<"+";
- cout<<n<<endl;
- list1.reverse();
- }
- list1.push_front(n);
- find_factor(sum-n,n-1);//n放在里面
- list1.pop_front();
- find_factor(sum,n-1);//n不放在里面
- }
- int main(void)
- {
- int sum,n;
- cin>>sum>>n;
- cout<<"所有可能的序列,如下:"<<endl;
- find_factor(sum,n);
- return 0;
- }