Problem Description
Given 5 integers: a, b, c, d, k, you're to find x in a...b, y in c...d that GCD(x, y) = k. GCD(x, y) means the greatest common divisor of x and y. Since the number of choices may be very large, you're only required to output the total number of different number pairs.
Please notice that, (x=5, y=7) and (x=7, y=5) are considered to be the same.
Yoiu can assume that a = c = 1 in all test cases.
Input
The input consists of several test cases. The first line of the input is the number of the cases. There are no more than 3,000 cases.
Each case contains five integers: a, b, c, d, k, 0 < a <= b <= 100,000, 0 < c <= d <= 100,000, 0 <= k <= 100,000, as described above.
Output
For each test case, print the number of choices. Use the format in the example.
Sample Input
2
1 3 1 5 1
1 11014 1 14409 9
Sample Output
Case 1: 9
Case 2: 736427
Hint
For the first sample input, all the 9 pairs of numbers are (1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (1, 5), (2, 3), (2, 5), (3, 4), (3, 5).
题意:给出a,b,c,d,k(c,d,k<=100000)其中a与c必然等于1,求x属于1~b,y属于1~d中gcd(x,y)=k的对数. (n1,n2)与(n2,n1)算一种
题解: 莫比乌斯反演真是一个神奇的玩意,有空一定会写一篇证明啊应用啊之类的博客(继续挖坑)
已知函数
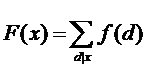
或者
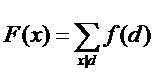
那么就可以通过莫比乌斯反演反演出来
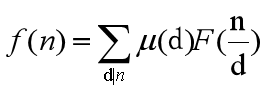
或者
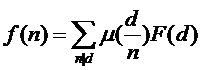
然后这道题让我们求的是
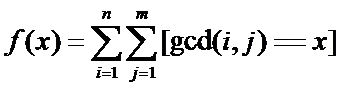
那么我们的F(x)是怎么样的呢?我们选择用后面的一种来求F(x)

这玩意是什么意思呢?
可以理解为i在1~n之中j在1~m之中使gcd(i,j)是x的倍数的对数
i和j一定是x的倍数,那么F(x)可以用O(1)的复杂度算出来
F(x)=[n/x]*[m/x]
然后根据反演,再搞回f(x)就行了。
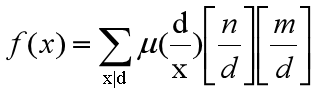
代码如下:
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int p[100010],vis[100010],mu[100010],cnt;
void get()
{
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
cnt=0;
vis[1]=1;
mu[1]=1;
for(int i=2;i<=100000;i++)
{
if(!vis[i])
{
p[cnt++]=i;
mu[i]=-1;
}
for(int j=0;j<cnt;j++)
{
if(p[j]*i>100000)
{
break;
}
vis[i*p[j]]=1;
if(i%p[j]==0)
{
mu[i*p[j]]=0;
break;
}
else
{
mu[i*p[j]]=-mu[i];
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int t,ttt=0;
int a,b,c,d,k;
get();
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
ttt++;
scanf("%d%d%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c,&d,&k);
if(k==0)
{
printf("Case %d: 0
",ttt);
continue;
}
b/=k;
d/=k;
if(b>d)
{
swap(b,d);
}
long long ans1=0;
for(int i=1;i<=b;i++)
{
ans1+=(long long)mu[i]*(b/i)*(d/i);
}
long long ans2=0;
for(int i=1;i<=b;i++)
{
ans2+=(long long)mu[i]*(b/i)*(b/i);
}
ans1-=ans2/2;
printf("Case %d: %lld
",ttt,ans1);
}
}