Tuple数据类型:
mixed_tuple = (1 , 2, ['a','b'])
print("mixed_tuple:" + str(mixed_tuple))
mixed_tuple[2][0]='c'
mixed_tuple[2][1]='d'
print("mixed_tuple after:" + str(mixed_tuple))
字典的应用:
# coding: utf-8
# 创建一个词典
phone_book= {'Tom':123,'sunliyuan':456,'shi':789}
mixed_dict={"Tom":'boy',11:23.5}
# 字典的调用
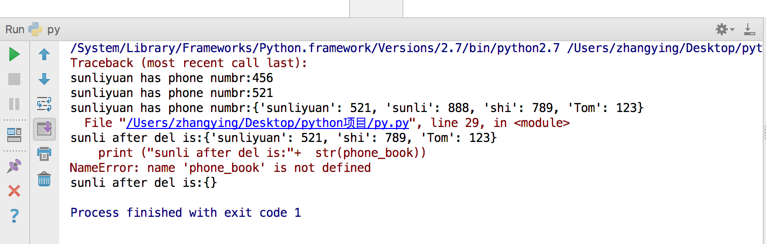
print ("sunliyuan has phone numbr:"+ str(phone_book["sunliyuan"]))
# 修改字典的值
phone_book['sunliyuan']=521
print ("sunliyuan has phone numbr:"+ str(phone_book["sunliyuan"]))
# 添加一个值
phone_book['sunli']=888
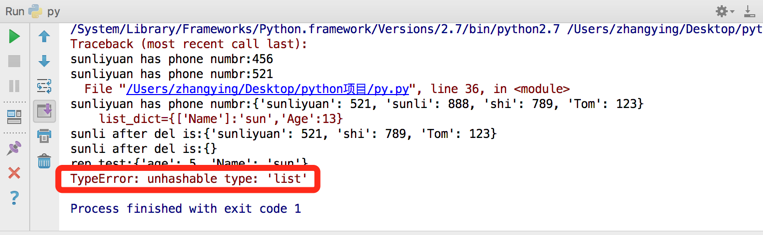
print ("sunliyuan has phone numbr:"+ str(phone_book))
# 删除字典中的元素和本身
del phone_book['sunli']
print ("sunli after del is:"+ str(phone_book))
# 清空字典的值
phone_book.clear()
print ("sunli after del is:"+ str(phone_book))
# 清空字典本身
del phone_book
print ("sunli after del is:"+ str(phone_book))
运行的效果图:
# 特性
# 不允许同一个键出现两次
rep_test={'Name':'aa','age':5,'Name':'sun'}
print("rep_test:"+str(rep_test))
# 键必须不可变 用数字和字符串充当键 不能用list充当
# list_dict={['Name']:'sun','Age':13}
#Tuple是可以的 (可变的)
list_dict={('Nam'):'sun','Age':13}
函数:
# coding: utf-8
# 没有参数和返回的函数
def say_hi():
print ("sunliyuan")
say_hi()
say_hi()
# 有参数 无返回值
def print_sum(a,b):
c=a+b
print (c)
print_sum(1,2)
def hellow(str):
print("hellow" + str + "!")
# 有参数有返回值的
def repatstr(str,times):
repeated_strs=str*times
return repeated_strs
repatstr_string=repatstr("sunliyuan",4)
print(repatstr_string)
# 全局变量和局部变量
x = 60
def foo(x):
print("x is :"+str(x))
x=3
print("change local x to"+str(x))
foo(x)
print ('x is still',str(x))
# 默认参数
def repeat_str(s, times = 1):
repeated_strs = s * times
return repeated_strs
repeated_strings = repeat_str("Happy Birthday!")
print(repeated_strings)
repeated_strings_2 = repeat_str("Happy Birthday!" , 4)
print(repeated_strings_2)
#不能在有默认参数后面跟随没有默认参数
#f(a, b =2)合法
#f(a = 2, b)非法
# 关键字参数: 调用函数时,选择性的传入部分参数
def func(a, b=4, c=8):
print('a is', a, 'and b is', b, 'and c is', c)
func(13, 17)
func(125, c=24)
func(c=40, a=80)


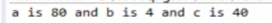
# VarArgs参数
def print_paras(fpara, *nums, **words):
print("fpara: " + str(fpara))
print("nums: " + str(nums))
print("words: " + str(words))
print_paras("hello", 1, 3, 5, 7, word="python", anohter_word="java")