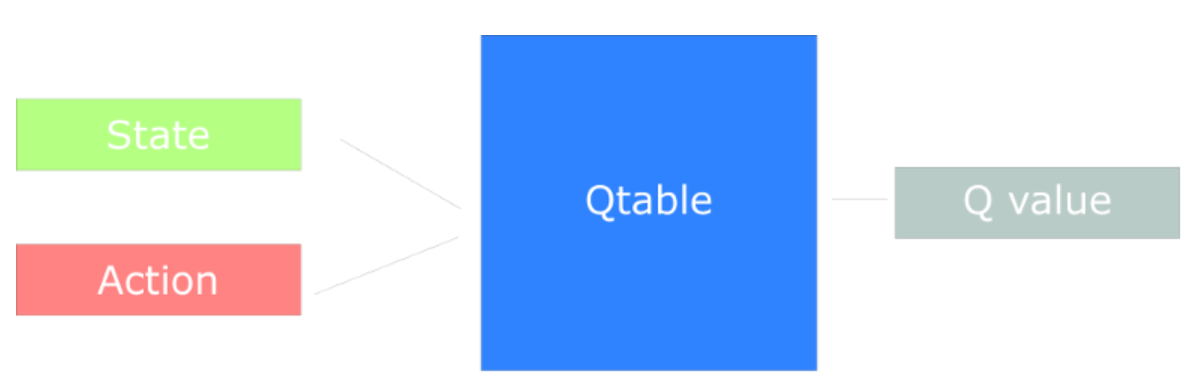
在前两篇文章强化学习基础:基本概念和动态规划和强化学习基础:蒙特卡罗和时序差分中介绍的强化学习的三种经典方法(动态规划、蒙特卡罗以及时序差分)适用于有限的状态集合$mathcal{S}$,以时序差分中的Q-Learning算法为例,一般来说使用n行(n = number of states)和m列(m= number of actions)的矩阵(Q table)来储存action-value function的值,如下图所示:
对于连续的状态集合$mathcal{S}$,上述方法就不能适用了,这时可以引入神经网络来估计Q的值,即Deep Q-Learning,如下图所示:

接下来介绍Deep Q-Learning中常用的几种技巧,用于提升学习效果:
- Stack States:对于连续的状态集合,单个状态不能很好地描述整体的状况。例如下图所示,要判断黑色方块的移动方向,仅凭一副图像是无法判断的,需要连续的多幅图像才能判断出黑色方块在向右移动

- Experience Replay:如下图所示,防止算法在训练过程中忘记了之前场景获得的经验,创建一个Replay Buffer,不断回放之前的场景对算法进行训练;另一方面,相邻的场景之间(例如$[S_{t},A_{t},R_{t+1},S_{t+1}]$与$[S_{t+1},A_{t+1},R_{t+2},S_{t+2}]$)有着一定的相关性,为了防止算法被固定在某些特定的状态空间,从Replay Buffer中随机抽样选取场景进行训练(打乱场景之间的顺序,减少相邻场景的相关性)

- Fixed Q-targets:针对Deep Q-Learning中计算Q值的神经网络的权重系数的更新,有公式如左图所示,此时将TD target近似为了$q_{pi}(S,A)$的真值,但是当不断更新权重系数时TD target也是不断变化的,这就会使得在训练过程中$q_{pi}(S,A)$的估计值要接近一个不断变化的值,加大了训练难度,减小了训练效率。解决方案如右图所示,使用相对固定的参数来估计TD target

- Double DQNs:解决TD target对$q_{pi}(S,A)$的真值可能高估的问题,方案是在计算TD target时使用两个不同的神经网络,将动作$a$的选择过程与TD target的计算过程进行分割。如果和Fixed Q-targets结合起来,可以直接使用$w$和$w^{-}$这两组参数(如下图所示)

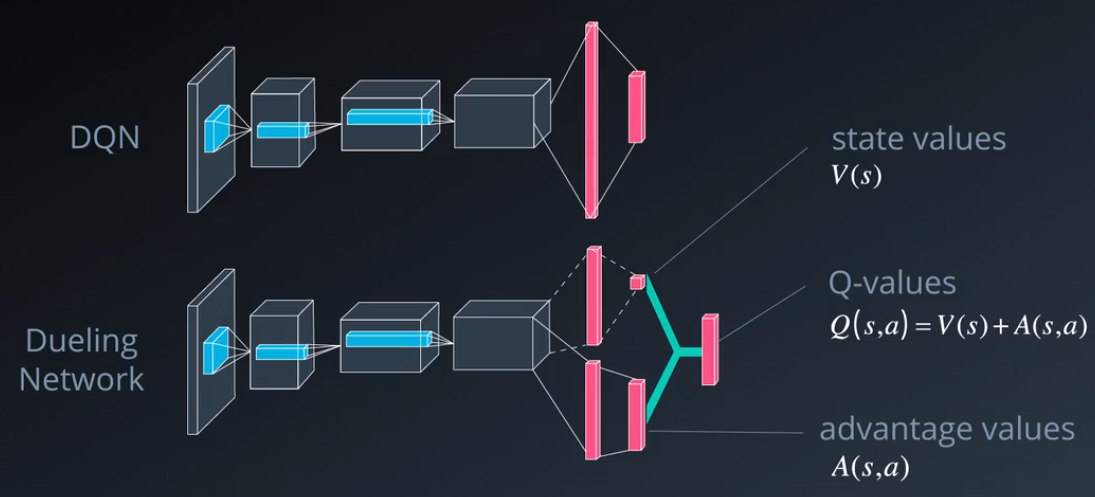
- Dueling DQN:如下图所示,相对于直接计算action-value function $Q(s,a)$,将$Q(s,a)$分解为state-value function $V(s)$与advantage-value function $A(s,a)$之和,这样做的原因是多数状态下采取何种行动对$Q(s,a)$的值影响不大,适合直接对状态函数$V(s)$进行估计,再叠加上不同行动对其的影响。在实际计算中,为了使得从$Q(s,a)$能够唯一确定$V(s)$与$A(s,a)$,可以令$A(s,a)$的均值(即$frac{1}{|mathcal{A}|}sum_{a^{prime}} A(s,a^{prime})$)为0
-
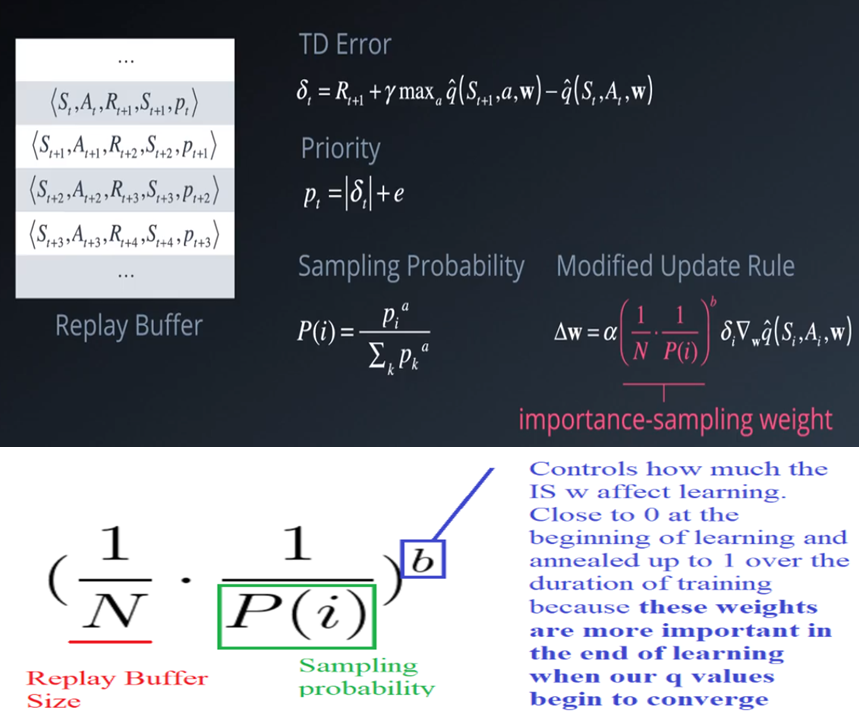
Prioritized Experience Replay:如下图所示,对Replay Buffer中的每个场景加入一个优先级,一个场景的TD error越大,它对应的优先级就越大。其中$e$是一个大于0的常数,防止抽样概率为0;$a$控制按优先级抽样和均匀抽样的比重,$a=1$时完全按优先级抽样,$a=0$时退化为均匀抽样;另外由于是按照优先级进行抽样,还需要改写神经网络中权重系数的更新规则,针对优先级高的场景减少权重更新的步长,使权重更新的过程与场景出现的真实概率一致(特别是在训练的后期,通过参数$b$控制),避免过拟合高优先级的场景
代码实现
使用vizdoom强化学习环境,以其中的一个任务为基础进行训练,该任务要确保玩家活着走到目标位置(要做到这一点,路上要躲避敌人的射击或者杀死敌人,否则不可能成功)。该任务每步的奖励与玩家和目标的距离变化有关(+dX for getting closer, -dX for getting further),此外若玩家死亡会有-100的惩罚。
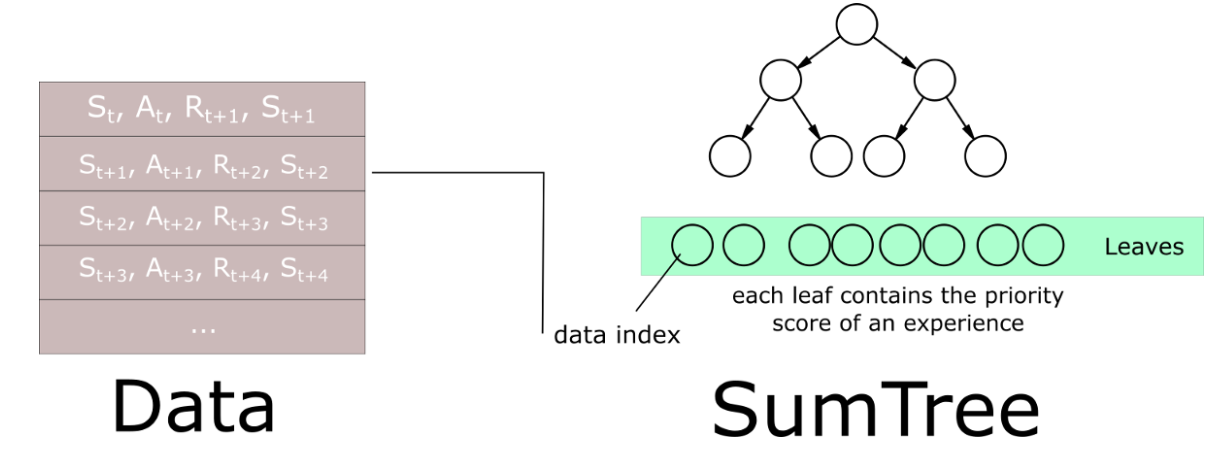
值得注意的是在代码中使用SumTree(二叉树,每个父节点的值是两个子节点的值的和)这一数据结构来存储Replay Buffer中的Priority,具体结构如下图所示,这样做的目的是方便按优先级进行抽样,可以使得每次抽样以及更新优先级的计算均为$O(ln{n})$。在抽样过程中抽得的叶子节点$x$满足$P(xleq{k})=frac{sum_{i=1}^{k}Priority_i}{sum_{i=1}^{n}Priority_i}, ext{ }kin{1,2,cdots,n}$

import tensorflow as tf # Deep Learning library import numpy as np # Handle matrices from vizdoom import * # Doom Environment import random # Handling random number generation import time # Handling time calculation from skimage import transform# Help us to preprocess the frames from collections import deque# Ordered collection with ends import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # Display graphs import warnings # This ignore all the warning messages that are normally printed during the training because of skiimage warnings.filterwarnings('ignore') ### Here we create our environment def create_environment(): game = DoomGame() # Load the correct configuration game.load_config("deadly_corridor.cfg") # Load the correct scenario (in our case deadly_corridor scenario) game.set_doom_scenario_path("deadly_corridor.wad") game.init() # Create an hot encoded version of our actions (7 possible actions) possible_actions = np.identity(7,dtype=int).tolist() return game, possible_actions game, possible_actions = create_environment() ### Preprocess(reduce the complexity of states and the training time) def preprocess_frame(frame): # Grayscale frame(color not add important information, already done by the config file) # Crop the screen (remove part that contains no information) cropped_frame = frame[15:-5,20:-20] #[Up: Down, Left: right] # Normalize Pixel Values normalized_frame = cropped_frame/255.0 # Resize preprocessed_frame = transform.resize(normalized_frame, [100,120]) return preprocessed_frame # 100x120x1 frame ### Stack frames stack_size = 4 #stack 4 frames # Initialize deque with zero-images, one array for each image stacked_frames = deque([np.zeros((100,120), dtype=np.int) for i in range(stack_size)], maxlen=4) def stack_frames(stacked_frames, state, is_new_episode): frame = preprocess_frame(state) #preprocess frame if is_new_episode: # Clear our stacked_frames stacked_frames = deque([np.zeros((100,120), dtype=np.int) for i in range(stack_size)], maxlen=4) # Because we're in a new episode, copy the same frame 4x stacked_frames.append(frame) stacked_frames.append(frame) stacked_frames.append(frame) stacked_frames.append(frame) # Stack the frames stacked_state = np.stack(stacked_frames, axis=2) else: # Append frame to deque, automatically removes the oldest frame stacked_frames.append(frame) # Build the stacked state stacked_state = np.stack(stacked_frames, axis=2) return stacked_state, stacked_frames ### Set the hyperparameters # MODEL HYPERPARAMETERS state_size = [100,120,4] # Our input is a stack of 4 frames hence 100x120x4 (Width, height, channels) action_size = game.get_available_buttons_size() # 7 possible actions learning_rate = 0.00025 # Alpha (i.e., learning rate) # TRAINING HYPERPARAMETERS total_episodes = 5000 # Total episodes for training max_steps = 5000 # Max possible steps in an episode batch_size = 64 # FIXED Q TARGETS HYPERPARAMETERS max_tau = 10000 # The number of steps where we update our target network # EXPLORATION HYPERPARAMETERS for epsilon greedy strategy explore_start = 1.0 # exploration probability at start explore_stop = 0.01 # minimum exploration probability decay_rate = 0.00005 # exponential decay rate for exploration prob # Q LEARNING hyperparameters gamma = 0.95 # Discounting rate # MEMORY HYPERPARAMETERS(If you have GPU change to 1 million) pretrain_length = 100000 # Number of experiences stored in the Memory when initialized for the first time memory_size = 100000 # Number of experiences the Memory can keep # MODIFY THIS TO FALSE IF YOU JUST WANT TO SEE THE TRAINED AGENT training = True ### Set up Deep Q network and Target network (both are Dueling Network) class DDDQNNet: def __init__(self, state_size, action_size, learning_rate, name): self.state_size = state_size self.action_size = action_size self.learning_rate = learning_rate self.name = name # use tf.variable_scope to know which network we're using (DQN or target_net) # it will be useful when we will update our w- parameters (by copy the DQN parameters) with tf.variable_scope(self.name): # create the placeholders self.inputs_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, *state_size], name="inputs") #[None,100,120,4] self.ISWeights_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None,1], name='IS_weights') self.actions_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, action_size], name="actions_") # Remember that target_Q is the R(s,a) + max Qhat(s', a') self.target_Q = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None], name="target") # first conv layer self.conv1 = tf.layers.conv2d(inputs = self.inputs_, filters = 32, kernel_size = [8,8], strides = [4,4], padding = "VALID", name = "conv1", kernel_initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer_conv2d()) self.conv1_out = tf.nn.elu(self.conv1, name="conv1_out") # second conv layer self.conv2 = tf.layers.conv2d(inputs = self.conv1_out, filters = 64, kernel_size = [4,4], strides = [2,2], padding = "VALID", name = "conv2", kernel_initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer_conv2d()) self.conv2_out = tf.nn.elu(self.conv2, name="conv2_out") # third conv layer self.conv3 = tf.layers.conv2d(inputs = self.conv2_out, filters = 128, kernel_size = [4,4], strides = [2,2], padding = "VALID", name = "conv3", kernel_initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer_conv2d()) self.conv3_out = tf.nn.elu(self.conv3, name="conv3_out") self.flatten = tf.layers.flatten(self.conv3_out) # Here we separate into two streams (Dueling Network) # The one that calculate V(s) self.value_fc = tf.layers.dense(inputs = self.flatten, units = 512, activation = tf.nn.elu, kernel_initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer(), name="value_fc") self.value = tf.layers.dense(inputs = self.value_fc, units = 1, activation = None, kernel_initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer(), name="value") # The one that calculate A(s,a) self.advantage_fc = tf.layers.dense(inputs = self.flatten, units = 512, activation = tf.nn.elu, kernel_initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer(), name="advantage_fc") self.advantage = tf.layers.dense(inputs = self.advantage_fc, units = self.action_size, activation = None, kernel_initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer(), name="advantages") # Agregating layer # Q(s,a) = V(s) + (A(s,a) - 1/|A| * sum A(s,a')) self.output = self.value + tf.subtract(self.advantage, tf.reduce_mean(self.advantage, axis=1, keepdims=True)) # Predicted Q value self.Q = tf.reduce_sum(tf.multiply(self.output, self.actions_), axis=1) # For computing priority and updating Sumtree self.absolute_errors = tf.abs(self.target_Q - self.Q) # The loss is modified because of Priority Experience Replay self.loss = tf.reduce_mean(self.ISWeights_ * tf.squared_difference(self.target_Q, self.Q)) self.optimizer = tf.train.RMSPropOptimizer(self.learning_rate).minimize(self.loss) # Reset the graph tf.reset_default_graph() # Instantiate the DQNetwork DQNetwork = DDDQNNet(state_size, action_size, learning_rate, name="DQNetwork") # Instantiate the target network TargetNetwork = DDDQNNet(state_size, action_size, learning_rate, name="TargetNetwork") ### Data Struture to store experience and priority(SumTree) class SumTree(object): data_pointer = 0 # Here we initialize the tree with all nodes = 0, and initialize the data with all values = 0 def __init__(self, capacity): self.capacity = capacity # Number of leaf nodes (final nodes) that contains experiences # Generate the tree with all nodes values = 0 # Parent nodes = capacity - 1, Leaf nodes = capacity self.tree = np.zeros(2 * capacity - 1) # Contains the experiences (so the size of data is capacity) self.data = np.zeros(capacity, dtype=object) # Here we add our priority score in the sumtree leaf and add the experience in data def add(self, priority, data): # Look at what index we want to put the experience tree_index = self.data_pointer + self.capacity - 1 # the leaves from left to right self.data[self.data_pointer] = data # Update data frames self.update(tree_index, priority) # Update the leaf self.data_pointer += 1 # Add 1 to data_pointer # If we're above the capacity, you go back to first index (we overwrite) if self.data_pointer >= self.capacity: self.data_pointer = 0 # Update the leaf priority score and propagate the change through tree def update(self, tree_index, priority): # Change = new priority score - former priority score change = priority - self.tree[tree_index] self.tree[tree_index] = priority # Propagate the change through tree while tree_index != 0: tree_index = (tree_index - 1) // 2 self.tree[tree_index] += change # Here we get the leaf and associated experience # the returned index is the smallest index satisfying: sum(leaf priority) >= v for leaf index <= returned index def get_leaf(self, v): parent_index = 0 while True: left_child_index = 2 * parent_index + 1 right_child_index = left_child_index + 1 # If we reach bottom, end the search if left_child_index >= len(self.tree): leaf_index = parent_index break else: # downward search if v <= self.tree[left_child_index]: parent_index = left_child_index else: v -= self.tree[left_child_index] parent_index = right_child_index data_index = leaf_index - self.capacity + 1 return leaf_index, self.tree[leaf_index], self.data[data_index] @property def total_priority(self): return self.tree[0] # Returns the root node ### Create Replay Buffer and Prioritized Experience Replay class Memory(object): PER_e = 0.01 # Hyperparameter that we use to avoid some experiences to have 0 probability of being taken PER_a = 0.6 # Hyperparameter that we use to make a tradeoff between taking only exp with high priority and sampling randomly PER_b = 0.4 # importance-sampling, from initial value increasing to 1 PER_b_increment_per_sampling = 0.001 absolute_error_upper = 1. # clipped abs error def __init__(self, capacity): # Making the tree self.tree = SumTree(capacity) # Store a new experience in our tree # Each new experience have a score of max_prority (it will be then improved when we use this exp to train our DDQN) def store(self, experience): # Find the max priority max_priority = np.max(self.tree.tree[-self.tree.capacity:]) # If the max priority = 0 we can't put priority = 0 since this exp will never have a chance to be selected # So we use an upper limit if max_priority == 0: max_priority = self.absolute_error_upper self.tree.add(max_priority, experience) # set the max p for new exp # First, to sample a minibatch of n size, the range [0, priority_total] is split into n ranges. # Then a value is uniformly sampled from each range # We search in the sumtree, the experience where priority score correspond to sample values are retrieved from # Finally, we calculate IS weights for each minibatch element def sample(self, n): memory_b = [] # Create a sample array that will contains the minibatch b_idx, b_ISWeights = np.empty((n,), dtype=np.int32), np.empty((n, 1), dtype=np.float32) priority_segment = self.tree.total_priority / n # priority segment # Here we increasing the PER_b each time we sample a new minibatch self.PER_b = np.min([1., self.PER_b + self.PER_b_increment_per_sampling]) # max = 1 # Calculating the max_weight p_min = np.min(self.tree.tree[-self.tree.capacity:]) / self.tree.total_priority max_weight = (p_min * n) ** (-self.PER_b) for i in range(n): # A value is uniformly sample from each range a, b = priority_segment * i, priority_segment * (i + 1) value = np.random.uniform(a, b) # Experience that correspond to each value is retrieved index, priority, data = self.tree.get_leaf(value) sampling_probabilities = priority / self.tree.total_priority # P(j) # IS = (1/N * 1/P(i))**b /max wi == (N*P(i))**-b /max wi b_ISWeights[i, 0] = np.power(n * sampling_probabilities, -self.PER_b)/ max_weight b_idx[i]= index experience = [data] memory_b.append(experience) return b_idx, memory_b, b_ISWeights # Update the priorities on the tree def batch_update(self, tree_idx, abs_errors): abs_errors += self.PER_e # convert to abs and avoid 0 clipped_errors = np.minimum(abs_errors, self.absolute_error_upper) ps = np.power(clipped_errors, self.PER_a) for ti, p in zip(tree_idx, ps): self.tree.update(ti, p) ### Deal with the empty memory problem (pre-populate memory by taking random actions and storing the experience) memory = Memory(memory_size) # Instantiate memory game.new_episode() # Render the environment for i in range(pretrain_length): # If it's the first step if i == 0: # First we need a state state = game.get_state().screen_buffer state, stacked_frames = stack_frames(stacked_frames, state, True) action = random.choice(possible_actions) # Random action reward = game.make_action(action) # Get the rewards done = game.is_episode_finished() # Look if the episode is finished # If the player is dead if done: # the episode ends so no next state next_state = np.zeros((120,140), dtype=np.int) next_state, stacked_frames = stack_frames(stacked_frames, next_state, False) # Add experience to memory experience = state, action, reward, next_state, done memory.store(experience) # Start a new episode game.new_episode() # First we need a state state = game.get_state().screen_buffer # Stack the frames state, stacked_frames = stack_frames(stacked_frames, state, True) else: # Get the next state next_state = game.get_state().screen_buffer next_state, stacked_frames = stack_frames(stacked_frames, next_state, False) # Add experience to memory experience = state, action, reward, next_state, done memory.store(experience) # Our state is now the next_state state = next_state ### Choose action from Q (use ϵ-greedy strategy) def predict_action(explore_start, explore_stop, decay_rate, decay_step, state, actions): exp_exp_tradeoff = np.random.rand() # First we randomize a number explore_probability = explore_stop + (explore_start - explore_stop) * np.exp(-decay_rate * decay_step) if (explore_probability > exp_exp_tradeoff): # Make a random action (exploration) action = random.choice(actions) else: # Get action from Q-network (exploitation) # Estimate the Qs values state Qs = sess.run(DQNetwork.output, feed_dict = {DQNetwork.inputs_: state.reshape((1, *state.shape))}) # Take the biggest Q value (= the best action) choice = np.argmax(Qs) action = actions[int(choice)] return action, explore_probability ### Copy the parameters of DQN to Target_network (used for Fixed Q-target and Double DQN) def update_target_graph(): # Get the parameters of our DQNNetwork from_vars = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES, "DQNetwork") # Get the parameters of our Target_network to_vars = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES, "TargetNetwork") op_holder = [] # Update our target_network parameters with DQNNetwork parameters for from_var,to_var in zip(from_vars,to_vars): op_holder.append(to_var.assign(from_var)) return op_holder ### Train the agent saver = tf.train.Saver() # Saver will help us to save our model if training == True: with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) # Initialize the variables decay_step = 0 # Initialize the decay step tau = 0 # Set tau = 0 game.init() # Init the game # Update the parameters of our TargetNetwork with DQN_weights update_target = update_target_graph() sess.run(update_target) for episode in range(total_episodes): step = 0 # Set step to 0 episode_rewards = [] # Initialize the rewards of the episode game.new_episode() # Make a new episode and observe the first state state = game.get_state().screen_buffer state, stacked_frames = stack_frames(stacked_frames, state, True) while step < max_steps: step += 1 tau += 1 decay_step +=1 # ϵ-greedy stragety action, explore_probability = predict_action(explore_start, explore_stop, decay_rate, decay_step, state, possible_actions) reward = game.make_action(action) # Do the action done = game.is_episode_finished() # Look if the episode is finished episode_rewards.append(reward) # Add the reward to total reward # If the game is finished if done: # the episode ends so no next state next_state = np.zeros((120,140), dtype=np.int) next_state, stacked_frames = stack_frames(stacked_frames, next_state, False) # Set step = max_steps to end the episode step = max_steps # Get the total reward of the episode total_reward = np.sum(episode_rewards) print('Episode: {}'.format(episode), 'Total reward: {}'.format(total_reward), 'Training loss: {:.4f}'.format(loss), 'Explore P: {:.4f}'.format(explore_probability)) # Add experience to memory experience = state, action, reward, next_state, done memory.store(experience) else: next_state = game.get_state().screen_buffer # Get the next state # Stack the frame of the next_state next_state, stacked_frames = stack_frames(stacked_frames, next_state, False) # Add experience to memory experience = state, action, reward, next_state, done memory.store(experience) state = next_state # LEARNING PART tree_idx, batch, ISWeights_mb = memory.sample(batch_size) # Obtain random mini-batch from memory states_mb = np.array([each[0][0] for each in batch], ndmin=3) actions_mb = np.array([each[0][1] for each in batch]) rewards_mb = np.array([each[0][2] for each in batch]) next_states_mb = np.array([each[0][3] for each in batch], ndmin=3) dones_mb = np.array([each[0][4] for each in batch]) target_Qs_batch = [] # DOUBLE DQN # Use DQNNetwork to select the action a' to take at next_state s' (action with the highest Q-value) # Use TargetNetwork to calculate the Q_val of Q(s',a') # Get Q values for next_state q_next_state = sess.run(DQNetwork.output, feed_dict = {DQNetwork.inputs_: next_states_mb}) # Calculate Qtarget for all actions at that state q_target_next_state = sess.run(TargetNetwork.output, feed_dict = {TargetNetwork.inputs_: next_states_mb}) # Set Q_target = r if the episode ends at s+1, otherwise set Q_target = r + gamma * Qtarget(s',a') for i in range(0, len(batch)): terminal = dones_mb[i] # We got a' action = np.argmax(q_next_state[i]) # If we are in a terminal state, only equals reward if terminal: target_Qs_batch.append(rewards_mb[i]) else: # Take the Qtarget for action a' target = rewards_mb[i] + gamma * q_target_next_state[i][action] target_Qs_batch.append(target) targets_mb = np.array([each for each in target_Qs_batch]) # Optimize _, loss, absolute_errors = sess.run([DQNetwork.optimizer, DQNetwork.loss, DQNetwork.absolute_errors], feed_dict={DQNetwork.inputs_: states_mb, DQNetwork.target_Q: targets_mb, DQNetwork.actions_: actions_mb, DQNetwork.ISWeights_: ISWeights_mb}) # Update priority memory.batch_update(tree_idx, absolute_errors) # Fixed Q target if tau > max_tau: # Update the parameters of our TargetNetwork with DQN_weights update_target = update_target_graph() sess.run(update_target) tau = 0 print("Model updated") # Save model every 5 episodes if episode % 5 == 0: save_path = saver.save(sess, "./models/model.ckpt") print("Model Saved") ### Watch the agent play with tf.Session() as sess: game = DoomGame() # Load the correct configuration (TESTING) game.load_config("deadly_corridor_testing.cfg") # Load the correct scenario (in our case deadly_corridor scenario) game.set_doom_scenario_path("deadly_corridor.wad") game.init() # Load the model saver.restore(sess, "./models/model.ckpt") for i in range(10): game.new_episode() state = game.get_state().screen_buffer state, stacked_frames = stack_frames(stacked_frames, state, True) while not game.is_episode_finished(): # EPSILON GREEDY STRATEGY exp_exp_tradeoff = np.random.rand() explore_probability = 0.01 if (explore_probability > exp_exp_tradeoff): # Make a random action (exploration) action = random.choice(possible_actions) else: # Get action from Q-network (exploitation) Qs = sess.run(DQNetwork.output, feed_dict = {DQNetwork.inputs_: state.reshape((1, *state.shape))}) choice = np.argmax(Qs) # Take the biggest Q value (= the best action) action = possible_actions[int(choice)] game.make_action(action) done = game.is_episode_finished() if done: break else: next_state = game.get_state().screen_buffer next_state, stacked_frames = stack_frames(stacked_frames, next_state, False) state = next_state score = game.get_total_reward() print("Score: ", score) game.close()
