前言
本篇文章是String系列的第二篇(第一篇可参考String的那些事),文章的主要内容为:多种字符串拼接技术以及效率比较。
正文
字符串的不变性与字符串拼接的关系?
我们在String系列的第一篇文章中说过:String类是一个final类,这意味着String对象一旦被初始化就不会被改变。那我们所说的字符串拼接又是怎么一回事呢?见下图:
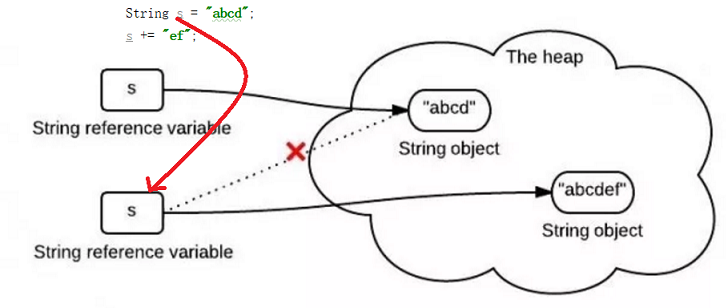
于是我们可以得知:当我们使用上面的方式进行字符串拼接时,最后会得到一个新的字符串对象。
字符串拼接的几种方式?
"+"
在Java中,拼接字符串最简单的方式就是直接使用符号+来拼接,就像下面这样:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "abcd";
String s2 = s1 + "ef";
}
}
那么这个"+"背后的原理是怎样的呢?我们反编译上面的字节码文件:
public class Test
{
public Test()
{
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
String s = "abcd";
String s1 = (new StringBuilder()).append(s).append("ef").toString();
}
}
通过反编译结果我们可以看到:Java中通过"+"对字符串的拼接,其实现原理其实是StringBuilder.append()。所以阿里巴巴Java开发手册有下面的建议:

concat()
示例代码如下所示:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "abcd";
String s2 = s1.concat("ef");
}
}
concat()源码如下:
public String concat(String str) {
int otherLen = str.length();
if (otherLen == 0) {
return this;
}
int len = value.length;
char buf[] = Arrays.copyOf(value, len + otherLen);
str.getChars(buf, len);
return new String(buf, true);
}
我们可以看到:concat()最后返回的是一个新的字符串对象。这也呼应了String类是一个final类的事实。
StringBuffer、StringBuilder
示例代码如下所示:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer sb2 = new StringBuffer("abcd");
StringBuilder sb1 = new StringBuilder("abcd");
sb1.append("ef");
sb2.append("ef");
}
}
append()的源码如下所示:
public AbstractStringBuilder append(String str) {
if (str == null)
return appendNull();
int len = str.length();
ensureCapacityInternal(count + len);
str.getChars(0, len, value, count);
count += len;
return this;
}
StringUtils.join()
示例代码如下所示:
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] str = {"abcd", ""};
String str2 = StringUtils.join(str, "ef");
System.out.println(str2);
}
}
join()的源码如下所示:
public static String join(Object[] array, String separator, int startIndex, int endIndex) {
if (array == null) {
return null;
} else {
if (separator == null) {
separator = "";
}
int noOfItems = endIndex - startIndex;
if (noOfItems <= 0) {
return "";
} else {
StringBuilder buf = newStringBuilder(noOfItems);
for(int i = startIndex; i < endIndex; ++i) {
if (i > startIndex) {
buf.append(separator);
}
if (array[i] != null) {
buf.append(array[i]);
}
}
return buf.toString();
}
}
}
可以看出join()底层也是StringBuilder实现的。