foreach标签所能遍历的collection对象一共有三种类型,分别为List、array、Map三种。
先初略的看一个例子:
<delete id="deleteBatch"> delete from user where id in <foreach collection="array" item="id" index="index" open="(" close=")" separator=","> #{id} </foreach> </delete>
若假如传入的参数是一个数组 int[] ids = {1,2,3,4,5},那么打印之后的SQL如下: delete form user where id in (1,2,3,4,5) 由这个例子,我们可以看到:
当传入的是一个array数组的时候,collection属性的值是array,
其item代表存储的元素,名字可以随便写但是要和后面的#{ }内的元素名相同,
而index是元素的索引位置,
open和close指定了sql语句中的括号,
其separator就指定了被遍历元素之间的分隔符逗号。———— 算下来foreach标签中共有6个属性
当然这个范例只能给人一点初略的理解。实际上要想真正熟悉完备的用法还得看更多的例子来总结。
下面我们从更多的例子中总结,而不是局限于文档中一系列抽象的描述里不知从何下手:
我们先讲List和数组(array)。——因为list和array在这里有相似的用法,而map则不一样,所以放在后面再讲。
List相关
传入的是list,且其中存储元素是基本数据类型包装类对象时:
映射文件:
<select id="dynamicForeachTest" resultType="Blog"> select * from t_blog where id in <foreach collection="list" index="index" item="item" open="(" separator="," close=")"> #{item} </foreach> </select>
接口:
public List<Blog> dynamicForeachTest(List<Integer> ids);
测试代码:
@Test public void dynamicForeachTest() { SqlSession session = Util.getSqlSessionFactory().openSession(); BlogMapper blogMapper = session.getMapper(BlogMapper.class); List<Integer> ids = new ArrayList<Integer>(); ids.add(1); ids.add(3); ids.add(6); List<Blog> blogs = blogMapper.dynamicForeachTest(ids); for (Blog blog : blogs) System.out.println(blog); session.close(); }
传入的是list,且其中存储元素是类对象时,此时我们要进行查询操作:
pojo: public class User{ public Integer id; public String name; public String bestFriend; public List<User> friendList; //这里省略getter和setter }
映射文件: <select id="countByUserList" resultType="int" parameterType="list"> <!—传入的参数直接就是list--> select count(*) from users <where> id in <foreach item="item" collection="list" separator="," open="(" close=")" index=""> #{item.id, jdbcType=NUMERIC} <!—我们的遍历条件是user中的成员属性id--> </foreach> </where> </select>
测试代码:
@Test public void shouldHandleComplexNullItem() { SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); try { Mapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(Mapper.class); User user1 = new User(); //创建一个对象 user1.setId(2); user1.setName("User2"); List<User> users = new ArrayList<User>(); //创建一个user集合容器,并存入前面的user1和null两个对象 users.add(user1); users.add(null); int count = mapper.countByUserList(users); //传入的是集合list,其中的元素是实例对象user Assert.assertEquals(1, count); } finally { sqlSession.close(); } }
传入的是list,且其中存储元素是类对象,此时我们要进行新增操作:
pojo: public class emp{ public String lastName; public String email; public String gender; public Department dept; }
映射文件:
<insert id="addEmps"> INSERT INTO tb1_emplyee(last_name,email,gender,d_id) VALUES <foreach collection="emps" item="emp" separator=","> (#{emp.lastName},#{emp.email},#{emp.gender},#{emp.dept.id}) <!--在对象成员的基础上继续取其成员值--> </foreach>
</insert>
对应的mapper接口: public void addEmps(@Param("emps")List<Employee> emps);
测试方法: @Test public void testBatchSave() throws IOException{ SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = getSqlSessionFactory(); //1、获取到的SqlSession不会自动提交数据 SqlSession openSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); try { EmployeeMapperDymanicSQL mapper=openSession.getMapper(EmployeeMapperDymanicSQL.class); List<Employee> emps=new ArrayList<Employee>(); emps.add(new Employee(null,"Eminem","Eminem@126.com","1",new Department(1))); emps.add(new Employee(null,"2Pac","2Pac@126.com","1",new Department(1))); mapper.addEmps(emps); openSession.commit(); } finally { openSession.close(); } }
传入的是一般类的对象,只是其中包含有一个List类型的成员属性:
pojo: public class QueryVo{ private User user; private List<Integer> ids; }
映射文件:
<!-- 根据ids查询用户 --> <select id="queryUserByIds" parameterType="queryVo" resultType="user"> <!--parameterType就是对象所属类--> SELECT * FROM `user` <where>
<foreach collection="ids" item="item" open="id IN (" close=")" separator=","> <!--collection直接就是这个类中的List类型成员--> #{item} </foreach> </where> </select>
<!--传入的parameterType直接就是对象的所属类,而collection就是这个类中类型为List的成员属性ids-->
测试方法 public void testQueryUserByIds() { // mybatis和spring整合,整合之后,交给spring管理 SqlSession sqlSession = this.sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); // 创建Mapper接口的动态代理对象,整合之后,交给spring管理 UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class); // 使用userMapper执行根据条件查询用户 QueryVo queryVo = new QueryVo(); List<Integer> ids = new ArrayList<>(); ids.add(1); ids.add(10); ids.add(24); queryVo.setIds(ids); List<User> list = userMapper.queryUserByIds(queryVo); for (User u : list) { System.out.println(u); } // mybatis和spring整合,整合之后,交给spring管理 sqlSession.close(); }
array相关
直接传入一个数组进行遍历查询
映射文件: <select id="dynamicForeach2Test" resultType="Blog"> select * from t_blog where id in <foreach collection="array" index="index" item="item" open="(" separator="," close=")"> #{item} </foreach> </select>
mapper接口: public List<Blog> dynamicForeach2Test(int[] ids);
测试代码: @Test public void dynamicForeach2Test() { SqlSession session = Util.getSqlSessionFactory().openSession(); BlogMapper blogMapper = session.getMapper(BlogMapper.class); int[] ids = new int[] {1,3,6,9}; List<Blog> blogs = blogMapper.dynamicForeach2Test(ids); for (Blog blog : blogs) System.out.println(blog); session.close(); }
将字符串处理成一个数组之后传入
字符串为: String approveStatus = new String("通过,不通过");
映射文件:
<if test="approveStatus != null and approveStatus!=''"> and i.approve_status IN <foreach collection="approveStatus.split(',')" item="status" open="(" separator="," close=")">
#{status}
</foreach>
</if>
map相关
传入一个map,其中包含了一个映射value是String类型,一个映射value是List集合类型。
映射文件: <select id="dynamicForeach3Test" resultType="Blog"> select * from t_blog where title like "%"#{title}"%" and id in <!--key值为title的映射--> <foreach collection="ids" index="index" item="item" open="(" separator="," close=")"> <!--key值为ids的list集合--> #{item} </foreach> </select>
接口代码: public List<Blog> dynamicForeach3Test(Map<String, Object> params);
测试方法: @Test public void dynamicForeach3Test() { SqlSession session = Util.getSqlSessionFactory().openSession(); BlogMapper blogMapper = session.getMapper(BlogMapper.class); final List<Integer> ids = new ArrayList<Integer>(); ids.add(1); ids.add(2); ids.add(3); ids.add(6); ids.add(7); ids.add(9); Map<String, Object> params = new HashMap<String, Object>(); params.put("ids", ids); //存入一个映射是List集合类型 params.put("title", "中国"); //另一个是String类型 List<Blog> blogs = blogMapper.dynamicForeach3Test(params); for (Blog blog : blogs) System.out.println(blog); session.close(); }
由此例可见:传入的参数就是map对象中的key值,mapper的sql中的条件名称和map的key值名称一模一样。
利用一个map存入所有的查询条件
创建一个map对象,将后期需要查询到所有条件都存进去: Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>(); //创建一个map容器
//将所有同类的条件都存进以下的集合或者赋给String对象 List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); //Stirng集合 String aa = "aa"; //单个String类对象 List<实体> objlist = new ArrayList<>(); //自定义类对象集合
//将以上条件都存入map容器中
map.put("stringList",list); map.put("aa",aa); map.put("objList",list);
映射文件:(传入的parameterType属性的值肯定是map类型的,这样collection属性的值就能够直接写成map中的key值)
(collection属性的值,除了在传入map时,可以不用写成array或者list而是直接写成map中的key之外。
在传入自定义类的对象时,也可以可以不用写成array或者list而是直接写成类中数据类型是array或者list的成员属性名)
<!--String集合的情况--> <if test="stringList!= null and stringList.size()>0"> <foreach collection="stringList" item="id"> OR A.ID=#{id} </foreach> </if>
<!--单个String类对象-->
<if test="aa != null and aa != ''">
AND A.ID=#{aa}
</if>
<!--自定义类对象集合-->
<if test="objList!= null and objList.size()>0">
<foreach collection="objList" item="obj"> OR A.ID=#{obj.id} </foreach> <!--在其中存储的对象的基础上继续取其成员属性的值-->
</if>
最后才放上抽象的参数说明,结合以上例子,应该能更好理解。
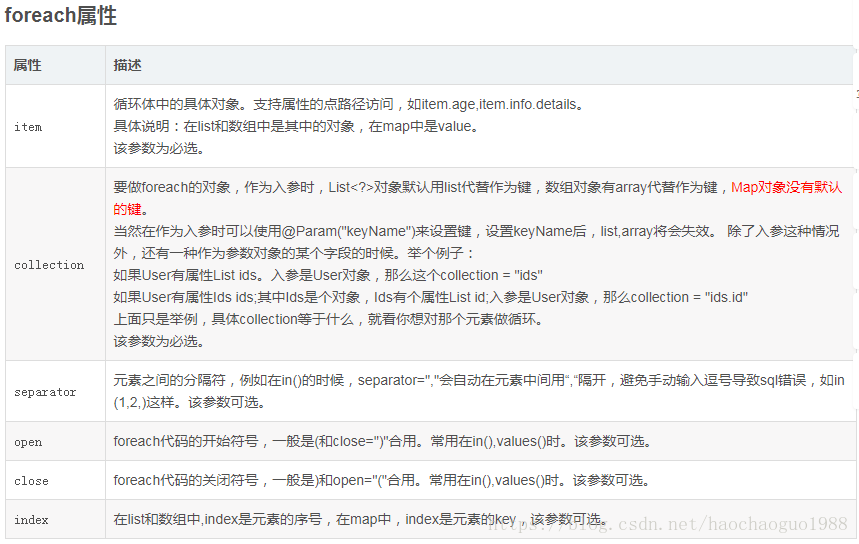
我们可以看到collection和item属性为必选,其他的为可选。