前面一章介绍了BST的结构和一些简单的基本功能,例如:insert,findMin,nextLarger等等。这一节主要讲解一些BST的delete node操作还有BST的height的分析以及一些潜在的问题。即本节主要包括以下2个部分;
1,Analysis of deletion
2,Tree height analysis
一:Node deletion
delete node的过程是需要依靠前一章的知识,需要了解nextLarger的过程和含义。然后在此基础之上,我们可以将删除node分为以下几类:
1)node是BST的leaf,即left child和right child 都为NULL;
2)node含有left subtree,但是没有right subtree;
3) node 含有right subtree, 但是没有left subtree;
4) node 含有right subtree和left subtree;
那么这4中情况下,如何删除相应的node,有什么规定需要遵守呢?如何删除的呢?下面2图分别展示了如何在上面的4中情况下删除相应的node
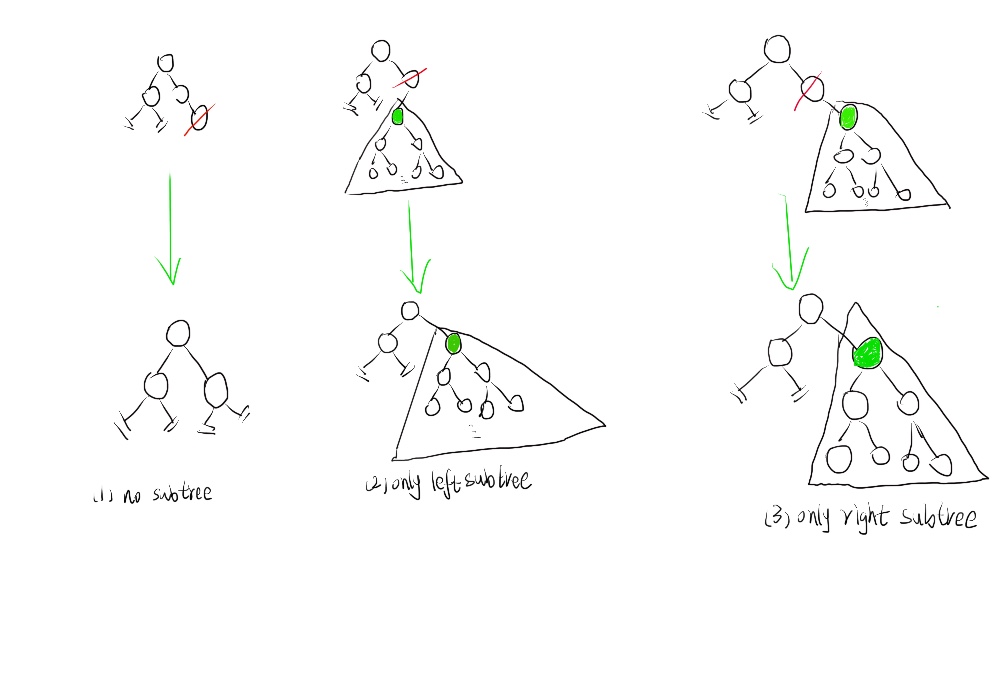

前三种的情况都比较简单,可以直观的了解。第四中情况,即node包含左右2个subtree的时候,情况就比较复杂了,我在这把流程解释一遍。当node包含左右2个subtree的时候,首先第一步是找到这个node的nextLarger,第二步copy nextLarger的key到node,第三步删除这个nextLarger node。至此删除node的操作结束。其具体的实现代码如下:(每个人的实现过程可能都不一样,仅供参考学习交流)
/* *Description: search the node's parent node * *parameters: 1. key //the value which we want to find within the BST 2. node//the node which we want to find out who is its parent node * *return Node * */ Node *BST::searchParent(int key, Node *node){ if (this->root == NULL) {//the BST has not initialzed yet return NULL; }else{ if (node==NULL) {//we have found all the nodes, but no one matches, which means it is not within the BST return NULL; }else if (key == node->getRight()->getKey()||key == node->getLeft()->getKey()) {//we spot on the key, return the node return node; }else if (key < node->getKey()){//the key is smaller than the node, so it is must be in the left subtree. return searchParent(key, node->getLeft()); }else{// the key is bigger than the node, so it is must be in the right subtree. return searchParent(key, node->getRight()); } } } /* *Description: delete a node from BST * * *parameter: * 1: key//the key that you want to delete * * 2:node //the node that we need to delete *return void * */ void BST::deleteNode(int key, Node *node){ Node *parentNode; if (node != this->root) {//node is not the root of the BST parentNode = searchParent(node->getKey(), this->root); }else{//the node is the root of BST parentNode = NULL; } if (node->getLeft() == nullptr && node->getRight() == nullptr) {//The node has not got any leaf if (parentNode->getKey()>node->getKey()) { parentNode->setLeft(NULL); }else{ parentNode->setRight(NULL); } delete(node); node = NULL; }else if (node->getRight() == nullptr){//has left tree if (parentNode->getKey()>node->getKey()) { parentNode->setLeft(node->getLeft()); }else{ parentNode->setRight(node->getLeft()); } delete node; node= NULL; }else if(node->getLeft() == nullptr){//has right tree if (parentNode->getKey()>node->getKey()) { parentNode->setLeft(node->getRight()); }else{ parentNode->setRight(node->getRight()); } delete node; node = NULL; }else{//has two subtrees Node *nextLargerNode = findNextLarger(node); int keyValue = nextLargerNode->getKey(); deleteNode(nextLargerNode->getKey(),nextLargerNode); node->setKey(keyValue); } }
二:BST height 分析
根据前面几节的分析,BST 的insert, nextLarger,search,delete的running time = O (h). 那么具体这个h是多少呢?它跟node 的数量有什么关系呢?根据现在所掌握的知识,一个随机任意的BST的h跟node的数量并没有具体的函数关系,但是我们至少可以知道h的范围是多少,即lgN<=h<=N。其原因如下图所示:
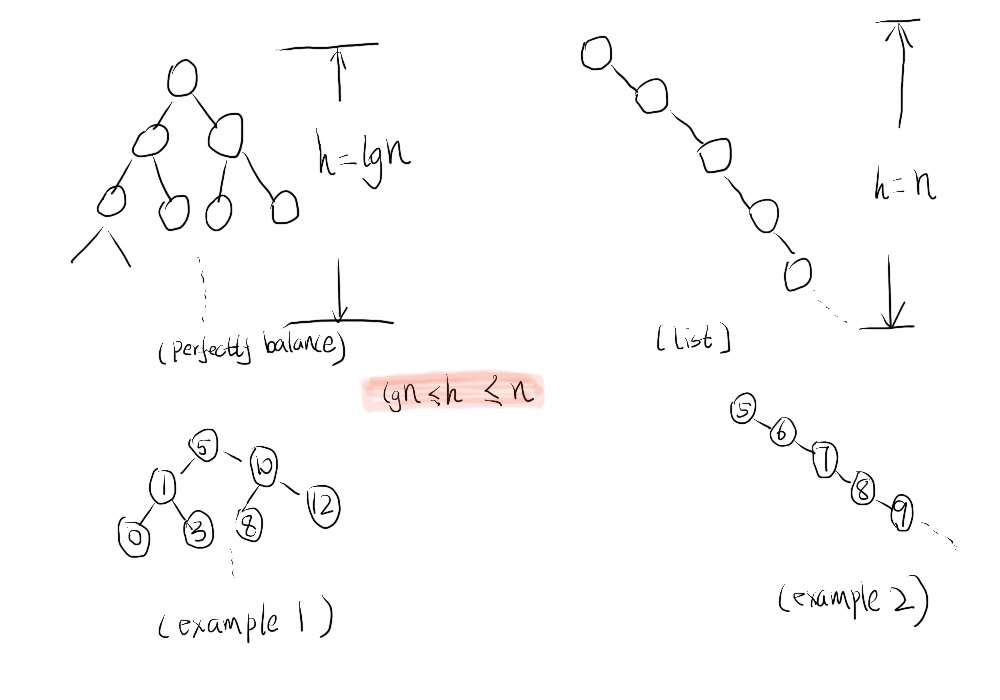
根据上图的实例和分析,我们可以很清晰的分辨出h的范围,所以对于一个不加处理随机的BST,它的时间复杂度是:O(lgN)<=running time<=O(N); 很显然我们只希望要lgN, 而不是线性的N; 因为如果是O(N)的话,BST的有些操作甚至效果不过Heap. 上图左边的视图是一个perfectly balanced的BST,它的时间复杂度是O(lgN),这正式我们想要的。上面的右图则是一个完全不平衡的BST,其时间复杂度=O(N),这种情况是我们应该避免的。 所以接下来的问题就是如何判断一个BST是不是平衡的, 如果不是平衡的,我们应该如何将不平衡的BST转化成平衡的BST。那么下一节我将介绍BST的rotation,平衡和AVL Tree。谢谢