目录
kibana安装 & 增删改查 & es集群搭建
一.kibana安装
es官网: https://www.elastic.co/
1)安装kibana
#上传代码包
[root@db01 ~]# rz kibana-6.6.0-x86_64.rpm
#安装
[root@db01 ~]# rpm -ivh kibana-6.6.0-x86_64.rpm
2)配置kibana
[root@db01 ~]# vim /etc/kibana/kibana.yml
[root@db01 ~]# grep "^[a-z]" /etc/kibana/kibana.yml
#进程的端口
server.port: 5601
#监听地址
server.host: "10.0.0.51"
#指定ES的地址
elasticsearch.hosts: ["http://10.0.0.51:9200"]
#kibana也会创建索引
kibana.index: ".kibana"
3)启动kibana
[root@db01 ~]# systemctl start kibana.service
#验证
[root@db01 ~]# netstat -lntp
tcp 0 0 10.0.0.51:5601 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 88636/node
4)访问页面
http://10.0.0.51:5601
二、ES数据操作
1.创建索引
#语法:
PUT /<index>
#示例:
PUT /qiudao
PUT zengdao
2.创建数据
1)数据结构
ES存储数据三个必要构成条件
| 构成条件 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| _index | 索引(数据存储的地方) |
| _type | 类型(数据对应的类) |
| _id | 数据唯一标识符 |
2)语法
PUT /<index>/_doc/<_id>
POST /<index>/_doc/
PUT /<index>/_create/<_id>
POST /<index>/_create/<_id>
index:索引名称,如果索引不存在,会自动创建
_doc:类型
<_id>:唯一识别符,创建一个数据时,可以自定义ID,也可以让他自动生成
3)使用自定义ID插入数据
PUT /student/user/4
{
"name":"congtianqi",
"sex":"male"
}
#企业使用该方式少
1.需要修改id值
2.当指定ID时,插入数据时会查询数据对比ID值
4)使用随机ID插入数据
POST /student/user/
{
"name":"liuxinyu",
"sex":"fmale"
}
5)添加指定字段
POST /student/user/
{
"id":"1",
"name":"liuxinyu",
"sex":"fmale"
}
#企业应用较多
3.查询数据
1)简单查询
#查看所有索引信息
GET _all
GET /_all
#查看所有索引的数据
GET _all/_search
#查看指定索引信息
GET student
#查看指定索引的数据
GET student/_search
#查看指定数据
GET student/user/1
2)条件查询
# 注意:
match在匹配时会对所查找的关键词进行分词,然后按分词匹配查找,而term会直接对关键词进行查找。一般模糊查找的时候,多用match,而精确查找时可以使用term。
1>方法一:
GET /student/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"age": {
"value": "18"
}
}
}
}
2>方法二:
GET /student/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"age":"18"
}
}
}
3>方法三:
GET /student/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"age": "18"
}
}
}
3)多条件查询
1>must查询(相当远sql中的and)
#查询条件必须全部满足
GET /student/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"term": {
"age": {
"value": "18"
}
}
},
{
"term": {
"name": {
"value": "lhd"
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
2>filter查询(和sql中的and差不多)
#跟must一样,只不过在数据量很大时,比must查询快一点
GET /student/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"filter": [
{
"term": {
"age": {
"value": "18"
}
}
},
{
"term": {
"name": {
"value": "lhd"
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
3>should查询(相当于sql中的or)
#多条件查询时,查询条件只要有一个满足就可以
GET /student/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"should": [
{
"term": {
"age": {
"value": "18"
}
}
},
{
"term": {
"name": {
"value": "lhd"
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
4>must_not查询(sql中的!=)
# 将年龄不为18,名字不为lhd的全部都显示出来
GET /student/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must_not": [
{"term": {
"name": {
"value": "lhd"
}
}},
{"term": {
"age": {
"value": "18"
}
}}
]
}
}
}
5>must和should结合
#查询年龄是21岁或者年龄是18岁并且名字是lhd的数据
GET /student/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"should": [
{
"term": {
"age": {
"value": "21"
}
}
},
{
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"term": {
"age": {
"value": "18"
}
}
},
{
"term": {
"name": {
"value": "lhd"
}
}
}
]
}
}
]
}
}
}
6>条件范围查询
# 将年龄大于20小于25的全部显示
GET /student/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"range": {
"age": {
"gte": 20,
"lte": 25
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
4.修改数据
#修改数据时指定id修改
PUT /student/user/1
{
"name":"song",
"sex":"fmale",
"age":"18"
}
#注意,修改数据时,除了要修改的值。其他的值也要带上,否则其他值直接被删除
PUT /student/user/2
{
"name":"lhd",
"sex":"man",
"age":"19"
}
5.删除数据
#删除指定ID数据
DELETE /student/user/4
#删除索引
DELETE /student
三、集群
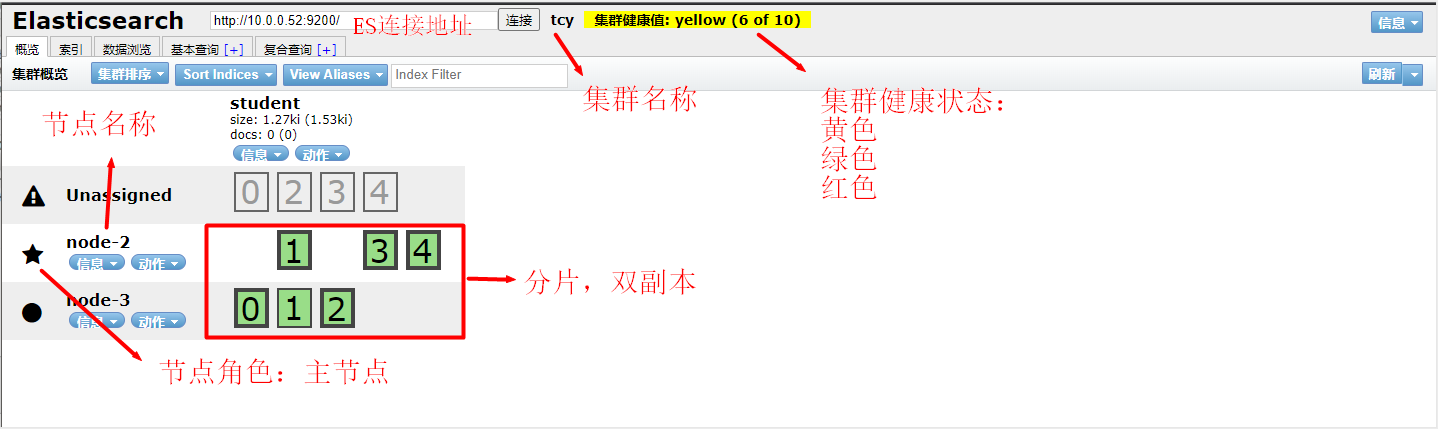
1.集群
1)集群状态
1.红色:数据都不完整
2.黄色:数据完整,但是副本有问题
3.绿色:数据和副本全都没有问题
2)节点类型
1.主节点:负责调度分配数据
2.数据节点:处理分配到自己的数据
3)分片
1.主分片:存储数据,负责读写数据
2.副本分片:主分片的备份
2.搭建集群
# 基本安装(三台都需要)
1. 安装ntp时间同步工具
[root@db01 ~]# yum install -y ntpdate
2.时间同步阿里云
[root@db01 ~]# ntpdate time1.aliyun.com
3.上传jdk包,安装jdk
[root@db01 ~]# rpm -ivh jdk-8u181-linux-x64.rpm
4.上传elasticsearch安装包,并且安装
[root@db01 ~]# rpm -ivh elasticsearch-6.6.0.rpm
5.修改启动文件,添加内存锁机制
[root@db01 system]# vim /usr/lib/systemd/system/elasticsearch.service
LimitMEMLOCK=infinity
6.启动服务
注:根据安装操作后提示进行服务启动
[root@db01 ~]# systemctl daemon-reload
[root@db01 ~]# systemctl enable elasticsearch.service
[root@db01 ~]# systemctl start elasticsearch.service
7.集群搭建配置(三台配置有所不同)
[root@db01 system]# grep '^[a-z]' /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml
cluster.name: tcy
node.name: node-1
path.data: /var/lib/elasticsearch
path.logs: /var/log/elasticsearch
bootstrap.memory_lock: true
network.host: 10.0.0.51,127.0.0.1
http.port: 9200
discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["10.0.0.51", "10.0.0.52", "10.0.0.53"]
discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes: 2
[root@db02 system]# grep '^[a-z]' /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml
cluster.name: tcy
node.name: node-2
path.data: /var/lib/elasticsearch
path.logs: /var/log/elasticsearch
bootstrap.memory_lock: true
network.host: 10.0.0.52,127.0.0.1
http.port: 9200
discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["10.0.0.51", "10.0.0.52", "10.0.0.53"]
discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes: 2
[root@db03 system]# grep '^[a-z]' /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml
cluster.name: tcy
node.name: node-3
path.data: /var/lib/elasticsearch
path.logs: /var/log/elasticsearch
bootstrap.memory_lock: true
network.host: 10.0.0.53,127.0.0.1
http.port: 9200
discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["10.0.0.51", "10.0.0.52", "10.0.0.53"]
discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes: 2
8.查看端口
[root@db01 system]# netstat -lntup
tcp6 0 0 10.0.0.51:9200 :::* LISTEN 9334/java
tcp6 0 0 127.0.0.1:9200 :::* LISTEN 9334/java
tcp6 0 0 10.0.0.51:9300 :::* LISTEN 9334/java
tcp6 0 0 127.0.0.1:9300 :::* LISTEN 9334/java
9.写入数据
[root@db01 system]# curl -XPUT '10.0.0.51:9200/student?pretty'
{
"acknowledged" : true,
"shards_acknowledged" : true,
"index" : "student"
}