
写在前面
本文版权归博客园和作者吴双本人共同所有 转载和爬虫请注明原文地址 cnblogs.com/tdws
After using OWIN for months for basic OAuth authentication, it’s apparent that Microsoft is abandoning OWIN . This isn’t necessarily a bad thing. .NET Core is built on a similar structure as that which was implemented in OWIN. Essentially, we have a familiar middleware pipeline.
这句话出自老外的博客,在使用Owin的OAuth身份认证几个月后,发现微软在逐渐放弃OWIN,这未必是一件坏事情,.NET Core在一个和OWIN所实现的相似结构之上。我们有一个和OWIN极为相似的中间件管道。
想必了解或者使用过OWIN的朋友们,在做.NET Core应用的时候都会有如上描述的这种感觉。就我个人的理解,微软在早几年推出OWIN的时候,就希望将管道留给用户,就以Startup.cs为管道配置和应用入口,OWIN脱离了Asp.Net管道事件,我们可以将任何中间件在管道中随意插拔。在OWIN中为我们提供了完备的认证流程,和一套完整的规范。比如 Microsoft.Owin.Security.OAuth等,在使用OWIN时,我们可以使用OWIN的默认实现,也可以实现其接口,自定义我们自己的实现方式。有关Microsoft OWIN的内容,不是本篇分享的主题,推荐腾飞的 MVC5 - ASP.NET Identity登录原理 - Claims-based认证和OWIN 和蟋蟀哥的 ASP.NET WebApi OWIN 实现 OAuth 2.0 。
Token
本篇分享主要关注在.NET Core的认证机制。无论我们是使用WebApi还是MvcWeb App,了解微软的认证机制总是有好处的。认证是应用API服务器识别用户身份的过程,token是更现代的认证方式,简化权限管理,降低服务器负载。在认证过程中,最重要的就是拿到token, token包含或者应该包含什么信息呢?
1.这个人是谁?
2.这个人可以用此token访问什么样的内容?(scope)
3.token的过期时间 (expire)
4.谁发行的token。
5.其他任何你希望加入的声明(Claims)
那我们为什么要使用token呢?使用session或者用redis来实现stateServer不好吗?
1.token是低(无)状态的,Statelessness
2.token可以与移动端应用紧密结合
3.支持多平台服务器和分布式微服务
拿到token后如何带入HTTP请求传给后台?
答案是两种方式,Cookies和Authorization Header。那么什么时候放到Cookies中,什么时候又放到Authentication中呢?
第一,如果是在Web应用,则放到Cookies当中,并且应该是HttpOnly的,js不能直接对其进行操作,安全性会比将其存在Web Stroage中好一些,因为在Web Storage当中的内容,可以很容的被潜在的XSS脚本攻击并获取。在HttpOnly的cookies当中会相对安全一些,不过也有潜在的CSRF跨站伪造请求的危险,不过这种hack的手段成功率是很低的,有兴趣的朋友可以自行看一下CSRF原理。
第二,如果是手机移动端应用的话,那一定是存储在App本地,并由Authorization Header带到后台并得到身份认证。
WebApp Cookies Authentication
上一段前两周写的最原始的小Demo吧,没有数据库访问等,可根据demo自行改变 ,现在的新代码已经加入了很多业务在其中
startup.cs代码
1 using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication.Cookies; 2 using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder; 3 using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting; 4 using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http; 5 using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http.Authentication; 6 using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration; 7 using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection; 8 using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging; 9 using System.Collections.Generic; 10 using System.Security.Claims; 11 using Wings.AuthenticationApp.Middleware; 12 13 namespace Wings.AuthenticationApp 14 { 15 public class Startup 16 { 17 public Startup(IHostingEnvironment env) 18 { 19 var builder = new ConfigurationBuilder() 20 .SetBasePath(env.ContentRootPath) 21 .AddJsonFile("appsettings.json", optional: false, reloadOnChange: true) 22 .AddJsonFile($"appsettings.{env.EnvironmentName}.json", optional: true) 23 .AddEnvironmentVariables(); 24 Configuration = builder.Build(); 25 26 } 27 28 public IConfigurationRoot Configuration { get; } 29 30 // This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to add services to the container. 31 public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) 32 { 33 // Add framework services. 34 services.AddMvc(); 35 } 36 37 // This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to configure the HTTP request pipeline. 38 public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env, ILoggerFactory loggerFactory) 39 { 40 loggerFactory.AddConsole(Configuration.GetSection("Logging")); 41 loggerFactory.AddDebug(); 42 43 app.UseCookieAuthentication(CookieAuthMiddleware.GetOptions()); 44 app.UseOwin(); 45 app.UseCors(a => { a.AllowAnyOrigin(); }); 46 app.UseMvc(); 47 // Listen for login and logout requests 48 app.Map("/login", builder => 49 { 50 builder.Run(async context => 51 { 52 var name = context.Request.Form["name"]; 53 var pwd = context.Request.Form["pwd"]; 54 if (name == "wushuang" && pwd == "wushuang") 55 { 56 57 var claims = new List<Claim>() { new Claim("name", name), new Claim("role", "admin") }; 58 var identity = new ClaimsIdentity(claims, "password"); 59 var principal = new ClaimsPrincipal(identity); 60 await context.Authentication.SignInAsync(CookieAuthenticationDefaults.AuthenticationScheme, principal); 61 context.Response.Redirect("http://www.baidu.com"); 62 } 63 else 64 { 65 await context.Authentication.SignOutAsync(CookieAuthenticationDefaults.AuthenticationScheme); 66 context.Response.Redirect("http://www.google.com"); 67 } 68 }); 69 }); 70 71 //app.Map("/logout", builder => 72 //{ 73 // builder.Run(async context => 74 // { 75 // // Sign the user out / clear the auth cookie 76 // await context.Authentication.SignOutAsync(CookieAuthenticationDefaults.AuthenticationScheme); 77 78 // // Perform a simple redirect after logout 79 // context.Response.Redirect("/"); 80 // }); 81 //}); 82 83 } 84 85 } 86 }
下面是Middleware---->CookieAuthMiddleware.cs的代码,
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication.Cookies; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http; using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Security.Claims; using System.Security.Principal; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Wings.AuthenticationApp.Middleware { public class CookieAuthMiddleware { public static CookieAuthenticationOptions GetOptions() { return new CookieAuthenticationOptions { AutomaticAuthenticate = true, AutomaticChallenge = true, LoginPath = new PathString("/login"), LogoutPath = new PathString("/logout"), AccessDeniedPath = new PathString("/test"), CookieHttpOnly = false, //默认就是True了 CookieName = "wings_access_token", SlidingExpiration = true, CookieManager = new ChunkingCookieManager() }; } } public static class IdentityExtension { public static string FullName(this IIdentity identity) { var claim = ((ClaimsIdentity)identity).FindFirst("name"); return (claim != null) ? claim.Value : string.Empty; } public static string Role(this IIdentity identity) { var claim = ((ClaimsIdentity)identity).FindFirst("role"); return (claim != null) ? claim.Value : string.Empty; } } }
对应如上demo,简单测试一下,结果如下:
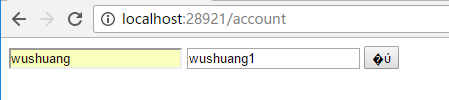
首先使用错误的密码,来请求token endpoint,接下来我们看一下即使窗口,当有请求进入的时候,我用如下代码判断用户的认证情况,拿到的结果必然是false:

接下来,我使用正确的账号密码,来打入token,判断结果一定为true,所以我使用自定义的拓展方法,来获取下,该用户token的信息:
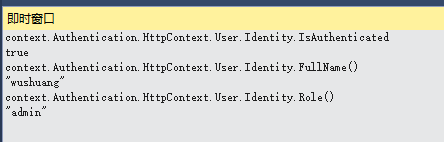
如上demo没有加入一些容错机制,请注意。在用户认证成功后,可以进入带有Authorize Attribute的Action,否则401.如下是几个重要参数的解释

自定义Authentication Middle生产Token
Startup.cs
1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using System.Linq; 4 using System.Threading.Tasks; 5 using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder; 6 using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting; 7 using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration; 8 using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection; 9 using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging; 10 using Wings.TokenAuth.Middleware; 11 using System.Security.Claims; 12 using Microsoft.IdentityModel.Tokens; 13 using System.Text; 14 using Microsoft.Extensions.Options; 15 16 namespace Wings.TokenAuth 17 { 18 public class Startup 19 { 20 public Startup(IHostingEnvironment env) 21 { 22 var builder = new ConfigurationBuilder() 23 .SetBasePath(env.ContentRootPath) 24 .AddJsonFile("appsettings.json", optional: false, reloadOnChange: true) 25 .AddJsonFile($"appsettings.{env.EnvironmentName}.json", optional: true) 26 .AddEnvironmentVariables(); 27 Configuration = builder.Build(); 28 } 29 30 public IConfigurationRoot Configuration { get; } 31 32 // This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to add services to the container. 33 public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) 34 { 35 // Add framework services. 36 services.AddMvc(); 37 } 38 39 // The secret key every token will be signed with. 40 // In production, you should store this securely in environment variables 41 // or a key management tool. Don't hardcode this into your application! 42 private static readonly string secretKey = "mysupersecret_secretkey!123"; 43 44 public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env, ILoggerFactory loggerFactory) 45 { 46 loggerFactory.AddConsole(LogLevel.Debug); 47 loggerFactory.AddDebug(); 48 49 app.UseStaticFiles(); 50 51 // Add JWT generation endpoint: 52 var signingKey = new SymmetricSecurityKey(Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(secretKey)); 53 var options = new TokenProviderOptions 54 { 55 Audience = "ExampleAudience", 56 Issuer = "ExampleIssuer", 57 SigningCredentials = new SigningCredentials(signingKey, SecurityAlgorithms.HmacSha256), 58 }; 59 60 app.UseMiddleware<TokenProviderMiddleware>(Options.Create(options)); 61 62 app.UseMvc(); 63 } 64 } 65 }
TokenProviderOptions.cs
1 using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http; 2 using Microsoft.Extensions.Options; 3 using Microsoft.IdentityModel.Tokens; 4 using Newtonsoft.Json; 5 using System; 6 using System.Collections.Generic; 7 using System.IdentityModel.Tokens.Jwt; 8 using System.Linq; 9 using System.Security.Claims; 10 using System.Threading.Tasks; 11 12 namespace Wings.TokenAuth.Middleware 13 { 14 public class TokenProviderOptions 15 { 16 public string Path { get; set; } = "/token"; 17 18 public string Issuer { get; set; } 19 20 public string Audience { get; set; } 21 22 public TimeSpan Expiration { get; set; } = TimeSpan.FromMinutes(5); 23 24 public SigningCredentials SigningCredentials { get; set; } 25 } 26 public class TokenProviderMiddleware 27 { 28 private readonly RequestDelegate _next; 29 private readonly TokenProviderOptions _options; 30 31 public TokenProviderMiddleware( 32 RequestDelegate next, 33 IOptions<TokenProviderOptions> options) 34 { 35 _next = next; 36 _options = options.Value; 37 } 38 39 public Task Invoke(HttpContext context) 40 { 41 // If the request path doesn't match, skip 42 if (!context.Request.Path.Equals(_options.Path, StringComparison.Ordinal)) 43 {
//use new JwtSecurityTokenHandler().ValidateToken() to valid token 44 return _next(context); 45 } 46 47 // Request must be POST with Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded 48 if (!context.Request.Method.Equals("POST") 49 || !context.Request.HasFormContentType) 50 { 51 context.Response.StatusCode = 400; 52 return context.Response.WriteAsync("Bad request."); 53 } 54 55 return GenerateToken(context); 56 } 57 private async Task GenerateToken(HttpContext context) 58 { 59 var username = context.Request.Form["username"]; 60 var password = context.Request.Form["password"]; 61 62 var identity = await GetIdentity(username, password); 63 if (identity == null) 64 { 65 context.Response.StatusCode = 400; 66 await context.Response.WriteAsync("Invalid username or password."); 67 return; 68 } 69 70 var now = DateTime.UtcNow; 71 72 // Specifically add the jti (random nonce), iat (issued timestamp), and sub (subject/user) claims. 73 // You can add other claims here, if you want: 74 var claims = new Claim[] 75 { 76 new Claim(JwtRegisteredClaimNames.Sub, username), 77 new Claim(JwtRegisteredClaimNames.Jti, Guid.NewGuid().ToString()), 78 new Claim(JwtRegisteredClaimNames.Iat, ToUnixEpochDate(now).ToString(), ClaimValueTypes.Integer64) 79 }; 80 81 // Create the JWT and write it to a string 82 var jwt = new JwtSecurityToken( 83 issuer: _options.Issuer, 84 audience: _options.Audience, 85 claims: claims, 86 notBefore: now, 87 expires: now.Add(_options.Expiration), 88 signingCredentials: _options.SigningCredentials); 89 var encodedJwt = new JwtSecurityTokenHandler().WriteToken(jwt); 90 91 var response = new 92 { 93 access_token = encodedJwt, 94 expires_in = (int)_options.Expiration.TotalSeconds 95 }; 96 97 // Serialize and return the response 98 context.Response.ContentType = "application/json"; 99 await context.Response.WriteAsync(JsonConvert.SerializeObject(response, new JsonSerializerSettings { Formatting = Formatting.Indented })); 100 } 101 102 private Task<ClaimsIdentity> GetIdentity(string username, string password) 103 { 104 // DON'T do this in production, obviously! 105 if (username == "wushuang" && password == "wushuang") 106 { 107 return Task.FromResult(new ClaimsIdentity(new System.Security.Principal.GenericIdentity(username, "Token"), new Claim[] { })); 108 } 109 110 // Credentials are invalid, or account doesn't exist 111 return Task.FromResult<ClaimsIdentity>(null); 112 } 113 114 public static long ToUnixEpochDate(DateTime date) 115 => (long)Math.Round((date.ToUniversalTime() - new DateTimeOffset(1970, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, TimeSpan.Zero)).TotalSeconds); 116 117 118 } 119 }
下面上测试结果:
使用错误的账户和密码请求token

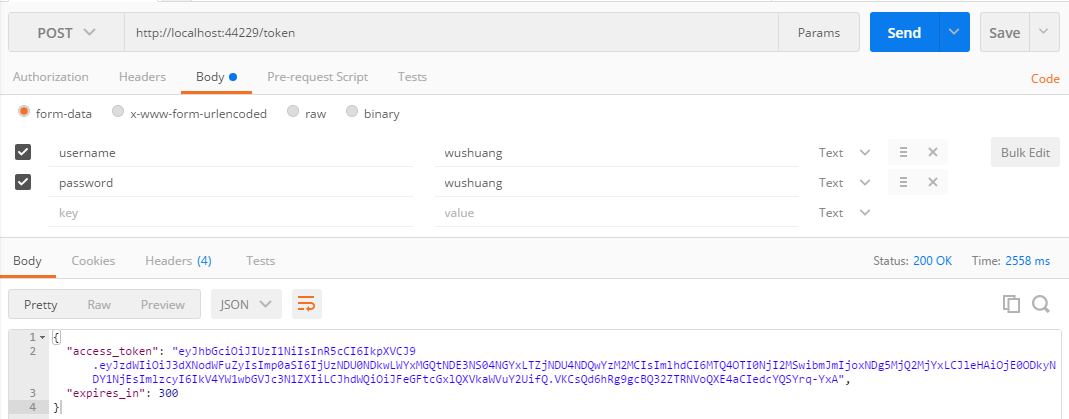
使用正确的账户和密码来请求,返回结果如下:
参考文章和论文,不仅限于如下几篇,感谢国外大佬们有深度的分享:
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/29055477/oauth-authorization-service-in-asp-net-core
https://stormpath.com/blog/token-authentication-asp-net-core
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/aspnet/core/fundamentals/middleware#fundamentals-middleware
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/aspnet/core/security/authentication/cookie#controlling-cookie-options
https://stormpath.com/blog/token-authentication-asp-net-core