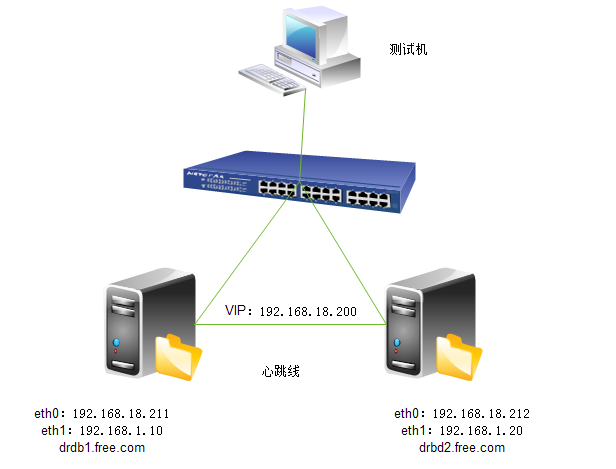
1.实验拓扑图
2.修改主机名
|
1
2
3
|
vim /etc/sysconfig/networkvim /etc/hostsdrbd1.free.com drbd2.free.com |
3.同步系统时间
|
1
2
|
ntp*/10 * * * * ntpdate 202.120.2.101 |
4.修改hosts可互相解析
|
1
|
vim /etc/hosts |
5.安装 drbd
|
1
2
|
rpm -ivh drbd83-8.3.13-2.el5.centos.x86_64.rpm //主文件安装rpm -ivh kmod-drbd83-8.3.13-1.el5.centos.x86_64.rpm --nodeps //内核文件安装 |
6.加载内核
|
1
2
|
modprobe drbdlsmod | grep drdb |
7.修改配置文件
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
vim /etc/drbd.conf //在末行模式下输入如下命令## please have a a look at the example configuration file in# /usr/share/doc/drbd83/drbd.conf## You can find an example in /usr/share/doc/drbd.../drbd.conf.exampleinclude "drbd.d/global_common.conf";include "drbd.d/*.res";: r /usr/share/doc/drbd83-8.3.13/drbd.conf |
8.创建共享空间
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
fdisk /dev/sdbn --- p1 --- +10Gwpartprobe |
9.配置全局文件
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
|
cd /etc/drbd.dcp global_common.conf global_common.conf.bakvim global_common.confglobal {usage-count no;# minor-count dialog-refresh disable-ip-verification}common {protocol C;handlers {pri-on-incon-degr "/usr/lib/drbd/notify-pri-on-incon-degr.sh; /usr/lib/drbd/notify-emergency-reboot.sh; echo b > /proc/sysrq-trigger ; reboot -f";pri-lost-after-sb "/usr/lib/drbd/notify-pri-lost-after-sb.sh; /usr/lib/drbd/notify-emergency-reboot.sh; echo b > /proc/sysrq-trigger ; reboot -f";local-io-error "/usr/lib/drbd/notify-io-error.sh; /usr/lib/drbd/notify-emergency-shutdown.sh; echo o > /proc/sysrq-trigger ; halt -f";# fence-peer "/usr/lib/drbd/crm-fence-peer.sh";# split-brain "/usr/lib/drbd/notify-split-brain.sh root";# out-of-sync "/usr/lib/drbd/notify-out-of-sync.sh root";# before-resync-target "/usr/lib/drbd/snapshot-resync-target-lvm.sh -p 15 -- -c 16k";# after-resync-target /usr/lib/drbd/unsnapshot-resync-target-lvm.sh;}startup {# wfc-timeout degr-wfc-timeout outdated-wfc-timeout wait-after-sb wfc-timeout 120; degr-wfc-timeout 120;}disk {# on-io-error fencing use-bmbv no-disk-barrier no-disk-flushes# no-disk-drain no-md-flushes max-bio-bvecson-io-error detach; fencing resource-only;}net {# sndbuf-size rcvbuf-size timeout connect-int ping-int ping-timeout max-buffers# max-epoch-size ko-count allow-two-primaries cram-hmac-alg shared-secret# after-sb-0pri after-sb-1pri after-sb-2pri data-integrity-alg no-tcp-corkcram-hmac-alg "sha1";shared-secret "mydrbdlab";}syncer {# rate after al-extents use-rle cpu-mask verify-alg csums-algrate 100M;}} |
10.定义资源
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
cd /etc/drbd.d/vim web.resresource web { on drbd1.free.com { device /dev/drbd0; disk /dev/sda6; address 192.168.18.211:7789; meta-disk internal; } on drbd2.free.com { device /dev/drbd0; disk /dev/sda6; address 192.168.18.212:7789; meta-disk internal; }} |
11.drbd1与drbd2上初始化资源Web
|
1
|
drbdadm create-md web |
12.启动drbd服务
|
1
|
service drbd start |
13.查看节点
|
1
|
drbd-overview |
14.将drbd1调整为主节点
|
1
2
|
drbdadm -- --overwrite-data-of-peer primary webdrbd-overview |
15.在主节点上创建文件系统
|
1
|
mkfs.ext3 -L drbdweb /dev/drbd0 |
16.在主节点上创建挂载点,挂载后,写入一个文件
|
1
2
3
4
|
mkdir /mnt/drbdmount /dev/debd0 /mnt/drbdcd /mnt/drbdvim index.html |
17.将drbd1.free.com配置成从节点,将drbd2.free.com配置成主节点
节点一
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
[root@drbd1 drbd]# cd[root@drbd1 ~]#[root@drbd1 ~]# umount /mnt/drbd[root@drbd1 ~]# drbdadm secondary web[root@drbd1 ~]# drbdadm role web Secondary/Primary |
节点二
|
1
2
3
|
[root@drbd2 ~]# drbdadm primary web[root@drbd2 ~]# drbd-overview0:web Connected Primary/Secondary UpToDate/UpToDate C r---- |
在节点二挂载,查看是否有内容
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
[root@drbd2 ~]# mkdir /mnt/drbd[root@drbd2 ~]# mount /dev/drbd0 /mnt/drbd[root@drbd2 ~]# ll /mnt/drbd/total 16-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jan 20 18:09 index.html //可以看到已经写入成功drwx------ 2 root root 16384 Jan 20 18:07 lost+found |
注: 测试成功
18.安装Heartbeat
|
1
|
yum install heartbeat* |
拷贝配置文件到/etc/ha.d/目录中
|
1
2
|
cd /usr/share/doc/heartbeat-2.1.3/cp ha.cf haresources authkeys /etc/ha.d/ |
19.配置结点
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
310
311
312
313
314
315
316
317
318
319
320
321
322
323
324
325
326
327
328
329
330
331
332
333
334
335
336
337
338
339
340
341
342
343
344
345
346
|
12cd /etc/ha.d/vim ha.cf##There are lots of options in this file. All you have to have is a set#of nodes listed {"node ...} one of {serial, bcast, mcast, or ucast},#and a value for "auto_failback".##ATTENTION: As the configuration file is read line by line,# THE ORDER OF DIRECTIVE MATTERS!##In particular, make sure that the udpport, serial baud rate#etc. are set before the heartbeat media are defined!#debug and log file directives go into effect when they#are encountered.##All will be fine if you keep them ordered as in this example.### Note on logging:# If any of debugfile, logfile and logfacility are defined then they# will be used. If debugfile and/or logfile are not defined and# logfacility is defined then the respective logging and debug# messages will be loged to syslog. If logfacility is not defined# then debugfile and logfile will be used to log messges. If# logfacility is not defined and debugfile and/or logfile are not# defined then defaults will be used for debugfile and logfile as# required and messages will be sent there.##File to write debug messages to#debugfile /var/log/ha-debug### File to write other messages to##logfile/var/log/ha-log###Facility to use for syslog()/logger#logfacilitylocal0###A note on specifying "how long" times below...##The default time unit is seconds#10 means ten seconds##You can also specify them in milliseconds#1500ms means 1.5 seconds###keepalive: how long between heartbeats?##keepalive 2##deadtime: how long-to-declare-host-dead?##If you set this too low you will get the problematic#split-brain (or cluster partition) problem.#See the FAQ for how to use warntime to tune deadtime.##deadtime 30##warntime: how long before issuing "late heartbeat" warning?#See the FAQ for how to use warntime to tune deadtime.##warntime 10###Very first dead time (initdead)##On some machines/OSes, etc. the network takes a while to come up#and start working right after you've been rebooted. As a result#we have a separate dead time for when things first come up.#It should be at least twice the normal dead time.##initdead 120###What UDP port to use for bcast/ucast communication?##udpport694##Baud rate for serial ports...##baud19200##serialserialportname ...#serial/dev/ttyS0# Linux#serial/dev/cuaa0# FreeBSD#serial /dev/cuad0 # FreeBSD 6.x#serial/dev/cua/a# Solaris###What interfaces to broadcast heartbeats over?#bcasteth1# Linux#bcasteth1 eth2# Linux#bcastle0# Solaris#bcastle1 le2# Solaris##Set up a multicast heartbeat medium#mcast [dev] [mcast group] [port] [ttl] [loop]##[dev]device to send/rcv heartbeats on#[mcast group]multicast group to join (class D multicast address#224.0.0.0 - 239.255.255.255)#[port]udp port to sendto/rcvfrom (set this value to the#same value as "udpport" above)#[ttl]the ttl value for outbound heartbeats. this effects#how far the multicast packet will propagate. (0-255)#Must be greater than zero.#[loop]toggles loopback for outbound multicast heartbeats.#if enabled, an outbound packet will be looped back and#received by the interface it was sent on. (0 or 1)#Set this value to zero.###mcast eth0 225.0.0.1 694 1 0##Set up a unicast / udp heartbeat medium#ucast [dev] [peer-ip-addr]##[dev]device to send/rcv heartbeats on#[peer-ip-addr]IP address of peer to send packets to##ucast eth0 192.168.1.2###About boolean values...##Any of the following case-insensitive values will work for true:#true, on, yes, y, 1#Any of the following case-insensitive values will work for false:#false, off, no, n, 0####auto_failback: determines whether a resource will#automatically fail back to its "primary" node, or remain#on whatever node is serving it until that node fails, or#an administrator intervenes.##The possible values for auto_failback are:#on- enable automatic failbacks#off- disable automatic failbacks#legacy- enable automatic failbacks in systems#where all nodes do not yet support#the auto_failback option.##auto_failback "on" and "off" are backwards compatible with the old#"nice_failback on" setting.##See the FAQ for information on how to convert#from "legacy" to "on" without a flash cut.#(i.e., using a "rolling upgrade" process)##The default value for auto_failback is "legacy", which#will issue a warning at startup. So, make sure you put#an auto_failback directive in your ha.cf file.#(note: auto_failback can be any boolean or "legacy")#auto_failback on### Basic STONITH support# Using this directive assumes that there is one stonith# device in the cluster. Parameters to this device are# read from a configuration file. The format of this line is:## stonith <stonith_type> <configfile>## NOTE: it is up to you to maintain this file on each node in the# cluster!##stonith baytech /etc/ha.d/conf/stonith.baytech## STONITH support# You can configure multiple stonith devices using this directive.# The format of the line is:# stonith_host <hostfrom> <stonith_type> <params...># <hostfrom> is the machine the stonith device is attached# to or * to mean it is accessible from any host.# <stonith_type> is the type of stonith device (a list of# supported drives is in /usr/lib/stonith.)# <params...> are driver specific parameters. To see the# format for a particular device, run:# stonith -l -t <stonith_type>###Note that if you put your stonith device access information in#here, and you make this file publically readable, you're asking#for a denial of service attack ;-)##To get a list of supported stonith devices, run#stonith -L#For detailed information on which stonith devices are supported#and their detailed configuration options, run this command:#stonith -h##stonith_host * baytech 10.0.0.3 mylogin mysecretpassword#stonith_host ken3 rps10 /dev/ttyS1 kathy 0#stonith_host kathy rps10 /dev/ttyS1 ken3 0##Watchdog is the watchdog timer. If our own heart doesn't beat for#a minute, then our machine will reboot.#NOTE: If you are using the software watchdog, you very likely#wish to load the module with the parameter "nowayout=0" or#compile it without CONFIG_WATCHDOG_NOWAYOUT set. Otherwise even#an orderly shutdown of heartbeat will trigger a reboot, which is#very likely NOT what you want.##watchdog /dev/watchdog# #Tell what machines are in the cluster#nodenodename ...-- must match uname -n#nodeken3#nodekathynodedrbd1.free.comnodedrbd2.free.com##Less common options...##Treats 10.10.10.254 as a psuedo-cluster-member#Used together with ipfail below...#note: don't use a cluster node as ping node##ping 10.10.10.254##Treats 10.10.10.254 and 10.10.10.253 as a psuedo-cluster-member# called group1. If either 10.10.10.254 or 10.10.10.253 are up# then group1 is up#Used together with ipfail below...##ping_group group1 10.10.10.254 10.10.10.253##HBA ping derective for Fiber Channel#Treats fc-card-name as psudo-cluster-member#used with ipfail below ...##You can obtain HBAAPI from http://hbaapi.sourceforge.net. You need#to get the library specific to your HBA directly from the vender#To install HBAAPI stuff, all You need to do is to compile the common#part you obtained from the sourceforge. This will produce libHBAAPI.so#which you need to copy to /usr/lib. You need also copy hbaapi.h to#/usr/include.##The fc-card-name is the name obtained from the hbaapitest program#that is part of the hbaapi package. Running hbaapitest will produce#a verbose output. One of the first line is similar to:#Apapter number 0 is named: qlogic-qla2200-0#Here fc-card-name is qlogic-qla2200-0.##hbaping fc-card-name###Processes started and stopped with heartbeat. Restarted unless#they exit with rc=100##respawn userid /path/name/to/run#respawn hacluster /usr/lib/heartbeat/ipfail##Access control for client api# default is no access##apiauth client-name gid=gidlist uid=uidlist#apiauth ipfail gid=haclient uid=hacluster#############################Unusual options.##############################hopfudge maximum hop count minus number of nodes in config#hopfudge 1##deadping - dead time for ping nodes#deadping 30##hbgenmethod - Heartbeat generation number creation method#Normally these are stored on disk and incremented as needed.#hbgenmethod time##realtime - enable/disable realtime execution (high priority, etc.)#defaults to on#realtime off##debug - set debug level#defaults to zero#debug 1##API Authentication - replaces the fifo-permissions-based system of the past###You can put a uid list and/or a gid list.#If you put both, then a process is authorized if it qualifies under either#the uid list, or under the gid list.##The groupname "default" has special meaning. If it is specified, then#this will be used for authorizing groupless clients, and any client groups#not otherwise specified.##There is a subtle exception to this. "default" will never be used in the#following cases (actual default auth directives noted in brackets)# ipfail (uid=HA_CCMUSER)# ccm (uid=HA_CCMUSER)# ping(gid=HA_APIGROUP)# cl_status(gid=HA_APIGROUP)##This is done to avoid creating a gaping security hole and matches the most#likely desired configuration.##apiauth ipfail uid=hacluster#apiauth ccm uid=hacluster#apiauth cms uid=hacluster#apiauth ping gid=haclient uid=alanr,root#apiauth default gid=haclient# message format in the wire, it can be classic or netstring,#default: classic#msgfmt classic/netstring#Do we use logging daemon?#If logging daemon is used, logfile/debugfile/logfacility in this file#are not meaningful any longer. You should check the config file for logging#daemon (the default is /etc/logd.cf)#more infomartion can be fould in http://www.linux-ha.org/ha_2ecf_2fUseLogdDirective#Setting use_logd to "yes" is recommended## use_logd yes/no##the interval we reconnect to logging daemon if the previous connection failed#default: 60 seconds#conn_logd_time 60###Configure compression module#It could be zlib or bz2, depending on whether u have the corresponding#libraryin the system.#compressionbz2##Confiugre compression threshold#This value determines the threshold to compress a message,#e.g. if the threshold is 1, then any message with size greater than 1 KB#will be compressed, the default is 2 (KB)#compression_threshold 2 |
20.配置认证文件authkeys
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
dd if=/dev/random bs=512 count=1 | openssl md5vim authkeys //两边节点要一致 drbd1 drbd2auth 33 md5 7eadaabaa7891f4f327918df9af10fc3chmod 600 authkeys |
21.手工创建文件killnfsd
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
vim resource.d/killnfsdkillall -9 nfsd;/etc/init.d/nfs restart;exit 0chmod 755 resource.d/killnfsd |
22.配置加载虚拟IP文件
|
1
2
|
vim haresourcesdrbd1.free.com IPaddr::192.168.18.200/24/eth0 drbddisk::webFilesystem::/dev/drbd0::/mnt/drbd::ext3 killnfsd |
23.配置NFS服务共享
编写共享
|
1
2
|
vim /etc/exports/mnt/drbd 192.168.18.0/24(ro) |
导出共享清单
|
1
2
|
vim /etc/exports/mnt/drbd 192.168.18.0/24(ro) |
修改nfs启动脚本
|
1
2
3
|
vim /etc/init.d/nfs122行killproc nfsd -9 |
启动nfs与heartbeat服务
|
1
2
|
service nfs startservice heartbeat start |
24.测试
|
1
2
3
|
mkdir /mnt/drbdmount 192.168.18.200:/mnt/drbd /mnt/drbd/mount |
主节点破坏掉,再检查情况
|
1
2
|
service heartbeat stopservice drbd status |
25.最后将所有服务加入开机自启动
|
1
2
3
|
chkconfig nfs onchkconfig drbd onchkconfig heartbeat on |