Problem Description
Edward is a worker for Aluminum Cyclic Machinery. His work is operating mechanical arms to cut out designed models. Here is a brief introduction of his work.
Assume the operating plane as a two-dimensional coordinate system. At first, there is a disc with center coordinates (0,0) and radius R. Then, m mechanical arms will cut and erase everything within its area of influence simultaneously, the i-th area of which is a circle with center coordinates (xi,yi) and radius ri (i=1,2,⋯,m). In order to obtain considerable models, it is guaranteed that every two cutting areas have no intersection and no cutting area contains the whole disc.
Your task is to determine the perimeter of the remaining area of the disc excluding internal perimeter.
Here is an illustration of the sample, in which the red curve is counted but the green curve is not.
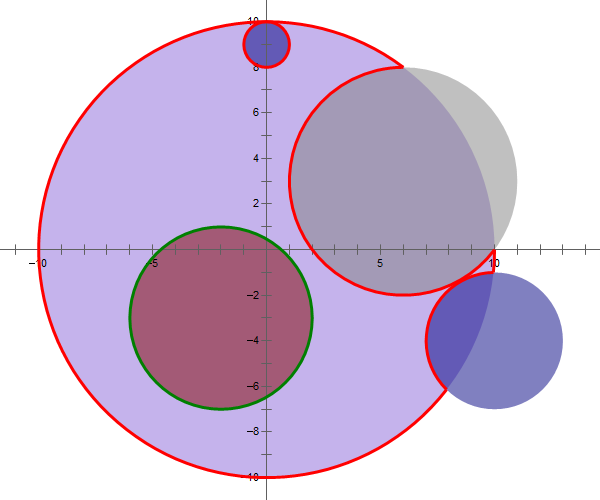
Assume the operating plane as a two-dimensional coordinate system. At first, there is a disc with center coordinates (0,0) and radius R. Then, m mechanical arms will cut and erase everything within its area of influence simultaneously, the i-th area of which is a circle with center coordinates (xi,yi) and radius ri (i=1,2,⋯,m). In order to obtain considerable models, it is guaranteed that every two cutting areas have no intersection and no cutting area contains the whole disc.
Your task is to determine the perimeter of the remaining area of the disc excluding internal perimeter.
Here is an illustration of the sample, in which the red curve is counted but the green curve is not.

Input
The first line contains one integer T, indicating the number of test cases.
The following lines describe all the test cases. For each test case:
The first line contains two integers m and R.
The i-th line of the following m lines contains three integers xi,yi and ri, indicating a cutting area.
1≤T≤1000, 1≤m≤100, −1000≤xi,yi≤1000, 1≤R,ri≤1000 (i=1,2,⋯,m).
The following lines describe all the test cases. For each test case:
The first line contains two integers m and R.
The i-th line of the following m lines contains three integers xi,yi and ri, indicating a cutting area.
1≤T≤1000, 1≤m≤100, −1000≤xi,yi≤1000, 1≤R,ri≤1000 (i=1,2,⋯,m).
Output
For each test case, print the perimeter of the remaining area in one line. Your answer is considered correct if its absolute or relative error does not exceed 10−6.
Formally, let your answer be a and the jury's answer be b. Your answer is considered correct if |a−b|max(1,|b|)≤10−6.
Formally, let your answer be a and the jury's answer be b. Your answer is considered correct if |a−b|max(1,|b|)≤10−6.
Sample Input
1
4 10
6 3 5
10 -4 3
-2 -4 4
0 9 1
Sample Output
81.62198908430238475376
Source
Recommend
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 #define N 120 4 #define pi acos(-1.0) 5 struct point{ 6 double x,y; 7 }; 8 struct circle{ 9 point po; 10 double r; 11 }cir[N]; 12 double dist (point a,point b){ 13 return sqrt((a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x)+(a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y)); 14 } 15 int t,m; 16 double R; 17 int main() 18 { 19 scanf("%d",&t); 20 while(t--) 21 { 22 scanf("%d%lf",&m,&R); 23 circle a; 24 a.po.x=0;a.po.y=0; 25 a.r=R; 26 for(int i=0;i<m;i++) 27 { 28 scanf("%lf%lf%lf",&cir[i].po.x,&cir[i].po.y,&cir[i].r); 29 } 30 double ans=2*pi*R; 31 for(int i=0;i<m;i++) 32 { 33 double dis=dist(a.po,cir[i].po); 34 if(dis-cir[i].r<a.r&&dis+cir[i].r>=a.r){ 35 double d1=2*acos((dis*dis+a.r*a.r-cir[i].r*cir[i].r)/(2*dis*a.r)); 36 double d2=2*acos((dis*dis+cir[i].r*cir[i].r-a.r*a.r)/(2*dis*cir[i].r)); 37 double l1=d1*a.r; 38 double l2=d2*cir[i].r; 39 ans-=l1; 40 ans+=l2; 41 } 42 } 43 printf("%.10f ",ans); 44 } 45 46 return 0; 47 } 48 /* 49 //判段两个圆的位置关系: 50 相离 : dis(a,b)>a.r+b.r 51 外切 : dis(a.b)==a.r+b.r 52 相交 : dis(a,b)-min(a.r,b.r)<max(a.r,b.r)&&dis(a,b)+min(a.r,b.r)>max(a.r,b.r) 53 内切 : dis(a,b)+min(a.r,b.r)==max(a.r,b.r) 54 内含 : dis(a,b)+min(a,r)<max(a.r,b.r) 55 */