lambda表达式的的本质是匿名方法。但是这个方法不是不是独立执行的,而是用于实现函数式接口定义的方法,因此lambda表达式会产生一个匿名类,lambda表达式通常也被称为闭包。
函数式接口是仅仅包含一个方法的接口,这个方法指明了接口的用途,所以函数式接口通常表示单个动作,比如Runnable接口就是一个标准的函数式接口,因为它只定义了一个run方法。此外函数式接口可以指定Object的任何共有方法,Object的lambda表达式的隐式成员,函数式接口的实例会默认实现它们。
lambda表达式的基本知识
() -> 123.45; () -> {return 123.45}; (n) -> (n%2) ==0;
以上三种情况是典型的简单的lambda表达式体,当参数只有一个的时候 () 也可以去掉
public interface MyNum { byte getValue(int a,int b); }
public class AAA { public static void main(String[] args) { //这里的 int 可以省略,可以从上下文推断出来 MyNum myNum = (int m,int n)->{ return (byte) (m+n); }; System.out.println(myNum.getValue(5, 4));//输出9 } }
以上是代码块类型的lambda块,代码块里面必须要写return,这个return 只是返回lambda体,不会导致lambda外部的方法返回。
函数式接口可以是泛型的 如下:
public interface MyDouble<RETURN,PARAM> { RETURN getValue(PARAM P); }
public class AAA { public static void main(String[] args) { MyDouble<Integer, Integer> md =(a) -> a+5; System.out.println(md.getValue(1));//6 MyDouble<String, Integer> md1 =(a) -> (a+5)+" is a String"; System.out.println(md1.getValue(1));//6 is a String } }
lambda作为参数传递
为了将lambda表达式作为参数传递,接受表达式的参数类型必须与该lambda表达式的函数式接口兼容
public interface TestFuncParam { String func(String str); }
public class BBB { static String stringOP(TestFuncParam t,String s) { return t.func(s); } public static void main(String[] args) { String instr = "bbb"; String outStr; //这里创建一个函数式接口TestFuncParam的一个实例 TestFuncParam aa = (str)->{ return str.toUpperCase(); }; //将实例 传递给stringOP方法参数中 并调用 outStr = stringOP(aa, instr); System.out.println(outStr);//输出BBB } }
lambda表达式的异常
lambda表达式可以抛出异常,但是抛出经检查的异常时,该异常就必须与函数式接口的抽象方法声明的异常兼容,
public interface DoubleParam { double func(double[] arr) throws EmptyArrException; }
public class EmptyArrException extends Exception { EmptyArrException(){ super("ARRAY EMPTY"); } }
public abstract class Test { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ double [] arr = {1.1,1.2,1.3}; double [] arr1 = {}; DoubleParam first = (arr2)->{ if(arr2.length==0) { throw new EmptyArrException(); }else { return arr2[0]; } }; System.out.println(first.func(arr));//输出1.1 System.out.println(first.func(arr1));//报异常 } }
lambda表达式的变量捕获
lambda表达式可以访问其外层类的实例,静态变量或者方法,但是当访问外层作用域内定义的局部变量时,会产生变量捕获的情况,lambda表达式实质上只能访问外层作用域的final变量(和匿名方法一样),因此一旦lambda表达式引用了外层作用域的变量,不管该变量是否显式的声明为final,该变量实际上已经成为final变量了,所以该变量是不能被修改的(不管是lambda表达式体内还是体外)
public interface MyFunc { int func(int n); }
public class TestFunc { private int constT = 1; public static void main(String[] args) { TestFunc testFunc = new TestFunc(); int num = 10; MyFunc fun = (n) -> { System.out.println(++testFunc.constT);//合法 输出2 int v = n+num; // num++; //不合法 final变量不能修改 return v; }; System.out.println(fun.func(10)); //输出20 // System.out.println(num++); //不合法 final变量不能修改 } }
方法引用
静态方法引用 语法为 ClassName::methodName
public interface StringFunc { String func(String str); }
public class Test { static String reverse(String str) { return str.toUpperCase(); } static String StringOps(StringFunc func,String str) { return func.func(str); } public static void main(String[] args) { String in = "aaaaa"; String out = StringOps(Test::reverse, in); System.out.println(out); } }
实例方法的引用 语法为 objRef::methodName
public interface StringFunc { String func(String str); }
public class Test { String reverse(String str) { return str.toUpperCase(); } static String StringOps(StringFunc func,String str) { return func.func(str); } public static void main(String[] args) { String in = "aaaaa"; Test test = new Test(); String out = StringOps(test::reverse, in); System.out.println(out); } }
下面的实例方法引用或许更加方便,只需指定类名和方法名,无需指定对象,其语法为ClassName::instaceName
public interface MyFunc<T> { boolean func(T v1,T v2); }
public class HighTemp { private int hTemp; HighTemp(int ht){ this.hTemp = ht; } boolean sameTemp(HighTemp ht) { return hTemp==ht.hTemp; } boolean lessThanTemp(HighTemp ht) { return hTemp<=ht.hTemp; } }
public class Test { static <T> int counter(T[] vals,MyFunc<T> f,T v) { int count =0; for(int i=0;i<vals.length;i++) { if(f.func(vals[i], v)) { count++; } } return count; } public static void main(String[] args) { int count ; HighTemp[] weekDayHigh = {new HighTemp(50),new HighTemp(50),new HighTemp(50),new HighTemp(50), new HighTemp(1),new HighTemp(99),new HighTemp(99),new HighTemp(99),}; count = counter(weekDayHigh, HighTemp::sameTemp, new HighTemp(50)); System.out.println(count);//输出4 count = counter(weekDayHigh, HighTemp::lessThanTemp, new HighTemp(1)); System.out.println(count);//输出1 } }
泛型中的方法引用
在泛型类或者泛型方法中也可以使用方法引用
public interface MyFunc<T> { int func(T[] vals,T v2); }
public class MyArrOps { static <T> int countMatch(T[] vals,T v) { int count =0; for(int i=0;i<vals.length;i++) { if(vals[i]== v) { count++; } } return count; } }
public class Test { static <T> int myOp(T[] vals,MyFunc<T> f,T v) { return f.func(vals, v); } public static void main(String[] args) { Integer [] arr1 = {1,2,3,4,4}; String [] arr2 = {"1","2","3","4"}; //这里的<Integer> 也可以省略,可以从上下文自动推断出来 int count = myOp(arr1, MyArrOps::<Integer>countMatch, 4);//输出2 System.out.println(count); int count1 = myOp(arr2, MyArrOps::<String>countMatch, "4");//输出1 System.out.println(count1); } }
方法引用lambda 真正的优势在于和集合一起使用,下面举一个例子,实现获取集合中最大的数,之前的做法是传递一个集合对象和Comparator<T>,并重写compare()方法,下面使用lambda实现
public class MyClass { private int val; MyClass(int val){this.val = val;} public int getVal() {return val;} public void setVal(int val) {this.val = val;} }
public class Test { static int compareMC(MyClass c1,MyClass c2) { return c1.getVal()-c2.getVal(); } public static void main(String[] args) { List<MyClass> list= new ArrayList<>(); list.add(new MyClass(1)); list.add(new MyClass(2)); list.add(new MyClass(3)); list.add(new MyClass(4)); list.add(new MyClass(4)); MyClass maxClass = Collections.max(list, Test::compareMC); System.out.println(maxClass.getVal());//输出4 } }
构造方法引用 语法为ClassName::new
public interface MyFunc { MyClass func(int n); }
public class MyClass { private int val; MyClass(int val){this.val = val;} public int getVal() {return val;} public void setVal(int val) {this.val = val;} }
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { MyFunc mf1 = MyClass::new; MyClass mc = mf1.func(11); System.out.println(mc.getVal());//输出11 } }
也可将上面的例子改成泛型版本的
public interface MyFunc<R,T> { R func(T t); }
public class MyClass<T> { private T val; MyClass(T t){val=t;} public T getVal() {return val;} public void setVal(T val) {this.val = val;} }
public class Test { static<R,T> R myClassFactory( MyFunc<R,T> func,T t) { return func.func(t); } public static void main(String[] args) { MyFunc<MyClass<Integer>, Integer> func1 =MyClass<Integer>::new; MyClass<Integer> class1 = myClassFactory(func1, 100); System.out.println(class1.getVal());//输出100 MyFunc<MyClass<String>, String> func2 =MyClass<String>::new; MyClass<String> class2 = myClassFactory(func2, "I am a String"); System.out.println(class2.getVal());//输出I am a String } }
以上的所有例子都定义了一个函数式接口,但我们很多时候并不需要自己定义这个接口,JDK8提供了java.util.function和java.util.stream包提供了一些预定义的函数式接口,后面我们将讨论他们,以下是它们的一些简介。
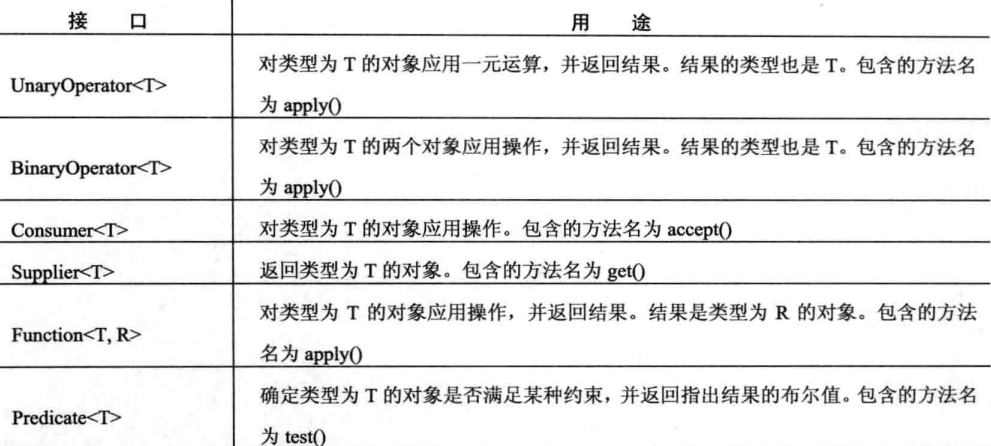
下面使用预定义函数式接口Function 来实现lambda。
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Function<Integer, String> function = (n)->{ return n.toString()+" is a number"; }; String result = function.apply(100); System.out.println(result);//输出 100 is a number } }
-------------------------------------------以下是常用的lambda使用例子和第二部分的lambda的使用-------------------------------------------------
https://www.cnblogs.com/franson-2016/p/5593080.html