
#include <stdio.h> #define MAX_VERtEX_NUM 20 //顶点的最大个数 #define VRType int //表示顶点之间的关系的变量类型 #define InfoType char //存储弧或者边额外信息的指针变量类型 #define VertexType int //图中顶点的数据类型 typedef enum{false,true}bool; //定义bool型常量 bool visited[MAX_VERtEX_NUM]; //设置全局数组,记录标记顶点是否被访问过 typedef struct { VRType adj; //对于无权图,用 1 或 0 表示是否相邻;对于带权图,直接为权值。 InfoType * info; //弧或边额外含有的信息指针 }ArcCell,AdjMatrix[MAX_VERtEX_NUM][MAX_VERtEX_NUM]; typedef struct { VertexType vexs[MAX_VERtEX_NUM]; //存储图中顶点数据 AdjMatrix arcs; //二维数组,记录顶点之间的关系 int vexnum,arcnum; //记录图的顶点数和弧(边)数 }MGraph; //根据顶点本身数据,判断出顶点在二维数组中的位置 int LocateVex(MGraph * G,VertexType v){ int i=0; //遍历一维数组,找到变量v for (; i<G->vexnum; i++) { if (G->vexs[i]==v) { break; } } //如果找不到,输出提示语句,返回-1 if (i>G->vexnum) { printf("no such vertex. "); return -1; } return i; } //构造无向图 void CreateDN(MGraph *G){ scanf("%d,%d",&(G->vexnum),&(G->arcnum)); for (int i=0; i<G->vexnum; i++) { scanf("%d",&(G->vexs[i])); } for (int i=0; i<G->vexnum; i++) { for (int j=0; j<G->vexnum; j++) { G->arcs[i][j].adj=0; G->arcs[i][j].info=NULL; } } for (int i=0; i<G->arcnum; i++) { int v1,v2; scanf("%d,%d",&v1,&v2); int n=LocateVex(G, v1); int m=LocateVex(G, v2); if (m==-1 ||n==-1) { printf("no this vertex "); return; } G->arcs[n][m].adj=1; G->arcs[m][n].adj=1;//无向图的二阶矩阵沿主对角线对称 } } int FirstAdjVex(MGraph G,int v) { //查找与数组下标为v的顶点之间有边的顶点,返回它在数组中的下标 for(int i = 0; i<G.vexnum; i++){ if( G.arcs[v][i].adj ){ return i; } } return -1; } int NextAdjVex(MGraph G,int v,int w) { //从前一个访问位置w的下一个位置开始,查找之间有边的顶点 for(int i = w+1; i<G.vexnum; i++){ if(G.arcs[v][i].adj){ return i; } } return -1; } void visitVex(MGraph G, int v){ printf("%d ",G.vexs[v]); } void DFS(MGraph G,int v){ visited[v] = true;//标记为true visitVex( G, v); //访问第v 个顶点 //从该顶点的第一个边开始,一直到最后一个边,对处于边另一端的顶点调用DFS函数 for(int w = FirstAdjVex(G,v); w>=0; w = NextAdjVex(G,v,w)){ //如果该顶点的标记位false,证明未被访问,调用深度优先搜索函数 if(!visited[w]){ DFS(G,w); } } } //深度优先搜索 void DFSTraverse(MGraph G){// int v; //将用做标记的visit数组初始化为false for( v = 0; v < G.vexnum; ++v){ visited[v] = false; } //对于每个标记为false的顶点调用深度优先搜索函数 for( v = 0; v < G.vexnum; v++){ //如果该顶点的标记位为false,则调用深度优先搜索函数 if(!visited[v]){ DFS( G, v); } } } int main() { MGraph G;//建立一个图的变量 CreateDN(&G);//初始化图 DFSTraverse(G);//深度优先搜索图 return 0; }
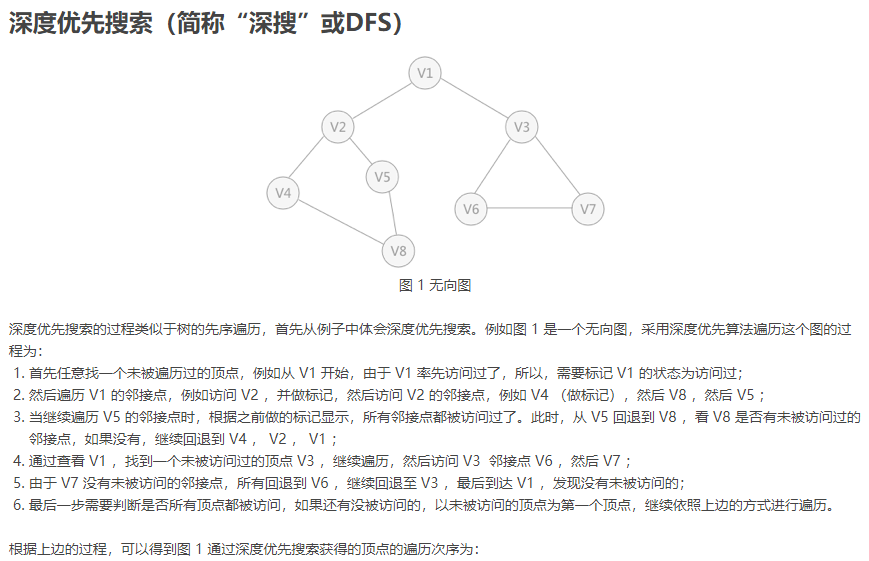
以图 1 为例,运行结果为: 8,9 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1,2 2,4 2,5 4,8 5,8 1,3 3,6 6,7 7,3 1 2 4 8 5 3 6 7

#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define MAX_VERtEX_NUM 20 //顶点的最大个数 #define VRType int //表示顶点之间的关系的变量类型 #define InfoType char //存储弧或者边额外信息的指针变量类型 #define VertexType int //图中顶点的数据类型 typedef enum{false,true}bool; //定义bool型常量 bool visited[MAX_VERtEX_NUM]; //设置全局数组,记录标记顶点是否被访问过 typedef struct Queue{ VertexType data; struct Queue * next; }Queue; typedef struct { VRType adj; //对于无权图,用 1 或 0 表示是否相邻;对于带权图,直接为权值。 InfoType * info; //弧或边额外含有的信息指针 }ArcCell,AdjMatrix[MAX_VERtEX_NUM][MAX_VERtEX_NUM]; typedef struct { VertexType vexs[MAX_VERtEX_NUM]; //存储图中顶点数据 AdjMatrix arcs; //二维数组,记录顶点之间的关系 int vexnum,arcnum; //记录图的顶点数和弧(边)数 }MGraph; //根据顶点本身数据,判断出顶点在二维数组中的位置 int LocateVex(MGraph * G,VertexType v){ int i=0; //遍历一维数组,找到变量v for (; i<G->vexnum; i++) { if (G->vexs[i]==v) { break; } } //如果找不到,输出提示语句,返回-1 if (i>G->vexnum) { printf("no such vertex. "); return -1; } return i; } //构造无向图 void CreateDN(MGraph *G){ scanf("%d,%d",&(G->vexnum),&(G->arcnum)); for (int i=0; i<G->vexnum; i++) { scanf("%d",&(G->vexs[i])); } for (int i=0; i<G->vexnum; i++) { for (int j=0; j<G->vexnum; j++) { G->arcs[i][j].adj=0; G->arcs[i][j].info=NULL; } } for (int i=0; i<G->arcnum; i++) { int v1,v2; scanf("%d,%d",&v1,&v2); int n=LocateVex(G, v1); int m=LocateVex(G, v2); if (m==-1 ||n==-1) { printf("no this vertex "); return; } G->arcs[n][m].adj=1; G->arcs[m][n].adj=1;//无向图的二阶矩阵沿主对角线对称 } } int FirstAdjVex(MGraph G,int v) { //查找与数组下标为v的顶点之间有边的顶点,返回它在数组中的下标 for(int i = 0; i<G.vexnum; i++){ if( G.arcs[v][i].adj ){ return i; } } return -1; } int NextAdjVex(MGraph G,int v,int w) { //从前一个访问位置w的下一个位置开始,查找之间有边的顶点 for(int i = w+1; i<G.vexnum; i++){ if(G.arcs[v][i].adj){ return i; } } return -1; } //操作顶点的函数 void visitVex(MGraph G, int v){ printf("%d ",G.vexs[v]); } //初始化队列 void InitQueue(Queue ** Q){ (*Q)=(Queue*)malloc(sizeof(Queue)); (*Q)->next=NULL; } //顶点元素v进队列 void EnQueue(Queue **Q,VertexType v){ Queue * element=(Queue*)malloc(sizeof(Queue)); element->data=v; element->next = NULL; Queue * temp=(*Q); while (temp->next!=NULL) { temp=temp->next; } temp->next=element; } //队头元素出队列 void DeQueue(Queue **Q,int *u){ (*u)=(*Q)->next->data; (*Q)->next=(*Q)->next->next; } //判断队列是否为空 bool QueueEmpty(Queue *Q){ if (Q->next==NULL) { return true; } return false; } //广度优先搜索 void BFSTraverse(MGraph G){// int v; //将用做标记的visit数组初始化为false for( v = 0; v < G.vexnum; ++v){ visited[v] = false; } //对于每个标记为false的顶点调用深度优先搜索函数 Queue * Q; InitQueue(&Q); for( v = 0; v < G.vexnum; v++){ if(!visited[v]){ visited[v]=true; visitVex(G, v); EnQueue(&Q, G.vexs[v]); while (!QueueEmpty(Q)) { int u; DeQueue(&Q, &u); u=LocateVex(&G, u); for (int w=FirstAdjVex(G, u); w>=0; w=NextAdjVex(G, u, w)) { if (!visited[w]) { visited[w]=true; visitVex(G, w); EnQueue(&Q, G.vexs[w]); } } } } } } int main() { MGraph G;//建立一个图的变量 CreateDN(&G);//初始化图 BFSTraverse(G);//广度优先搜索图 return 0; }
例如,使用上述程序代码遍历图 1 中的无向图,运行结果为: 8,9 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1,2 2,4 2,5 4,8 5,8 1,3 3,6 6,7 7,3 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
总结
本节介绍了两种遍历图的方式:深度优先搜索算法和广度优先搜索算法。深度优先搜索算法的实现运用的主要是回溯法,类似于树的先序遍历算法。广度优先搜索算法借助队列的先进先出的特点,类似于树的层次遍历。