Spring缓存支持 Spring框架定义了org.springframework.cache.CacheManager和org.springframework.cache.Cache接口来统一不同的缓存技术。针对不同的缓存技术,需要实现不同的CacheManager。例如,我们使用EhCache作为缓存技术时,需要注册实现CacheManager的Bean,示例代码如下: @Bean public EhCacheCacheManager cacheManager(CacheManager ehCacheCacheManager) { return new EhCacheCacheManager(ehCacheCacheManager); }
一旦配置好Spring缓存支持,就可以在Spring容器管理的Bean中使用缓存注解(基于AOP原理),一般情况下,都是在业务层(Service类)使用这些注解。 1.@Cacheable 2.@CacheEvict 3.@CachePut 4.@Caching 5.@CacheConfig
@Cacheable可以标记在一个方法上,也可以标记在一个类上。当标记在一个方法上时表示该方法是支持缓存的,当标记在一个类上时则表示该类所有的方法都是支持缓存的。对于一个支持缓存的方法,在方法执行前,Spring先检查缓存中是否存在方法返回的数据,如果存在,则直接返回缓存数据;如果不存在,则调用方法并将方法返回值存入缓存。 @Cacheable注解经常使用value、key、condition等属性。 value:缓存的名称,指定一个或多个缓存名称。如@Cacheable(value="mycache")或者@Cacheable(value={"cache1","cache2"})。该属性与cacheNames属性意义相同。 key:缓存的key,可以为空,如果指定需要按照SpEL表达式编写,如果不指定,则缺省按照方法的所有参数进行组合。如@Cacheable(value="testcache",key="#student.id")。 condition:缓存的条件,可以为空,如果指定需要按照SpEL编写,返回true或者false,只有为true才进行缓存。如@Cacheable(value="testcache",condition="#student.id>2")。该属性与unless相反,条件成立时,不进行缓存。
@CacheEvict是用来标注在需要清除缓存元素的方法或类上的。当标记在一个类上时表示其中所有方法的执行都会触发缓存的清除操作。@CacheEvict可以指定的属性有value、key、condition、allEntries和beforeInvocation。其中value、key和condition的语义与@Cacheable对应的属性类似。 allEntries:是否清空所有缓存内容,缺省为false,如果指定为true,则方法调用后将立即清空所有缓存。如@CacheEvict(value="testcache", allEntries=true)。 beforeInvocation:是否在方法执行前就清空,缺省为false,如果指定为true,则在方法还没有执行时就清空缓存,缺省情况下,如果方法执行抛出异常,则不会清空缓存。
@CachePut也可以声明一个方法支持缓存功能,与@Cacheable不同的是使用@CachePut标注的方法在执行前不会去检查缓存中是否存在之前执行过的结果,而是每次都会执行该方法,并将执行结果以键值对的形式存入指定的缓存中。
@CachePut也可以标注在类上和方法上。@CachePut的属性与@Cacheable的属性一样。
@Caching注解可以让我们在一个方法或者类上同时指定多个Spring Cache相关的注解。其拥有三个属性:cacheable、put和evict,分别用于指定@Cacheable、@CachePut和@CacheEvict。示例如下: @Caching( cacheable = @Cacheable("cache1"), evict = { @CacheEvict("cache2"),@CacheEvict(value = "cache3", allEntries = true) } )
@CacheConfig
所有的Cache注解都需要提供Cache名称,如果每个Service方法上都包含相同的Cache名称,可能写起来重复。此时,可以使用@CacheConfig注解作用在类上,设置当前缓存的一些公共设置。
在Spring中使用缓存技术的关键是配置缓存管理器CacheManager,而Spring Boot为我们自动配置了多个CacheManager的实现。Spring Boot的CacheManager的自动配置位于org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache包中。
在Spring Boot应用中,使用缓存技术只需在应用中引入相关缓存技术的依赖,并在配置类中使用@EnableCaching注解开启缓存支持即可。
1.创建基于spring-boot-starter-cache和spring-boot-starter-data-jpa依赖的Spring Boot Web应用ch6_10 2.配置application.properties文件 3.修改pom.xml文件,添加MySQL连接依赖 4.创建持久化实体类 5.创建数据访问接口 6.创建业务层 7.创建控制器层 8.开启缓存支持 9.运行测试
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.cache</groupId> <artifactId>SpringBootCache</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.0.0.RELEASE</version> <relativePath /> <!-- lookup parent from repository --> </parent> <properties> <!-- 声明项目配置依赖编码格式为 utf-8 --> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding> <fastjson.version>1.2.24</fastjson.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- 添加MySQL依赖 --> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <scope>runtime</scope> <version>8.0.13</version><!--$NO-MVN-MAN-VER$ --> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId> <configuration> <source>1.8</source> <target>1.8</target> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
使用Spring Data JPA访问MySQL数据库。所以,在application.properties文件中配置数据库连接信息,但因为使用默认的缓存技术ConcurrentMapCacheManager,所以不需要缓存的相关配置。 server.servlet.context-path=/ch6_10 spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springbootjpa?serverTimezone=UTC&autoReconnect=true spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=admin #spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver spring.jpa.database=MYSQL spring.jpa.show-sql=true spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update spring.jackson.serialization.indent-output=true
package com.ch.ch6_10.entity; import java.io.Serializable; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import javax.persistence.GenerationType; import javax.persistence.Id; import javax.persistence.Table; import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonIgnoreProperties; @Entity @Table(name = "student_table") @JsonIgnoreProperties(value = { "hibernateLazyInitializer" }) public class Student implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) private int id;// 主键 private String sno; private String sname; private String ssex; public Student() { super(); } public Student(int id, String sno, String sname, String ssex) { super(); this.id = id; this.sno = sno; this.sname = sname; this.ssex = ssex; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getSno() { return sno; } public void setSno(String sno) { this.sno = sno; } public String getSname() { return sname; } public void setSname(String sname) { this.sname = sname; } public String getSsex() { return ssex; } public void setSsex(String ssex) { this.ssex = ssex; } }
package com.ch.ch6_10.repository; import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository; import com.ch.ch6_10.entity.Student; public interface StudentRepository extends JpaRepository<Student, Integer>{ }
package com.ch.ch6_10.service; import com.ch.ch6_10.entity.Student; public interface StudentService { public Student saveStudent(Student student); public void deleteCache(Student student); public Student selectOneStudent(Integer id); }
package com.ch.ch6_10.service; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheEvict; import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachePut; import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import com.ch.ch6_10.entity.Student; import com.ch.ch6_10.repository.StudentRepository; @Service public class StudentServiceImpl implements StudentService { @Autowired private StudentRepository studentRepository; @Override @CachePut(value = "student", key = "#student.id") public Student saveStudent(Student student) { Student s = studentRepository.save(student); System.out.println("为key=" + student.getId() + "数据做了缓存"); return s; } @Override @CacheEvict(value = "student", key = "#student.id") public void deleteCache(Student student) { System.out.println("删除了key=" + student.getId() + "的数据缓存"); } @Override @Cacheable(value = "student") public Student selectOneStudent(Integer id) { Student s = studentRepository.getOne(id); System.out.println("为key=" + id + "数据做了缓存"); return s; } }
package com.ch.ch6_10.controller; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import com.ch.ch6_10.entity.Student; import com.ch.ch6_10.service.StudentService; @RestController public class TestCacheController { @Autowired private StudentService studentService; @RequestMapping("/savePut") public Student save(Student student) { return studentService.saveStudent(student); } @RequestMapping("/selectAble") public Student select(Integer id) { return studentService.selectOneStudent(id); } @RequestMapping("/deleteEvict") public String deleteCache(Student student) { studentService.deleteCache(student); return "ok"; } }
package com.ch.ch6_10; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching; @EnableCaching @SpringBootApplication public class Ch610Application { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(Ch610Application.class, args); } }
1)测试@Cacheable 启动应用程序的主类后,第一次访问http://localhost:8080/ch6_10/selectAble?id=4,第一次访问时将调用方法查询数据库,并将查询到的数据存储到缓存student中。
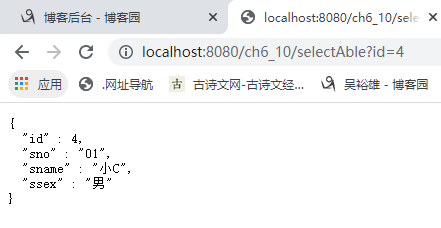
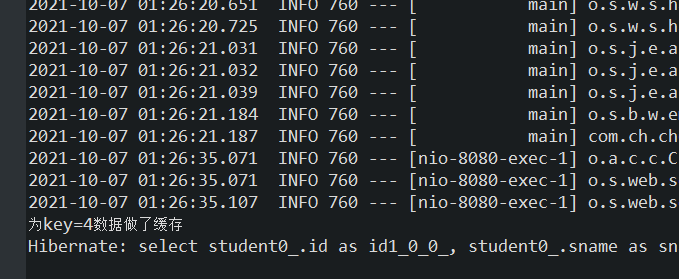
再次访问http://localhost:8080/ch6_10/selectAble?id=4,此时控制台没有输出“为key=4数据做了缓存”以及Hibernate的查询语句,这表明没有调用查询方法,页面数据直接从数据缓存中获得。
http://localhost:8080/ch6_10/savePut?sname=天黑了&sno=555&ssex=男
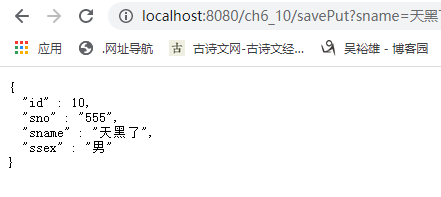
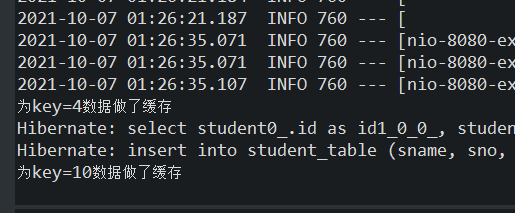
这时我们访问http://localhost:8080/ch6_10/selectAble?id=10,控制台无输出,从缓存直接获得数据
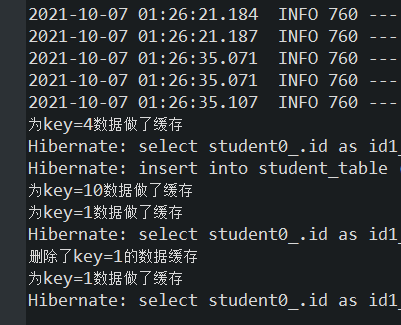
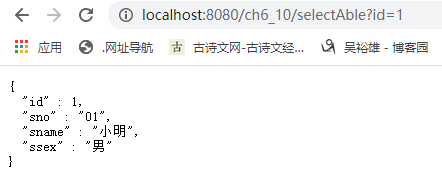
重启应用程序的主类,首先,访问http://localhost:8080/ch6_10/selectAble?id=1,为key为1的数据做缓存,再次访问http://localhost:8080/ch6_10/selectAble?id=1,确认数据已从缓存中获取。然后,访问http://localhost:8080/ch6_10/deleteEvict?id=1从缓存student中删除key为1的数据,此时控制台输出结果
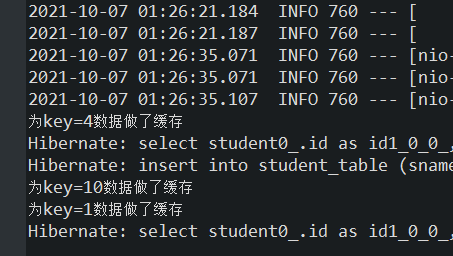
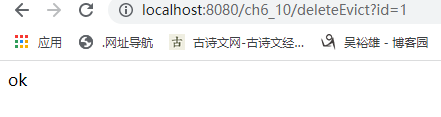
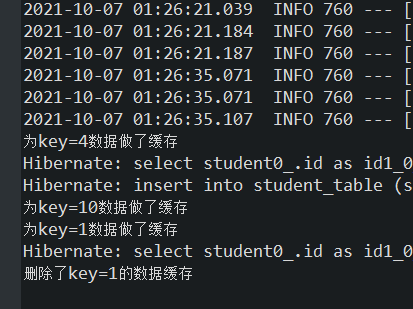
最后,再次访问http://localhost:8080/ch6_10/selectAble?id=1此时重新做了缓存,控制台输出结果