INI文件多用于存储程序的初始化信息,如记录程序连接数据库的名称、上一次用户登陆的名称、用户的注册信息等。
INI文件基本结构
一个典型的INI文件主要有节名、键名和键值3部分构成
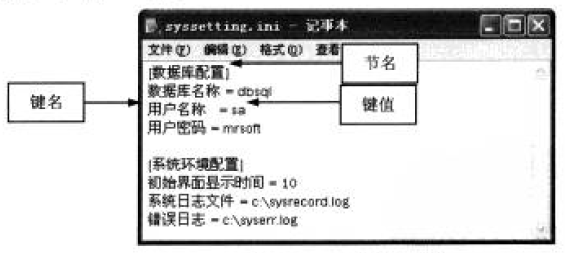
在INI文件中,节名由“[]”标识,其后是键名,键名之后有一个等号,然后是键值
键名与“=”之间和键值与“=”之间的空格数量可以是任意的,它们不会影响键名和键值
读写INI文件
WritePrivateProfileString 该函数用于向INI文件中写入一个字符串数据
BOOL WritePrivateProfileString( LPCTSTR lpAppName, // INI文件中的一个字段名[节名]可以有很多个节名LPCTSTR lpKeyName, // lpAppName 下的一个键名,也就是里面具体的变量名 LPCTSTR lpString, // 键值,也就是数据 LPCTSTR lpFileName // INI文件的路径 );
GetPrivateProfileString 该函数用于获取INI文件中的字符串数据
DWORD GetPrivateProfileString( LPCTSTR lpAppName, // INI文件中的一个字段名[节名]可以有很多个节名 LPCTSTR lpKeyName, // lpAppName 下的一个键名,也就是里面具体的变量名 LPCTSTR lpDefault, // 如果lpReturnedString为空,则把个变量赋给lpReturnedString LPTSTR lpReturnedString, // 存放键值的指针变量,用于接收INI文件中键值(数据)的接收缓冲区 DWORD nSize, // lpReturnedString的缓冲区大小 LPCTSTR lpFileName // INI文件的路径 );
GetPrivateProfileInt 该函数用于从INI文件中获取整型数据
UINT GetPrivateProfileInt( LPCTSTR lpAppName, // INI文件中的一个字段名[节名]可以有很多个节名 LPCTSTR lpKeyName, // lpAppName 下的一个键名,也就是里面具体的变量名 INT nDefault, // 如果没有找到指定的数据返回,则把个变量值赋给返回值 LPCTSTR lpFileName // INI文件的路径 );
GetPrivateProfileSectionNames 该函数用于返回INI文件中的所有节名
GetPrivateProfileSection 该函数返回指定节下所有的键名和键值
void COperateIniFileDlg::OnOK() { CString section,keyOne,keyTwo,keyThree, valOne,valTwo,valThree; m_Section.GetWindowText(section); m_KeyOne.GetWindowText(keyOne); m_KeyTwo.GetWindowText(keyTwo); m_KeyThree.GetWindowText(keyThree); m_ValOne.GetWindowText(valOne); m_ValTwo.GetWindowText(valTwo); m_ValThree.GetWindowText(valThree); WritePrivateProfileString(section,keyOne,valOne,"c:\setting.ini"); WritePrivateProfileString(section,keyTwo,valTwo,"c:\setting.ini"); WritePrivateProfileString(section,keyThree,valThree,"c:\setting.ini"); } void COperateIniFileDlg::OnRead() { CString section; GetPrivateProfileSectionNames(section.GetBuffer(0),100,"c:\setting.ini"); char keys[MAX_PATH]= {0}; GetPrivateProfileSection(section,keys,MAX_PATH,"c:\setting.ini"); char *cmp = "="; int pos = strcspn(keys,cmp); char vals[MAX_PATH] = {0}; strncpy(vals,keys,pos); char* ptmp = keys+pos+1; m_Section.SetWindowText(section); m_KeyOne.SetWindowText(vals); m_ValOne.SetWindowText(ptmp); int len = strlen(ptmp); ptmp +=len+1; pos = strcspn(ptmp,cmp); memset(vals,0,MAX_PATH); strncpy(vals,ptmp,pos); m_KeyTwo.SetWindowText(vals); ptmp +=pos+1; m_ValTwo.SetWindowText(ptmp); len = strlen(ptmp); ptmp +=len+1; pos = strcspn(ptmp,cmp); memset(vals,0,MAX_PATH); strncpy(vals,ptmp,pos); ptmp += pos+1; m_KeyThree.SetWindowText(vals); m_ValThree.SetWindowText(ptmp); }