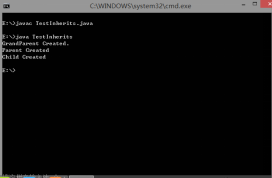
运行 TestInherits.java 示例,观察输出,注意总结父类与子类之间构造方法的调用关系修改Parent构造方法的代码,显式调用GrandParent的另一个构造函数,注意这句调用代码是否是第一句,影响重大!
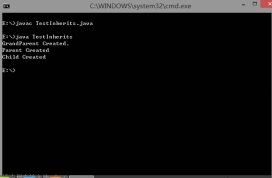
放在第一句:
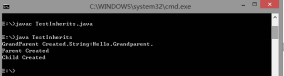
不放在第一句:
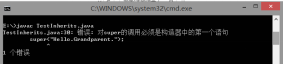
为什么子类的构造方法在运行之前,必须调用父类的构造方法?能不能反过来?为什么不能反过来?
构造函数的主要作用:构造函数是类的一个特殊方法,这个方法用来生成实例时由系统自动调用,程序员无法直接调用。构造函数方法名同类名相同且参数为空。子类继承父类后默认继承父类的构造函数,即:子类存在隐含方法:super(),如果子类重写构造函数则子类也隐含调用super()。
Super的用法1.调用父类的构造方法 子类可以调用由父类声明的构造方法。但是必须在子类的构造方法中使用super关键字来调用。其具体的语法格式如下: super([参数列表]); 如果父类的构造方法中包括参数,则参数列表为必选项,用于指定父类构造方法的入口参数。 下面将以5.4.3节介绍的实例为例介绍如何在子类中调用父类的构造方法。 在Animal类中添加一个默认的构造方法和一个带参数的构造方法,具体代码如下: public Animal(){ } public Animal(String strSkin){ skin=strSkin; } 这时,如果想在子类Bird中使用父类的带参数的构造方法,则需要在子类Bird的构造方法中通过以下代码进行调用。 public Bird(){ super("羽毛"); } 2.操作被隐藏的成员变量和被覆盖的成员方法 如果想在子类中操作父类中被隐藏的成员变量和被覆盖的成员方法,也可以使用super关键字,具体格式如下: super.成员变量名 super.成员方法名([参数列表]) 例如,如果想在子类Bird的方法中改变父类Animal的成员变量skin的值可以使用以下代码: super.skin="羽毛"; 如果想在子类Bird的方法中使用父类Animal的成员方法move()可以使用以下代码: super.move();
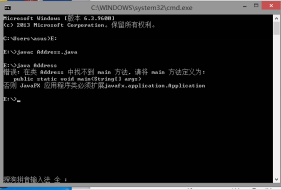
1.Address.java
public final class Address
{
private final String detail;
private final String postCode;
//在构造方法里初始化两个实例属性
public Address()
{
this.detail = "";
this.postCode = "";
}
public Address(String detail , String postCode)
{
this.detail = detail;
this.postCode = postCode;
}
//仅为两个实例属性提供getter方法
public String getDetail()
{
return this.detail;
}
public String getPostCode()
{
return this.postCode;
}
//重写equals方法,判断两个对象是否相等。
public boolean equals(Object obj)
{
if (obj instanceof Address)
{
Address ad = (Address)obj;
if (this.getDetail().equals(ad.getDetail()) && this.getPostCode().equals(ad.getPostCode()))
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public int hashCode()
{
return detail.hashCode() + postCode.hashCode();
}
}
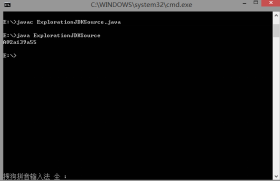
2.ExplorationJDKSource.java
public class ExplorationJDKSource {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(new A());
}
}
class A{}//调用的是object();
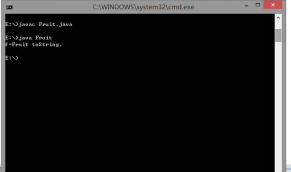
3.Fruit.java
public class Fruit
{
public String toString()
{
return "Fruit toString.";
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Fruit f=new Fruit();
System.out.println("f="+f);
// System.out.println("f="+f.toString());
}
}
4.TestInherits.java
class Grandparent {
public Grandparent() {
System.out.println("GrandParent Created.");
}
public Grandparent(String string) {
System.out.println("GrandParent Created.String:" + string);
}
}
class Parent extends Grandparent {
public Parent() {
//super("Hello.Grandparent.");
//父类参数变量同名,显示区分
System.out.println("Parent Created");
// super("Hello.Grandparent.");
}
}
class Child extends Parent {
public Child() {
System.out.println("Child Created");
}
}
public class TestInherits {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Child c = new Child();
}
}