★问题描述:

★数据输入:
第一行有一个正整数 k,表示有 k 个一元实系数多项式。接下来有 k(k<=20)个数据块,每个数据块的第 1行是 1 个正整数 s,表示该数据块共有 s行。接下来的 s 行中,每行由实数 a和整数 b组成,表示多项式中的项
a
x
b
。紧接着 k 个数据块的是长度为 k-1 的字符串,每个字符是“+”,“-”,“*”这 3 个字符之一。
★数据输出:
文件的第一行是计算得到的多项式 g(x),输出多项式时,
x
k
用 x^k 表示。例如,
5
x
k
应表示为 5x^5。注意输出的结果应该符合数学中手写习惯。例如,x不应输出为 1x^1,实系数 保留 6位有效数字。(数据保证多项式项数不大于 500)
★补充说明
整数 b 满足 b 为非负整数
输出的多项式结果,按项的幂次从高到低排序,参见样例
★Hint
c++中可以使用 setprecision 操作符来控制显示浮点数值的有效数的数量
输入示例1
2
4
-1 4
8.75 3
0.5556666 2
1234.456 1
1
6007.0012 0
+
输出示例1
-x4+8.75x3+0.555667x^2+1234.46x+6007
输入示例2
3
3
3 3
4 1
6 0
2
6 2
1 0
1
3 1
+*
输出示例2
9x4+18x3+12x^2+21x
//思路复杂,方法不够简便,运行时间过长。
总之,这道题的代码我自己还不太满意,日后可能会优化一下。
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
struct x
{
double xishu, mi;
x* next;
};
struct x* add_x(struct x*end)
{
struct x* newx = new x;
newx->next = NULL;
cin >> newx->xishu >> newx->mi;
end->next = newx;
end = newx;
return newx;
}
struct x* creat()
{
struct x* newx = new x;
newx->next = NULL;
cin >> newx->xishu >> newx->mi;
return newx;
}
struct x* mult(struct x* temp1,struct x*temp2)
{
struct x* newx = new x;
newx->mi = temp1->mi+temp2->mi;
newx->xishu = temp1->xishu*temp2->xishu;
newx->next = NULL;
return newx;
}
void sort(x head[])//检查多项式是否按照幂次从高到低排列
{
for (x* temp2 = head; temp2 != NULL; temp2 = temp2->next)
{
for (x* temp1 = head; temp1->next != NULL; temp1 = temp1->next)
{
if (temp1->mi < temp1->next->mi)
{
double xi, m;
m=temp1->mi;
xi = temp1->xishu;
temp1->mi = temp1->next->mi;
temp1->xishu = temp1->next->xishu;
temp1->next->mi = m;
temp1->next->xishu = xi;
}
}
}
for (x* temp1 = head; temp1!=NULL ; )
{
if (temp1->next!=NULL&&temp1->mi == temp1->next->mi)
{
temp1->xishu += temp1->next->xishu;
x* same = temp1->next;
if (temp1->next->next != NULL)
temp1->next = temp1->next->next;
else
temp1->next = NULL;
free(same);
}else
{
temp1=temp1->next;
}
}
};
void display(x head[])
{
int l = 1;
for (x* temp = head/*[0]*/; temp != NULL; temp = temp->next)
{
if (l > 1 && temp->xishu > 0)
{
cout << "+";
}
if (temp->xishu == 0) continue;
if (temp->xishu == 1)
{
if (temp->mi != 0)
{
cout << "x";
if (temp->mi != 1 && temp->mi != 0)
{
cout << "^" << temp->mi;
}
}
else
{
cout << "1";
}
}
else if (temp->xishu == -1)
{
if (temp->mi != 1 && temp->mi != 0)
{
cout << "-x";
if (temp->mi != 1)
{
cout << "^" << temp->mi;
}
}
else if(temp->mi==1)
{
cout<<"-x";
}
else if (temp->mi == 0)
{
cout << "-1";
}
}
else
{
if (temp->mi != 0 && temp->mi != 1)
cout << temp->xishu << "x^" << temp->mi;
else if (temp->mi == 1)
{
cout << temp->xishu << "x";
}
else if (temp->mi == 0)
{
cout << temp->xishu;
}
}
l++;
}
if (l == 1) cout << 0;
}
int main()
{
int k;
cin >> k;
int* s;
string oper;
struct x** head = new x*[k];
struct x** end = new x*[k];
s = new int[k];
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
cin >> s[i];
head[i] = creat();
end[i] = head[i];
for (int j = 1; j < s[i]; j++)
{
end[i]=add_x(end[i]);
}
}
cin >> oper;
for (int i = 0; i < k - 1; i++)
{
if (oper[i] == '+')
{
x* temp1 = head[0];
x* temp2 = head[i + 1];
x* temp;
for (temp = head[0]; temp->next != NULL; temp = temp->next)
{
}
temp->next = head[i + 1];
end[0] = end[i + 1];
sort(head[0]);
////测试
//display(head[0]);
//cout << endl;
}
else if (oper[i] == '-')
{
x* temp = head[i + 1];
while (temp!= NULL)
{
temp->xishu *= -1.0;
temp = temp->next;
}
end[0]->next = head[i + 1];
end[0] = end[i + 1];
sort(head[0]);
////测试
//display(head[0]);
//cout << endl;
}
else if (oper[i] == '*')
{
struct x* temphead = NULL,*tempend=NULL;
int count = 1;
for (x* temp1 = head[0]; temp1!=NULL; temp1 = temp1->next)
{
for (x* temp2 = head[i+1]; temp2!=NULL;temp2 = temp2->next)
{
if (count == 1)
{
temphead = mult(temp1, temp2);
tempend = temphead;
}
else
{
tempend->next = mult(temp1, temp2);
tempend = tempend->next;
}
count++;
}
}
head[0] = temphead;
end[0] = tempend;
sort(head[0]);
//sort(head[0]);
////测试
//display(head[0]);
//cout << endl;
}
}
display(head[0]);
}
★实验任务
在 x 轴上水平放置着 n个条形图。条形图的轮廓是消去这 n 个条形图的隐藏线后得到的图形,如图所示。
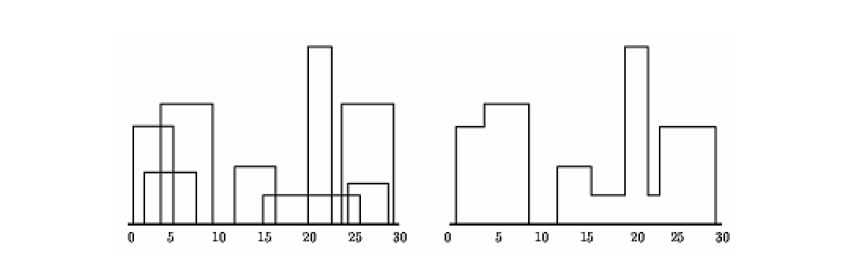
每个条形图由 3元组(Li,Hi,Ri)表示。其中,Li 和 Ri分别为条形图左右竖线的 x 坐标值,Hi 为条形图的高度。例如,上图的 8个条形图表示为:(1,11,5),(2,6,7),(3,13,9),(12,7,16),(14,3,25),(19,18,22),(23,13,29),(24,4,28)。条形图的轮廓可用轮廓向量(V1,V2,…,Vm)表示。当 i 为奇数时,Vi 表示条形图轮廓中一条竖线的 x 坐标值:当i 为偶数时,Vi 表示条形图轮廓中一条横线的高度。
例如,上图的条形图轮廓向量为(1,11,3,13,9,0,12,7,16,3,19,18,22,3,23,13,29,0)。
现在,对于给点的 n个条形图,计算其条形图轮廓。
★数据输入
第一行一个正整数 n,表示 n 个条形图(1 <= n <= 4000)。
接下来 n 行,每行有 3 个整数(Li,Hi,Ri),Li 和 Ri 分别为条形图左右竖线的 x 坐标值,Hi 为条形图的高度(-3000 <= Li,Ri<= 3000, 1 <= Hi <= 1000)。
★数据输出
输出计算出的条形图轮廓向量。
输入示例
8
1 11 5
2 6 7
3 13 9
12 7 16
14 3 25
19 18 22
23 13 29
24 4 28
输出示例
1 11 3 13 9 0 12 7 16 3 19 18 22 3 23 13 29 0
比较暴力的一种算法,思路和代码简单。有更好的算法,然而我暂时看不懂
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int H[6002] = { 0 };
int main()
{
int r, l, h;
int minr = 3000, maxl= -3000;
int k;
cin >> k;
for (int i = 0; i <k; i++)
{
cin >> r >> h >> l;
if (r < minr) minr = r;
if (l > maxl) maxl = l;
for (int i = r; i < l; i++)
{
if (H[i+3000] < h)
{
H[i+3000] = h;
}
}
}
int temph = H[minr + 3000];
for (int i = minr+3000; i <= maxl+3000; i++)
{
if (i == minr+3000)
{
cout << i - 3000 << ' ' << H[i]<<' ';
}
else if(i>minr+3000&&i<maxl+3000)
{
if (H[i] != temph)
{
cout << i - 3000 << ' ' << H[i] << ' ';
temph = H[i];
}
}
else if (i == maxl + 3000)
{
cout << maxl << ' ' << 0;
}
}
}