一 __del__ 魔术方法(析构方法)
1.1 介绍
- 触发时机:当对象被内存回收的时候自动触发[1.页面执行完毕回收所有变量 2.所有对象被del的时候]
- 功能:对象使用完毕后资源回收
- 参数:一个self接受对象
- 返回值:无
1.2 页面执行完毕回收所有变量
class Plane():
def __init__(self,name):
self.name = name
def fly(self):
print ("我的飞机是{}飞的很快".format(self.name))
def __del__(self):
print ("析构被触发")
obj = Plane("高超音速")
obj.fly()
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py 我的飞机是高超音速飞的很快 析构被触发
1.3 所有对象被del的时候
删除对象
class Plane():
def __init__(self,name):
self.name = name
def fly(self):
print ("我的飞机是{}飞的很快".format(self.name))
def __del__(self):
print ("析构被触发")
obj = Plane("高超音速")
print ("<=======================start del=========================>")
del obj
print ("<=======================end del=========================>")
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py <=======================start del=========================> 析构被触发 <=======================end del=========================>
当只删除一个对象,还有剩余对象,也不会触发
class Plane():
def __init__(self,name):
self.name = name
def fly(self):
print ("我的飞机是{}飞的很快".format(self.name))
def __del__(self):
print ("析构被触发")
obj = Plane("高超音速")
obj2 = obj
print ("<=======================start del=========================>")
del obj
print ("<=======================end del=========================>")
执行,是在页面执行完毕是触发
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py <=======================start del=========================> <=======================end del=========================> 析构被触发
1.4 删除所有对象
- 两个不同的变量指向同一个对象,只有把这两个变量都删除了,
- 这个对象没有变量引用了,才会真正的删除对象.
class Plane():
def __init__(self,name):
self.name = name
def fly(self):
print ("我的飞机是{}飞的很快".format(self.name))
def __del__(self):
print ("析构被触发")
obj = Plane("高超音速")
obj2 = obj
print ("<=======================start del=========================>")
del obj
del obj2
print ("<=======================end del=========================>")
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py <=======================start del=========================> 析构被触发 <=======================end del=========================>
1.5 模拟文件读的操作
fp = open("ceshi.txt","r",encoding="utf-8")
res = fp.read()
print (res)
执行
[root@node10 python]# cat ceshi.txt 君临天下 [root@node10 python]# python3 test.py 君临天下
有这个文件,就创建一个对象
fp = open("ceshi.txt","r",encoding="utf-8")
res = fp.read()
fp.close()
print (res)
import os
class ReadFile():
def __new__(cls,name):
if os.path.exists(name):
return object.__new__(cls)
return print("没有这个文件")
obj=ReadFile("ceshi.txt")
print (obj)
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py 君临天下 <__main__.ReadFile object at 0x7f5c2271b518>
如果不存在
fp = open("ceshi.txt","r",encoding="utf-8")
res = fp.read()
fp.close()
print (res)
import os
class ReadFile():
def __new__(cls,name):
if os.path.exists(name):
return object.__new__(cls)
return print("没有这个文件")
obj=ReadFile("ceshii11.txt")
print (obj)
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py 君临天下 没有这个文件 None
1.6 对对象进行初始化
import os
class ReadFile():
def __new__(cls,name):
if os.path.exists(name):
return object.__new__(cls)
return print("没有这个文件")
def __init__(self,name):
self.fp = open("ceshi.txt","r",encoding="utf-8")
def readcontent(self):
res = self.fp.read()
return (res)
def __del__(self):
self.fp.close()
obj=ReadFile("ceshi.txt")
print (obj)
res = obj.readcontent()
print (res)
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py <__main__.ReadFile object at 0x7f601b50e470> 君临天下
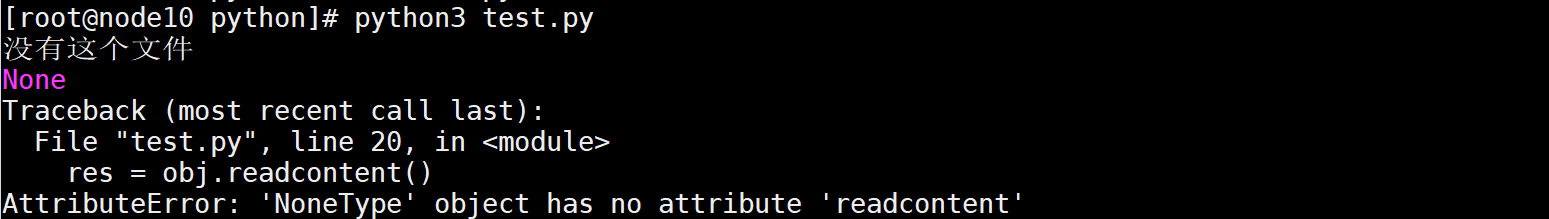
如果文件不存在
import os class ReadFile():
#创建对象 def __new__(cls,name): if os.path.exists(name): return object.__new__(cls) return print("没有这个文件") def __init__(self,name):
#把文件对象赋值给该对象的fp成员属性 self.fp = open("ceshi.txt","r",encoding="utf-8")
#读取文件内容 def readcontent(self): res = self.fp.read() return (res)
#关闭文件 def __del__(self): self.fp.close() obj=ReadFile("ceshi111.txt") print (obj) res = obj.readcontent() print (res)
执行
二 __call__ 魔术方法
2.1 介绍
- 触发时机:把对象当作函数调用的时候自动触发
- 功能: 模拟函数化操作
- 参数: 参数不固定,至少一个self参数
- 返回值: 看需求
2.2 基本用法
把对象当成函数进行调用,自动触发__call__
class MyClass():
def __call__(self):
print ("call方法被调用")
obj = MyClass()
obj()
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py call方法被调用
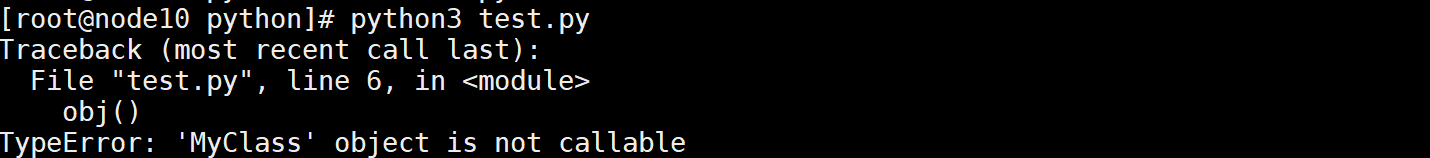
如果没有__call__调用就会出错
class MyClass():
# def __call__(self): # print ("call方法被调用") pass obj = MyClass() obj()
执行报错
2.3 模拟购物过程
class Shopping():
def __init__(self,who):
self.who = who
def step1(self):
print ("{}出门".format(self.who))
def step2(self):
print ("{}开车去商场".format(self.who))
def step3(self):
print ("{}买完东西回家".format(self.who))
obj = Shopping("女朋友")
obj.step1()
obj.step2()
obj.step3()
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py 女朋友出门 女朋友开车去商场 女朋友买完东西回家
2.4 使用__call__方法
class Shopping():
def __init__(self,who):
self.who = who
def __call__(self):
self.step1()
self.step2()
self.step3()
def step1(self):
print ("{}出门".format(self.who))
def step2(self):
print ("{}开车去商场".format(self.who))
def step3(self):
print ("{}买完东西回家".format(self.who))
obj = Shopping("女朋友")
obj()
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py 女朋友出门 女朋友开车去商场 女朋友买完东西回家
2.5 优化1
class Shopping():
def __init__(self,who):
self.who = who
def __call__(self,shop):
self.shop = shop
print ("我的{}要去{}".format(self.who,self.shop))
self.step1()
self.step2()
self.step3()
def step1(self):
print ("{}出门".format(self.who))
def step2(self):
print ("{}开车去商场".format(self.who))
def step3(self):
print ("{}买完东西回家".format(self.who))
obj = Shopping("女朋友")
obj("购物")
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py 我的女朋友要去购物 女朋友出门 女朋友开车去商场 女朋友买完东西回家
2.6 不使用初始化
class Shopping():
def __call__(self,who):
self.who = who
print ("我的{}要去购物".format(self.who))
self.step1()
self.step2()
self.step3()
def step1(self):
print ("{}出门".format(self.who))
def step2(self):
print ("{}开车去商场".format(self.who))
def step3(self):
print ("{}买完东西回家".format(self.who))
obj = Shopping()
obj("女朋友")
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py 我的女朋友要去购物 女朋友出门 女朋友开车去商场 女朋友买完东西回家
2.7 优化2
class Shopping():
def __call__(self,who,shop):
self.who = who
self.shop = shop
print ("我的{}要去{}".format(self.who,self.shop))
self.step1()
self.step2()
self.step3()
def step1(self):
print ("{}出门".format(self.who))
def step2(self):
print ("{}开车去商场".format(self.who))
def step3(self):
print ("{}买完东西回家".format(self.who))
obj = Shopping()
obj("女朋友","购物")
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py 我的女朋友要去购物 女朋友出门 女朋友开车去商场 女朋友买完东西回家
2.8 模拟内置int强转方法 myint
import math
class MyInt():
def __call__(self,num):
if isinstance(num,bool):
if num == True:
return 1
else:
return 0
elif isinstance(num,int):
return num
elif isinstance(num,float):
if num < 0:
return math.ceil(num)
else:
return math.floor(num)
myint = MyInt()
print (myint(True))
print (myint(False))
print ("<int type>")
print (myint(55))
print ("<float type>")
print (myint(6.9))
print (myint(-6.9))
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py 1 0 <int type> 55 <float type> 6 -6
判断字符串类型
import math
class MyInt():
# sign 代表符号,默认正值
def myfunc(self,strvar,sign = 1):
isnull = strvar.lstrip("0")
# 判断是否处理完的字符串是不是空的,如果是空的,这个串是"0000.."是因为eval("")会出现错误
if isnull == "":
return 0
res = eval(strvar) * sign
return res
def __call__(self,num):
if isinstance(num,bool):
if num == True:
return 1
else:
return 0
elif isinstance(num,int):
return num
elif isinstance(num,float):
if num < 0:
return math.ceil(num)
else:
return math.floor(num)
elif isinstance(num,str):
if (num[0] == "+" or num[0] == "-") and num[1:].isdecimal():
if num[0] == "+":
sign = 1
else:
sign = -1
return self.myfunc(num[1:],sign)
elif num.isdecimal():
return self.myfunc(num)
else: return "对不起,处理不了这个数据类型"
myint = MyInt()
print (myint(True))
print (myint(False))
print ("<int type>")
print (myint(55))
print ("<float type>")
print (myint(6.9))
print (myint(-6.9))
print ("<str type>")
print(myint("11122233"),type(myint("11122233")))
# print(myint("00001223"))
print(myint("-11122233"),type(myint("-11122233")))
print(myint([1,2,3,4]))
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py 1 0 <int type> 55 <float type> 6 -6 <str type> 11122233 <class 'int'> -11122233 <class 'int'>
对不起,处理不了这个数据类型
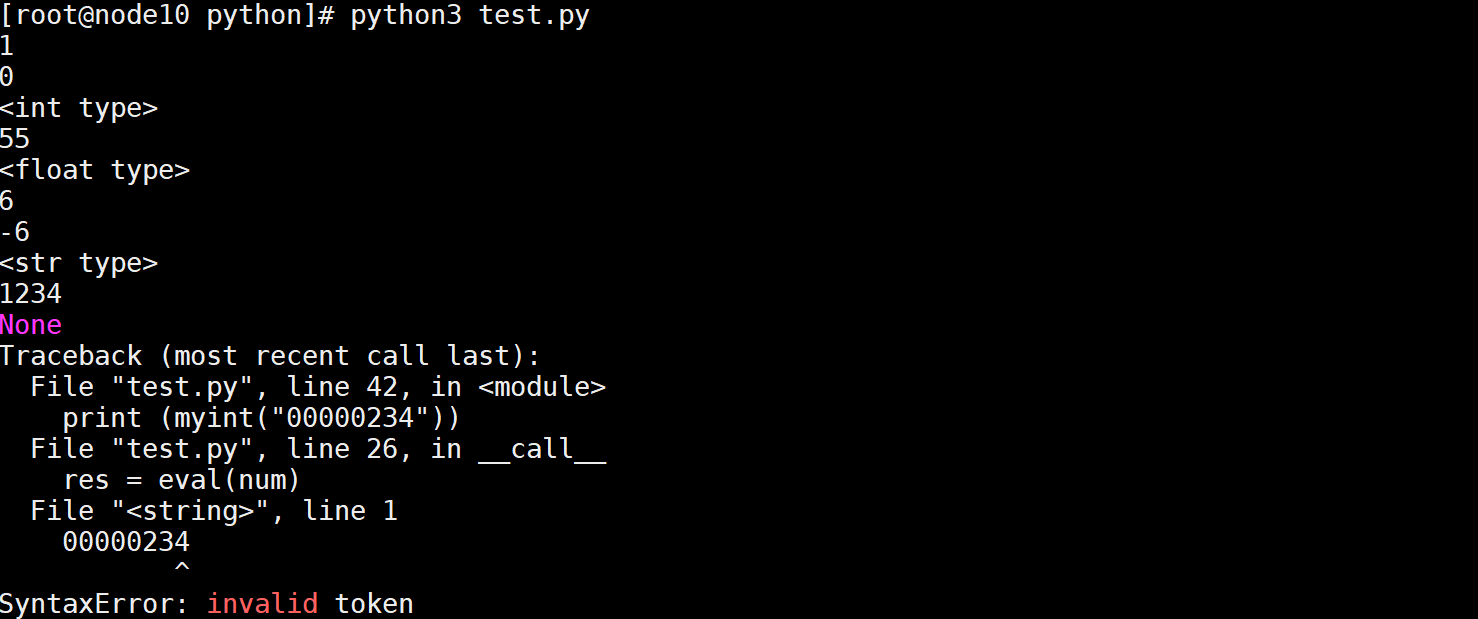
使用eval可以转化为数字,但是在特殊情况下并不能执行
但是空值,带-号的会
[root@node10 python]# cat test.py
import math
class MyInt():
# sign 代表符号,默认正值
def myfunc(self,strvar,sign = 1):
isnull = strvar.lstrip("0")
# 判断是否处理完的字符串是不是空的,如果是空的,这个串是"0000.."
if isnull == "":
return 0
res = eval(strvar) * sign
return res
def __call__(self,num):
if isinstance(num,bool):
if num == True:
return 1
else:
return 0
elif isinstance(num,int):
return num
elif isinstance(num,float):
if num < 0:
return math.ceil(num)
else:
return math.floor(num)
elif isinstance(num,str):
if num.isdecimal():
#或者使用self.myfunc(num)
res = eval(num)
return res
else: return "对不起,处理不了这个数据类型"
myint = MyInt()
print (myint(True))
print (myint(False))
print ("<int type>")
print (myint(55))
print ("<float type>")
print (myint(6.9))
print (myint(-6.9))
print ("<str type>")
print (myint("1234"))
print (myint("-234"))
print (myint("00000234"))
执行
2.9 使用__call__方法实现装饰器
普通方式
class Show():
def showtime(func):
def newfunc():
print ("准备演出")
func()
print ("退出演出")
return newfunc
@Show.showtime
def func():
print ("张靓颖正在鸟巢演出")
func()
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py 准备演出 张靓颖正在鸟巢演出 退出演出
使用__call__
[root@node10 python]# cat test.py
class Show():
def __call__(self,func):
return self.showtime(func)
def showtime(self,func):
def newfunc():
print ("准备演出")
func()
print ("退出演出")
return newfunc
@Show() #@obj =>func = obj(func) => 返回的新函数替换旧函数
def func():
print ("张靓颖正在鸟巢演出")
func()
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py 准备演出 张靓颖正在鸟巢演出 退出演出
@有两个作用
(1)自动把装饰器下面的函数当成参数进行传递 (2)把返回的新函数,自动赋值,用来替换旧函数
执行过程
Show()返回一个obj对象
@obj发动技能,把参数传递给obj
obj(func)返回newfunc
@发动技能,把新函数替换旧函数
func = newfunc,则func()就等价于newfunc()
