一、自定义标签简介
//java类
public class ViewPortTag extends TagSupport{
@Override
public int doStartTag() throws JspException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest)this.pageContext.getRequest();
JspWriter out = this.pageContext.getOut();
int port = request.getRemotePort();
try {
out.print(port);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);//让调用者知道报错
}
return super.doStartTag();
}
}
<!--ku6.tld -->
<taglib xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee/web-jsptaglibrary_2_0.xsd"
version="2.0">
<description>A tag library exercising SimpleTag handlers.</description>
<tlib-version>1.0</tlib-version>
<short-name>SimpleTagLibrary</short-name>
<uri>http://www.hgnc.net/jsp2-tag</uri>
<tag>
<description>show client IP</description>
<name>ViewPortTag</name>
<tag-class>com.ku6.web.tag.ViewPortTag</tag-class>
<body-content>empty</body-content>
</tag>
</taglib>
<!-- jsp -->
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@ taglib prefix="ku6" uri="http://www.hgnc.net/jsp2-tag"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
port:<ku6:ViewPortTag/>
</body>
</html>
查看编译后的jsp源码

package org.apache.jsp;
import com.ku6.web.tag.ViewPortTag;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.el.ExpressionFactory;
import javax.servlet.ServletConfig;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.jsp.JspApplicationContext;
import javax.servlet.jsp.JspFactory;
import javax.servlet.jsp.JspWriter;
import javax.servlet.jsp.PageContext;
import javax.servlet.jsp.SkipPageException;
import org.apache.jasper.runtime.HttpJspBase;
import org.apache.jasper.runtime.InstanceManagerFactory;
import org.apache.jasper.runtime.JspSourceDependent;
import org.apache.jasper.runtime.TagHandlerPool;
import org.apache.tomcat.InstanceManager;
public final class NewFile_jsp extends HttpJspBase
implements JspSourceDependent
{
private static final JspFactory _jspxFactory = JspFactory.getDefaultFactory();
private static Map<String, Long> _jspx_dependants = new HashMap(1);
private TagHandlerPool _005fjspx_005ftagPool_005fku6_005fViewPortTag_005fnobody;
private ExpressionFactory _el_expressionfactory;
private InstanceManager _jsp_instancemanager;
static
{
_jspx_dependants.put("/WEB-INF/ku6.tld", Long.valueOf(1448265099457L));
}
public Map<String, Long> getDependants()
{
return _jspx_dependants;
}
public void _jspInit() {
this._005fjspx_005ftagPool_005fku6_005fViewPortTag_005fnobody = TagHandlerPool.getTagHandlerPool(getServletConfig());
this._el_expressionfactory = _jspxFactory.getJspApplicationContext(getServletConfig().getServletContext()).getExpressionFactory();
this._jsp_instancemanager = InstanceManagerFactory.getInstanceManager(getServletConfig());
}
public void _jspDestroy() {
this._005fjspx_005ftagPool_005fku6_005fViewPortTag_005fnobody.release();
}
public void _jspService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws IOException, ServletException
{
JspWriter out = null;
JspWriter _jspx_out = null;
PageContext _jspx_page_context = null;
try
{
response.setContentType("text/html; charset=UTF-8");
PageContext pageContext = _jspxFactory.getPageContext(this, request, response,
null, true, 8192, true);
_jspx_page_context = pageContext;
pageContext.getServletContext();
pageContext.getServletConfig();
pageContext.getSession();
out = pageContext.getOut();
_jspx_out = out;
out.write("
");
out.write("
");
out.write("<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
");
out.write("<html>
");
out.write("<head>
");
out.write("<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1">
");
out.write("<title>Insert title here</title>
");
out.write("</head>
");
out.write("<body>
");
out.write(" port:");
if (_jspx_meth_ku6_005fViewPortTag_005f0(_jspx_page_context))
return;
out.write("
");
out.write("</body>
");
out.write("</html>");
} catch (Throwable t) {
if (!(t instanceof SkipPageException)) {
out = _jspx_out;
if ((out != null) && (out.getBufferSize() != 0)) try {
out.clearBuffer(); } catch (IOException localIOException) {
} if (_jspx_page_context != null) _jspx_page_context.handlePageException(t); else
throw new ServletException(t);
}
} finally {
_jspxFactory.releasePageContext(_jspx_page_context);
}
}
private boolean _jspx_meth_ku6_005fViewPortTag_005f0(PageContext _jspx_page_context)
throws Throwable
{
_jspx_page_context.getOut();
ViewPortTag _jspx_th_ku6_005fViewPortTag_005f0 = (ViewPortTag)this._005fjspx_005ftagPool_005fku6_005fViewPortTag_005fnobody.get(ViewPortTag.class);
_jspx_th_ku6_005fViewPortTag_005f0.setPageContext(_jspx_page_context);
_jspx_th_ku6_005fViewPortTag_005f0.setParent(null);
_jspx_th_ku6_005fViewPortTag_005f0.doStartTag();
if (_jspx_th_ku6_005fViewPortTag_005f0.doEndTag() == 5) {
this._005fjspx_005ftagPool_005fku6_005fViewPortTag_005fnobody.reuse(_jspx_th_ku6_005fViewPortTag_005f0);
return true;
}
this._005fjspx_005ftagPool_005fku6_005fViewPortTag_005fnobody.reuse(_jspx_th_ku6_005fViewPortTag_005f0);
return false;
}
}
二、Tag接口的执行流程
1、public void setPageContext(PageContext pc), JSP引擎实例化标签处理器后,将调用setPageContext方法将JSP页面的pageContext对象传递给标签处理器,标签处理器以后可以通过这个pageContext对象与JSP页面进行通信.
2、public void setParent(Tag t),setPageContext方法执行完后,WEB容器接着调用的setParent方法将当前标签的父标签传递给当前标签处理器,如果当前标签没有父标签,则传递给setParent方法的参数值为null.
3、public int doStartTag(),调用了setPageContext方法和setParent方法之后,WEB容器执行到自定义标签的开始标记时,就会调用标签处理器的doStartTag方法.
4、public int doEndTag(),WEB容器执行完自定义标签的标签体后,就会接着去执行自定义标签的结束标记,此时,WEB容器会去调用标签处理器的doEndTag方法.
5、public void release(),通常WEB容器执行完自定义标签后,标签处理器会驻留在内存中,为其它请求服务器,直至停止web应用时,web容器才会调用release方法.
三、自定义标签功能扩展
四、简单标签
由于传统标签使用三个标签接口来完成不同的功能,显得过于繁琐,不利于标签技术的推广, SUN公司为降低标签技术的学习难度,在JSP 2.0中定义了一个更为简单、便于编写和调用的SimpleTag接口来实现标签的功能.实现SimpleTag接口的标签通常称为简单标签.
**简单标签和传统标签的原理相同,只是api不同而已,实际开发中不会让自己写标签,会用就可以.
五、JSTL标签库 *重点
1、<c:out>标签

例:
<c:out value="aabbcc<br/>" escapeXml="false"></c:out>
<c:out value="<a href=''>点点</a>" escapeXml="true"></c:out>
<%
request.setAttribute("data",null);
%>
<c:out default="bbbbbbbbbbbbb" value="${data}"></c:out>
2、<c:set>标签

*只要在标签中看到Var就表示把当前标签的执行结果以var定义的名称为关键字存在某个域里面.
<c:set var="dd" value="ddvalue" scope="page"/>
${dd}<br/>
<% Map map=new HashMap();
request.setAttribute("map",map);
%>
<c:set property="dd" value="xxx" target="${map}" />
${map.dd }<br/>
<%
Person p=new Person();
request.setAttribute("p",p);
%>
<c:set property="name" value="namevalue" target="${p}"></c:set>
<c:out value="${p.name}"></c:out>
3、<c:remove>标签
<c:remove var="varName" [scope="{page|request|session|application}"] />
4、<c:catch>标签
<c:catch [var="varName"]>nested actions</c:catch>
<c:catch var="myex">
<%
int i=10/0;
%>
</c:catch>
<c:out value="${myex}" /><br />
<c:out value="${myex.message}" /><br />
<c:out value="${myex.cause}" /><br />
<c:out value="${myex.stackTrace}" />
5、<c:if>标签
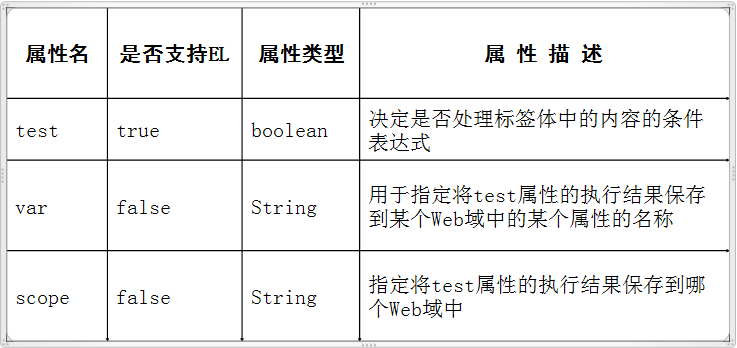
例:
<c:if var="aaa" test="${user==null}" scope="page"></c:if>
${aaa }
6、<c:choose>标签
<c:set value="2" var="count" />
<c:choose>
<c:when test="${count == 0}">
对不起,没有符合您要求的记录.
</c:when>
<c:otherwise>
符合您要求的记录共有${count}条.
</c:otherwise>
</c:choose>
7、<c:forEach>标签

ps:上面没有列出varStatus.
例1,没有items:
<c:forEach var="i" begin="1" end="9" step="1" >
${i}
</c:forEach>
例2,实现表格隔行变色:
<% List list=new ArrayList();
list.add("aaa");
list.add("bbb");
list.add("ccc");
list.add("ddd");
request.setAttribute("list",list);
%>
<style>
.odd{background-color: blue;}
.even{background-color: red;}
tr:hover{background-color: green;}
//如果不支持鼠标放上去变色,可从tomact默认网页上拷头<!DOCTYPE html>
</style>
<table>
<c:forEach var="str" items="${list}" varStatus="status">
<tr class="${status.count%2==0?'even':'odd'}"><td> ${status} ::: ${str }</td></tr>//el表达式可以写各种java表达式,但是不能实现字符串拼接,像个bug一样
</c:forEach>
</table>
例3,varStatus的属性:
<%
String atts[] = new String [5];
atts[0]="hello";
atts[1]="this";
atts[2]="is";
atts[3]="a";
atts[4]="pen";
request.setAttribute("atts", atts);
%>
<c:forEach items="${atts}" var="item" varStatus="s">
<c:out value="${item}"/>的四种属性:
index:${s.index}</br>
count:${s.count}</br>
first:${s.first}</br>
last:${s.last}</br>
</c:forEach>
8、<c:url>标签 ,<c:param>标签 , *重点
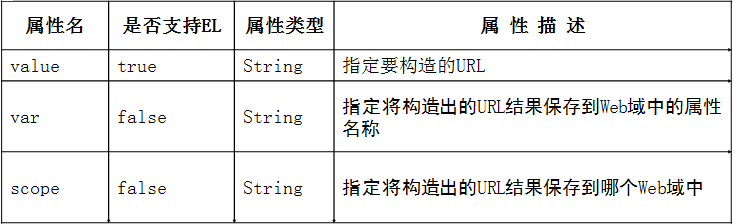
2>在JSP页面进行URL的相关操作时,经常要在URL地址后面附加一些参数.<c:param>标签可以嵌套在<c:url>或<c:redirect>标签内,为这些标签所使用的URL地址附加参数.<c:param>标签在为一个URL地址附加参数时,将自动对参数值进行URL编码,例如,如果传递的参数值为“中国”,则将其转换为“%d6%d0%b9%fa”后再附加到URL地址后面,这也就是使用<c:param>标签的最大好处.
例:
<c:url var="url" value="/index.jsp">
<c:param name="name" value="中国"></c:param>
</c:url>
<a href="${url }">购买</a>//会自动补全路径
9、<c:redirect>标签,用于实现请求重定向

10、forTokens标签,分割字符串
<% String data="aa,bb,cc,dd";
request.setAttribute("data",data);
%>
<c:forTokens items="${data}" delims="\," var="c">${c}
