sklearn实战-乳腺癌细胞数据挖掘(博客主亲自录制视频教程)
https://study.163.com/course/introduction.htm?courseId=1005269003&utm_campaign=commission&utm_source=cp-400000000398149&utm_medium=share
Natural Language Toolkit
NLTK is a leading platform for building Python programs to work with human language data. It provides easy-to-use interfaces to over 50 corpora and lexical resources such as WordNet, along with a suite of text processing libraries for classification, tokenization, stemming, tagging, parsing, and semantic reasoning, wrappers for industrial-strength NLP libraries, and an active discussion forum.
Thanks to a hands-on guide introducing programming fundamentals alongside topics in computational linguistics, plus comprehensive API documentation, NLTK is suitable for linguists, engineers, students, educators, researchers, and industry users alike. NLTK is available for Windows, Mac OS X, and Linux. Best of all, NLTK is a free, open source, community-driven project.
NLTK has been called “a wonderful tool for teaching, and working in, computational linguistics using Python,” and “an amazing library to play with natural language.”
Natural Language Processing with Python provides a practical introduction to programming for language processing. Written by the creators of NLTK, it guides the reader through the fundamentals of writing Python programs, working with corpora, categorizing text, analyzing linguistic structure, and more. The book is being updated for Python 3 and NLTK 3. (The original Python 2 version is still available at http://nltk.org/book_1ed.)
Some simple things you can do with NLTK
Tokenize and tag some text:
>>> import nltk
>>> sentence = """At eight o'clock on Thursday morning
... Arthur didn't feel very good."""
>>> tokens = nltk.word_tokenize(sentence)
>>> tokens
['At', 'eight', "o'clock", 'on', 'Thursday', 'morning',
'Arthur', 'did', "n't", 'feel', 'very', 'good', '.']
>>> tagged = nltk.pos_tag(tokens)
>>> tagged[0:6]
[('At', 'IN'), ('eight', 'CD'), ("o'clock", 'JJ'), ('on', 'IN'),
('Thursday', 'NNP'), ('morning', 'NN')]
Identify named entities:
>>> entities = nltk.chunk.ne_chunk(tagged)
>>> entities
Tree('S', [('At', 'IN'), ('eight', 'CD'), ("o'clock", 'JJ'),
('on', 'IN'), ('Thursday', 'NNP'), ('morning', 'NN'),
Tree('PERSON', [('Arthur', 'NNP')]),
('did', 'VBD'), ("n't", 'RB'), ('feel', 'VB'),
('very', 'RB'), ('good', 'JJ'), ('.', '.')])
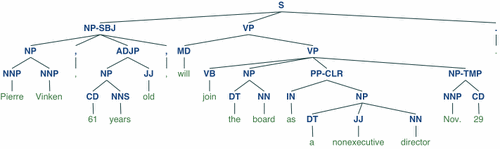
Display a parse tree:
>>> from nltk.corpus import treebank
>>> t = treebank.parsed_sents('wsj_0001.mrg')[0]
>>> t.draw()
NB. If you publish work that uses NLTK, please cite the NLTK book as follows:
Bird, Steven, Edward Loper and Ewan Klein (2009), Natural Language Processing with Python. O’Reilly Media Inc.