python机器学习-乳腺癌细胞挖掘(博主亲自录制视频)
https://study.163.com/course/introduction.htm?courseId=1005269003&utm_campaign=commission&utm_source=cp-400000000398149&utm_medium=share
貌似一个不相关的变量,可能对结果有显著影响
多元回归可以分析独立变量与因变量是否显著相关。但解释能力不如因子分析
因子分析对变量相关性解释能力更强
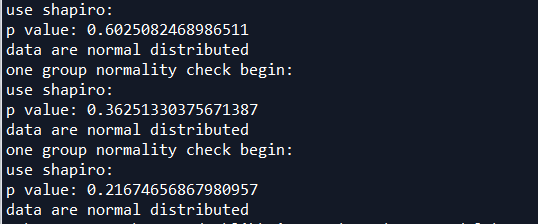
正态分布检验OK
三组数据呈现正态分布,可以用回归检测
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
'''
Author:Toby
QQ:231469242,all right reversed,no commercial use
normality_check.py
正态性检验脚本
'''
import scipy
from scipy.stats import f
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import scipy.stats as stats
# additional packages
from statsmodels.stats.diagnostic import lillifors
#对一列数据进行正态分布测试
def check_normality(testData):
print("one group normality check begin:")
#20<样本数<50用normal test算法检验正态分布性
if 20<len(testData) <50:
p_value= stats.normaltest(testData)[1]
if p_value<0.05:
print("use normaltest")
print("p value:",p_value)
print ("data are not normal distributed")
return False
else:
print("use normaltest")
print("p value:",p_value)
print ("data are normal distributed")
return True
#样本数小于50用Shapiro-Wilk算法检验正态分布性
if len(testData) <50:
p_value= stats.shapiro(testData)[1]
if p_value<0.05:
print ("use shapiro:")
print("p value:",p_value)
print ("data are not normal distributed")
return False
else:
print ("use shapiro:")
print("p value:",p_value)
print ("data are normal distributed")
return True
if 300>=len(testData) >=50:
p_value= lillifors(testData)[1]
if p_value<0.05:
print ("use lillifors:")
print("p value:",p_value)
print ("data are not normal distributed")
return False
else:
print ("use lillifors:")
print("p value:",p_value)
print ("data are normal distributed")
return True
if len(testData) >300:
p_value= stats.kstest(testData,'norm')[1]
if p_value<0.05:
print ("use kstest:")
print("p value:",p_value)
print ("data are not normal distributed")
return False
else:
print ("use kstest:")
print("p value:",p_value)
print ("data are normal distributed")
return True
#测试结束
print("-"*100)
#对所有样本组进行正态性检验
def NormalTest(list_groups):
for group in list_groups:
#正态性检验
status=check_normality(group)
if status==False :
return False
group1=[5,2,4,2.5,3,3.5,2.5,3]
group2=[1.5,2,1.5,2.5,3.3,2.3,4.2,2.5]
group3=[96,90,95,92,95,94,94,94]
list_groups=[group1,group2,group3]
list_total=group1+group2+group3
#对所有样本组进行正态性检验
NormalTest(list_groups)
下图可见,独立变量x1和x2没有相关,R调整平方为0.19
x1和yR调整平方0.59的关系--存在很弱关系
x2和y存在R调整平方-0.19,即没有关系
但x1和x2与y存在0.886R调整平方关系,非常强

且x1和x2与y结合后,残差服从正态分布,AIC和BIC值很小,
prob (F-statistic)=0.00187,小于0.05,说明回归方程显著
参数t检验显著,x1和x2的t分数P值分别为0.001和0.01,小于0.05,否定H0,表示x1和x2显著,说明此模型拟合度很好
说明貌似一个不相关的变量,可能对结果有显著影响

# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Tue Jul 18 09:37:15 2017
@author: toby
"""
# Import standard packages
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
from sklearn import datasets, linear_model
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
font_set = FontProperties(fname=r"c:windowsfontssimsun.ttc", size=15)
# additional packages
import sys
import os
sys.path.append(os.path.join('..', '..', 'Utilities'))
try:
# Import formatting commands if directory "Utilities" is available
from ISP_mystyle import showData
except ImportError:
# Ensure correct performance otherwise
def showData(*options):
plt.show()
return
# additional packages ...
# ... for the 3d plot ...
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
from matplotlib import cm
# ... and for the statistic
from statsmodels.formula.api import ols
#生成组合
from itertools import combinations
x1=[5,2,4,2.5,3,3.5,2.5,3]
x2=[1.5,2,1.5,2.5,3.3,2.3,4.2,2.5]
y=[96,90,95,92,95,94,94,94]
#自变量列表
list_x=[x1,x2]
#绘制多元回归三维图
def Draw_multilinear():
df = pd.DataFrame({'x1':x1,'x2':x2,'y':y})
# --- >>> START stats <<< ---
# Fit the model
model = ols("y~x1+x2", df).fit()
param_intercept=model.params[0]
param_x1=model.params[1]
param_x2=model.params[2]
rSquared_adj=model.rsquared_adj
#generate data,产生矩阵然后把数值附上去
x = np.linspace(-5,5,101)
(X,Y) = np.meshgrid(x,x)
# To get reproducable values, I provide a seed value
np.random.seed(987654321)
Z = param_intercept + param_x1*X+param_x2*Y+np.random.randn(np.shape(X)[0], np.shape(X)[1])
# 绘图
#Set the color
myCmap = cm.GnBu_r
# If you want a colormap from seaborn use:
#from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
#myCmap = ListedColormap(sns.color_palette("Blues", 20))
# Plot the figure
fig = plt.figure("multi")
ax = fig.gca(projection='3d')
surf = ax.plot_surface(X,Y,Z, cmap=myCmap, rstride=2, cstride=2,
linewidth=0, antialiased=False)
ax.view_init(20,-120)
ax.set_xlabel('X')
ax.set_ylabel('Y')
ax.set_zlabel('Z')
ax.set_title("multilinear with adj_Rsquare %f"%(rSquared_adj))
fig.colorbar(surf, shrink=0.6)
outFile = '3dSurface.png'
showData(outFile)
#检查独立变量之间共线性关系
def Two_dependentVariables_compare(x1,x2):
# Convert the data into a Pandas DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({'x':x1, 'y':x2})
# Fit the model
model = ols("y~x", df).fit()
rSquared_adj=model.rsquared_adj
print("rSquared_adj",rSquared_adj)
if rSquared_adj>=0.8:
print("high relation")
return True
elif 0.6<=rSquared_adj<0.8:
print("middle relation")
return False
elif rSquared_adj<0.6:
print("low relation")
return False
#比较所有参数,观察是否存在多重共线
def All_dependentVariables_compare(list_x):
list_status=[]
list_combine=list(combinations(list_x, 2))
for i in list_combine:
x1=i[0]
x2=i[1]
status=Two_dependentVariables_compare(x1,x2)
list_status.append(status)
if True in list_status:
print("there is multicorrelation exist in dependent variables")
return True
else:
return False
#回归方程,支持哑铃变量
def regressionModel(x1,x2,y):
'''Multilinear regression model, calculating fit, P-values, confidence intervals etc.'''
# Convert the data into a Pandas DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({'x1':x1,'x2':x2,'y':y})
# --- >>> START stats <<< ---
# Fit the model
model = ols("y~x1+x2", df).fit()
# Print the summary
print((model.summary()))
return model._results.params # should be array([-4.99754526, 3.00250049, -0.50514907])
# Function to show the resutls of linear fit model
def Draw_linear_line(X_parameters,Y_parameters,figname,x1Name,x2Name):
#figname表示图表名字,用于生成独立图表fig1 = plt.figure('fig1'),fig2 = plt.figure('fig2')
plt.figure(figname)
#获取调整R方参数
df = pd.DataFrame({'x':X_parameters, 'y':Y_parameters})
# Fit the model
model = ols("y~x", df).fit()
rSquared_adj=model.rsquared_adj
#处理X_parameter1数据
X_parameter1 = []
for i in X_parameters:
X_parameter1.append([i])
# Create linear regression object
regr = linear_model.LinearRegression()
regr.fit(X_parameter1, Y_parameters)
plt.scatter(X_parameter1,Y_parameters,color='blue',label="real value")
plt.plot(X_parameter1,regr.predict(X_parameter1),color='red',linewidth=4,label="prediction line")
plt.title("linear regression %s and %s with adj_rSquare:%f"%(x1Name,x2Name,rSquared_adj))
plt.xlabel('x', fontproperties=font_set)
plt.ylabel('y', fontproperties=font_set)
plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(())
plt.legend()
plt.show()
#绘制多元回归三维图
Draw_multilinear()
#比较所有参数,观察是否存在多重共线
All_dependentVariables_compare(list_x)
Draw_linear_line(x1,x2,"fig1","x1","x2")
Draw_linear_line(x1,y,"fig4","x1","y")
Draw_linear_line(x2,y,"fig5","x2","y")
regressionModel(x1,x2,y)
'''
训练数据
x1=[2,6,8,3,2,7,9,8,4,6]
x2=[1,0,1,0,1,1,0,0,1,1]
y=[2900,3000,4800,1800,2900,4900,4200,4800,4400,4500]
x=[89,66,78,111,44,77,80,66,109,76]
y=[4,1,3,6,1,3,3,2,5,3]
z=[7,5.4,6.6,7.4,4.8,6.4,7,5.6,7.3,6.4]
x1=[89,66,78,111,44,77,80,66,109,76]
x2=[4,1,3,6,1,3,3,2,5,3]
x3=[3.84,3.19,3.78,3.89,3.57,3.57,3.03,3.51,3.54,3.25]
y=[7,5.4,6.6,7.4,4.8,6.4,7,5.6,7.3,6.4]
'''