封装 继承 多态
一,抽象的概念
把一类事物的共有的属性(成员属性)和行为(成员方法)提取出来,形成一个模型,这种研究问题的方法就是抽象
二.封装
将抽象出的数据和对数据的操作封装在一起,数据被保护在内部,程序的其他部分只有通过被授权的操作(成员方法),才能对数据进行操作
封装的具体实现--访问修饰符:public protected private
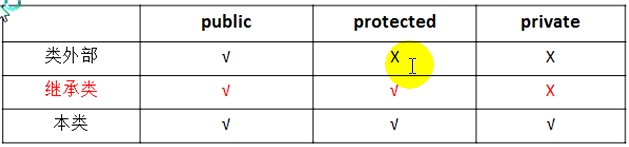
1.如何访问protected和private属性的三种方式
①魔术方法__get和__set
缺点:不能单独控制某一个属性
<?php
class Person{
public $name;
protected $nickname;
private $address;
//初始化数据
public function __construct($name,$nickname,$address){
$this->name = $name;
$this->nickname = $nickname;
$this->address = $address;
}
//魔术方法
//参数:$pro_name 属性名 $pro_val 属性值
public function __set($pro_name,$pro_val){
if(property_exists($this,$pro_name)){
$this->$pro_name = $pro_val;
}else{
echo '属性不存在';
}
}
public function __get($pro_name){
if(property_exists($this,$pro_name)){
return $this->$pro_name;
}
}
}
$p1 = new Person('小明','明明','花果山');
$p1->nickname = '红红';
$p1->address = '泰山';
echo $p1->nickname;
echo $p1->address;
②对每一个protected和private属性提供一堆get/set方法,这样就可以分别控制各个属性
优点:可以对每个属性进行单独操作
缺点:每个属性会有一对get和set方法,所以属性越多 get和set方法越多
<?php
class Person{
public $name;
protected $nickname;
private $address;
public function __construct($name,$nickname,$address){
$this->name = $name;
$this->nickname = $nickname;
$this->address = $address;
}
//单独定义方法去设置相应的属性
public function setNickname($pro_name){
$this->nickname = $pro_name;
}
public function getNickname(){
return $this->nickname;
}
}
$p1 = new Person('小明','明明','花果山');
$p1->setNickname('红红');
$p1->getNickname();
var_dump($p1);
var_dump($p1->getNickname());
③写一个成员方法,可以根据业务逻辑,一次性对多个属性进行批量操作
class Movie{
//Movie(名称,导演,成本,票房)
public $name;
public $director;
protected $cost;
private $tickeoffice;
public function __construct($name,$director,$cost){
$this->name = $name;
$this->director = $director;
$this->cost = $cost;
}
//显示一下电影信息
public function showAllInfo(){
echo '<br> 电影信息如下:';
echo '<br> name = '.$this->name;
echo '<br> director = '.$this->director;
echo '<br> cost = '.$this->cost;
echo '<br> tickeoffice = '.$this->tickeoffice;
}
public function updateInfo($director,$cost,$tickeoffice){
//简单方式
$this->director = $director;
// $this->cost = $cost;
// $this->tickeoffice = $tickeoffice;
//另外一种方法
$this->setCost($cost);
$this->setickeoffice($tickeoffice);
}
//修改成本
public function setCost($cost){
//加入数据的验证和判断 is_numeric()用来判断是不是数字格式
if(is_numeric($cost)&&$cost>0.0){
$this->cost = $cost;
}else{
echo '输入成本格式有问题';
}
}
//修改票房
public function setickeoffice($tickeoffice){
//加入数据的验证和判断 is_numeric()用来判断是不是数字格式
if(is_numeric($tickeoffice)&&$tickeoffice>0.0){
$this->tickeoffice = $tickeoffice;
}else{
echo '输入票房格式有问题';
}
}
}
$movie = new Movie('葫芦娃','老爷子',60000);
$movie->updateInfo('小明','80000','620000');
$movie->showAllInfo();
2,封装的细节
普通属性定义时必须写访问修饰符,public protected 或private,如果用var定义默认为公有
静态属性定义时,可以写访问修饰符,public protected 或private,如果是公有时可以不写public
类的方法可以定义为public protected 或private,如果是公有时可以不写public
3.对象运算符的连用
//学生类
class student{
public $name;
private $school;
//构造函数
public function __construct($name,$school){
$this->name = $name;
$this->school = $school;
}
//给$school 提供setX学习和setXxx方法
public function getSchool(){
return $this->school;
}
public function setSchool(){
$this->school = $school;
}
}
//学校类
class School{
public $name;
public $address;
private $my_class;
//构造函数
public function __construct($name,$address,$my_class){
$this->name = $name;
$this->address = $address;
$this->my_class = $my_class;
}
//给$my_class 提供setX学习和setXxx方法
public function getMyclass(){
return $this->my_class;
}
public function setMyclass(){
$this->my_class = $my_class;
}
}
//班级类
class Myclass{
protected $name;
protected $stu_num;
private $introduce;
//构造函数
public function __construct($name,$stu_num,$introduce){
$this->name = $name;
$this->stu_num = $stu_num;
$this->introduce = $introduce;
}
//$introduce 提供setX学习和setXxx方法
public function getintroduce(){
return $this->introduce;
}
public function setMyclass(){
$this->introduce = $introduce;
}
}
//创建班级对象
$myClass = new Myclass('2005级应化一班',32,'2005级化学院');
//var_dump($myClass);
//创建学校对象
$school = new School('山东农业大学','山东泰安',$myClass);
//var_dump($school);
//创建学生对象
$student = new student('小明',$school);
//var_dump($student);
//通过$student对象,找到对应的班级信息
var_dump($student->getSchool()->getMyclass()->getintroduce());