在使用AIDL通信的时候,在Stub类中都会生成一个asInterface函数,以《Android开发艺术探索》中的例子来分析,其生成的asInterface函数源码为:
1 /** 2 * Cast an IBinder object into an com.willhua.demoaidl.aidl.IBookManager 3 * interface, generating a proxy if needed. 4 */ 5 public static com.willhua.demoaidl.aidl.IBookManager asInterface( 6 android.os.IBinder obj) { 7 if ((obj == null)) { 8 return null; 9 } 10 android.os.IInterface iin = obj.queryLocalInterface(DESCRIPTOR); 11 if (((iin != null) && (iin instanceof com.willhua.demoaidl.aidl.IBookManager))) { 12 return ((com.willhua.demoaidl.aidl.IBookManager) iin); 13 } 14 return new com.willhua.demoaidl.aidl.IBookManager.Stub.Proxy(obj); 15 }
我们知道asInterface的作用是根据调用是否属于同进程而返回不同的实例对象,但是对于该过程是怎么进行的,返回的到底是什么东西,可能很多童鞋不是很清楚,就这个问题分享一点我的理解。显然,通过代码可知,决定返回何种对象的关键在obj.queryLocalInterface(DESCRIPTOR)的返回结果。
下面我们通过实际DEMO来了解其过程。代码基于《Android开发艺术探索》中的例子。
DEMO中有主要有两个东西,一个就是MainActivity,一个就是BookService,MainActivity会去bind BookService,而BookService通过在Manifest中设置android:process而使之分别与MainActivity运行在同进程和异进程。
主要代码:
public class BookService extends Service { private Binder mBinder = new IBookManager.Stub() { ... }; @Override public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub LOG("BookService onBind mBinder:" +mBinder.getClass().getName() + " Process:" + Process.myPid()); return mBinder; } }
public class MainActivity extends Activity{ private IBookManager mService; private Button mQuery; private TextView mOutInfo; ... @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); connectService(); } private void connectService(){ Intent intent = new Intent(getApplicationContext(), BookService.class); bindService(intent, new ServiceConnection() { @Override public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } @Override public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub LOG("onServiceConnected " + service); mService = IBookManager.Stub.asInterface(service); } }, BIND_AUTO_CREATE); } ... }
public static abstract class Stub extends android.os.Binder implements com.willhua.demoaidl.aidl.IBookManager { private static final java.lang.String DESCRIPTOR = "com.willhua.demoaidl.aidl.IBookManager"; /** Construct the stub at attach it to the interface. */ public Stub() { this.attachInterface(this, DESCRIPTOR); } /** * Cast an IBinder object into an com.willhua.demoaidl.aidl.IBookManager * interface, generating a proxy if needed. */ public static com.willhua.demoaidl.aidl.IBookManager asInterface( android.os.IBinder obj) { if ((obj == null)) { return null; } android.os.IInterface iin = obj.queryLocalInterface(DESCRIPTOR); if (((iin != null) && (iin instanceof com.willhua.demoaidl.aidl.IBookManager))) { return ((com.willhua.demoaidl.aidl.IBookManager) iin); } return new com.willhua.demoaidl.aidl.IBookManager.Stub.Proxy(obj); } ... }
androd.os.Binder部分源码:
public class Binder implements IBinder { //... /** * Convenience method for associating a specific interface with the Binder. * After calling, queryLocalInterface() will be implemented for you * to return the given owner IInterface when the corresponding * descriptor is requested. */ public void attachInterface(IInterface owner, String descriptor) { mOwner = owner; mDescriptor = descriptor; } /** * Use information supplied to attachInterface() to return the * associated IInterface if it matches the requested * descriptor. */ public IInterface queryLocalInterface(String descriptor) { if (mDescriptor.equals(descriptor)) { return mOwner; } return null; } //... final class BinderProxy implements IBinder { //... public IInterface queryLocalInterface(String descriptor) { return null; } //... } }
通过LOG,我们发现,在onServiceConnected函数中,如果MainActivity与BookService同进程,则打印的log为:

如果MainActivity与BookService异进程,及MainActivity跨进程绑定BookService服务,则打印的log为:
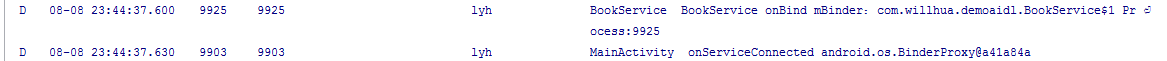
先分析同进程,
在同进程中,onServiceConnected接收得到的service对象的类型为BookServices$1,我们知道$表示的是BookServices中的内部类,而在BookServices的定义中,我们只在mBinder的初始化中定义了一个IBookManager.Stub()的子类,即同进程时,在onServiceConnected接收到的是IBookManager.Stub()类型。而IBookManager.Stub() extenders android.os.Binder implements IBookManager,其queryLocalInterface方法来源于超类android.os.Binder。对于方法中传入的descriptor,通过asInterface的代码可知就是Stub中定义的DESCRIPTOR,而Binder中定义的mDescriptor,其赋值过程是在attachInterface函数中,而attachInterface函数是在Stub的构造函数中被调用,其调用为
this.attachInterface(this, DESCRIPTOR);
而在onServiceConnected中的调用为:
mService = IBookManager.Stub.asInterface(service);
注意sercice为IBookManager.Stub,从而我们可以知道,
if (mDescriptor.equals(descriptor))
判断语句中的mDescriptor和descriptor都为IBookManager.Stub中定义的DESCRIPTOR,则queryLocalInterface返回的是mOwer。那么mOwer又是什么呢?细心的童鞋估计已经知道答案,在Stub的构造函数调用中attachInterface的时候,已经给mOwer赋值,且赋值为this,即该Stub对象本身!再回去对照asInterface的逻辑,我们即可以得出结论:同进程时,调用asInterface返回的是Stub对象,其实就是在onBind中返回的mBinder。
再来分析跨进程调用的情形
由上面的log可知,跨进程调用时,onSericeConnected中接收到的service为android.os.BinderProxy类型,而上面的源码已经给出,BinderProxy为final类,且其queryLocalInterface方法直接返回的null,结合asInterface的代码逻辑,就知道它返回的为IBookManager.Stub.Proxy对象,得出结论:同进程时,调用asInterface返回的是Stub.Proxy对象。
至此,开篇提到的问题应该已经明了。但其实又引出了一个新的问题:为什么跨进程调时,在onServiceConnected中接收到的是os.BinderProxy,而同进程调用时接收到的是IBookManager.Stub?
且听下回。。。