1.ConcurrentHashMap和HashTable区别
ConcurrentHashMap融合了hashtable和hashMap二者的优势;
hashTable是做了同步的,hashMap没有同步,所以hashMap在单线程情况下效率高,hashTable在多线程情况下,同步操作能保证程序执行的正确性;
但是hashTable每次同步执行都要锁住整个结构;
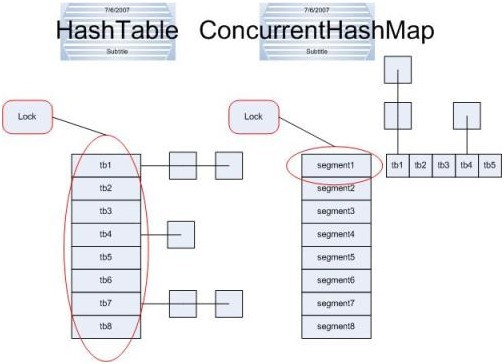
ConcurrentHashMap锁的方式是稍微细粒度的(分段锁机制),ConcurrentHashMap将hash表分为16个桶(默认值);
2.ConcurrentHashMap jdk1.7和jdk1.8底层实现的区别
2.1 JDK1.7 ConcurrentHashMap
底层采用:Segment+HashEntry
底层一个Segment数组,存储一个Segments对象,一个Segments中存储一个Entry数组,存储的每一个Entry对象又是一个链表头结点;
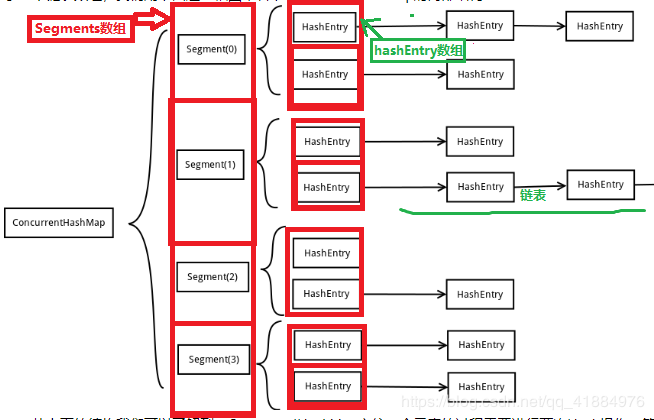
当数据添加时,根据key值找到Segment对应的数据段,然后匹配数据块,采用链表方式进行存储;
2.2 JDK1.8 ConcurrentHashMap
底层采用:数组+链表+红黑树,类似于HashMap(JDK1.8)
数组使用用来存放树或者链表的头结点当一个链表中的数量达到一个数目时,会使查询速率降低,所以达到一定阈值时,会将一个链表转换为一个红黑二叉树,通告查询的速率;
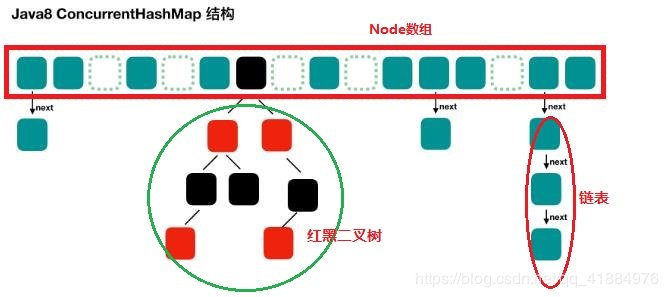
ConcurrentHashMap取消了Segment分段锁的机制,从而实现一段数据进行加锁,减少了并发,CAS(读)+synchronized(写)
3.ConcurrentHashMap底层put()方法
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(key, value, false);
}
进入putVal()方法:
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
//判断key和value是否为空,如果为空则报异常
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
//重新计算key的hash值,有效减少hash值冲突
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
//用于记录相应链表的长度
int binCount = 0;
//遍历当前数组当中所有的数据
for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) {
Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh;
//判断数组是否为空
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
//如果为空要进行数组的初始化操作
tab = initTable();
//根据key的hash值找到位置,如果该位置没有元素
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
//获取到空的元素,然后重新创建一个新的node放进去
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,
new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null)))
break; // no lock when adding to empty bin
}
//判断当前数组元素状态是否需要扩容
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
else {
//如果f是头结点
V oldVal = null;
synchronized (f) {
//加锁
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
//头结点的hash值大于0,说明是链表
if (fh >= 0) {
//链表的长度+1
binCount = 1;
for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) {
K ek;
//判断添加的key和原有key践行hash值判断以及key值判断,如果相等则覆盖
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
oldVal = e.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.val = value;
break;
}
Node<K,V> pred = e;
//判断当前节点的下一个节点是否为空,如果为空则添加到下一个节点当中
if ((e = e.next) == null) {
pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key,
value, null);
break;
}
}
}
//判断当前节点是否为红黑树
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
Node<K,V> p;
binCount = 2;
//如果为红黑树则创建一个树节点
if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,
value)) != null) {
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value;
}
}
}
}
if (binCount != 0) {
//根据当前循环次数判断链表中存在多少个数据,如果数据阈值大于等于8
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
//则进行红黑树转换
treeifyBin(tab, i);
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
addCount(1L, binCount);
return null;
}
对于putVal函数的流程大体如下:
1.判断存储的key,value是否为空,若为空,则抛出异常;
2.计算key的hash值,随后进入无限循环,该无限循环可以确保成功插入数据,若table表为空或者长度为0,则初始化table表;
3.根据key的hash值取出table表中的结点元素,若取出的结点元素为空(该桶为空),则使用CAS将key,value,hash值生成的结点放入桶中;
4.若该节点的hash值为MOVED,则对该桶中的结点进行转移;
5.对桶中的第一个结点进行加锁,对该桶进行遍历,桶中的结点的hash值与key值与给定的hash值和key值相等,则根据标识选择是否进行更新操作(用给定的value值替换该结点的value值),若遍历完桶仍没有找到hash值与key值和指定的hash值与key值相等的结点,则直接新生一个结点并赋值为之前最后一个结点的下一个结点;
6.若binCount值达到红黑树转化的阈值,则将桶中的结构转化为红黑树存储,最后,增加binCount的值;
4.ConcurrentHashMap底层get()方法
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> e, p; int n, eh; K ek;
//计算key的hash值
int h = spread(key.hashCode());
//表不为空并且表的长度大于0并且key所在的桶不为空
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) != null) {
//表中的元素的hash值与key的hash相等
if ((eh = e.hash) == h) {
//键相等
if ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))
return e.val;
}
//结点hash值小于0
else if (eh < 0)
//在桶中查找
return (p = e.find(h, key)) != null ? p.val : null;
//对于结点hash值大于0的情况
while ((e = e.next) != null) {
if (e.hash == h &&
((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))))
return e.val;
}
}
return null;
}
get函数根据key的hash值来计算在哪个桶中,再遍历桶,查找元素,若找到则返回该结点,否则,返回null;