ASP.NET works in conjunction with IIS, the .NET Framework, and the underlying
security services provided by the operating system, to provide a range of authentication
and authorization mechanisms. These are summarized in Figure 1
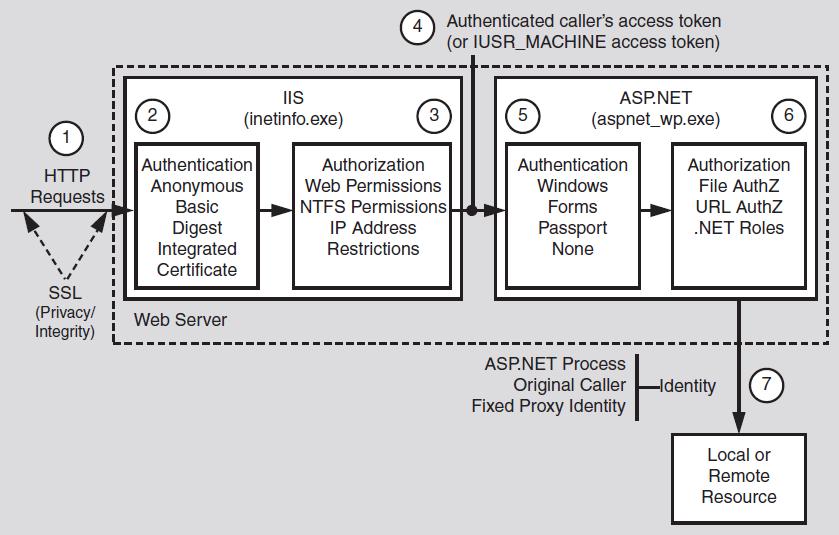
Figure 1 illustrates the authentication and authorization mechanisms provided by
IIS and ASP.NET. When a client issues a Web request, the following sequence of
authentication and authorization events occurs:
1. The HTTP(S) Web request is received from the network. SSL can be used to
ensure the server identity (using server certificates) and, optionally, the client
identity.
Note: SSL also provides a secure channel to protect sensitive data passed between client
and server (and vice-versa).
2. IIS authenticates the caller by using Basic, Digest, Integrated (NTLM or
Kerberos), or Certificate authentication. If all or part of your site does not require
authenticated access, IIS can be configured for anonymous authentication. IIS
creates a Windows access token for each authenticated user. If anonymous
authentication is selected, IIS creates an access token for the anonymous Internet
user account (which, by default, is IUSR_MACHINE).
3. IIS authorizes the caller to access the requested resource. NTFS permissions
defined by ACLs attached to the requested resource are used to authorize access.
IIS can also be configured to accept requests only from client computers with
specific IP addresses.
4. IIS passes the authenticated caller’s Windows access token to ASP.NET (this may
be the anonymous Internet user’s access token, if anonymous authentication is
being used).
5. ASP.NET authenticates the caller.
If ASP.NET is configured for Windows authentication, no additional authentication
occurs at this point. ASP.NET will accept any token it receives from IIS.
If ASP.NET is configured for Forms authentication, the credentials supplied by
the caller (using an HTML form) are authenticated against a data store; typically
a Microsoft® SQL Server™ database or Active Directory® directory service. If
ASP.NET is configured for Passport authentication, the user is redirected to a
Passport site and the Passport authentication service authenticates the user.
6. ASP.NET authorizes access to the requested resource or operation.
The UrlAuthorizationModule (a system provided HTTP module) uses authorization
rules configured in Web.config (specifically, the <authorization> element)
to ensure that the caller can access the requested file or folder.
With Windows authentication, the FileAuthorizationModule (another HTTP
module) checks that the caller has the necessary permission to access the requested
resource. The caller’s access token is compared against the ACL that
protects the resource.
.NET roles can also be used (either declaratively or programmatically) to ensure
that the caller is authorized to access the requested resource or perform the
requested operation.
Chapter 8: ASP.NET Security 139
7. Code within your application accesses local and/or remote resources by using a
particular identity. By default, ASP.NET performs no impersonation and as a
result, the configured ASP.NET process account provides the identity. Alternate
options include the original caller’s identity (if impersonation is enabled), or a
configured service identity.