个人博客网:https://wushaopei.github.io/ (你想要这里多有)
一、myBatis的注解使用方式
package com.webcode.mapper;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Delete;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.SelectKey;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Update;
import com.webcode.pojo.User;
public interface UserMapper {
@Select("select id,last_name lastName,sex from t_user where id = #{id}")
public User queryUserById(Integer id);
//@Select("select id,last_name lastName,sex from t_user")
public List<User> queryUsers();
@SelectKey(statement = "select last_insert_id()", before = false, keyProperty = "id", resultType = Integer.class)
@Insert(value = "insert into t_user(last_name,sex) values(#{lastName},#{sex})")
public int saveUser(User user);
@Delete("delete from t_user where id = #{id}")
public int deleteUserById(Integer id);
@Update("update t_user set last_name = #{lastName},sex = #{sex} where id = #{id}")
public int updateUser(User user);
}二、mybatis的参数传递
1、一个普通数据类型
Mapper接口的方法:
public interface UserMapper {
public User queryUserById(Integer id);
}mapper.xml配置文件:
<select id="queryUserById" resultType="com.webcode.pojo.User">
select id,last_name lastName,sex from t_user where id = #{id}
</select>2、多个普通数据类型
方法代码:
public List<User> queryUserByNameAndSex(String name, Integer sex);
配置文件:
<select id="queryUserByNameAndSex" resultType="com.webcode.pojo.User">
<!--
多个普通类型的参数,在配置sql语句的时候,
方案一:那么在#{}占位符中,可以写0,1
0表示第一个参数,1表示第二个参数。(不推荐使用)
方案二:那么在#{}占位符中,可以写param1,param2……
param1表示第一参数
param2表示第二个参数
以此类推 第n个参数,就是paramn
-->
select id,last_name lastName,sex from t_user where last_name = #{param1} and sex = #{param2}
</select>2、@Param注解命名参数
方法代码:
public List<User> queryUserByNameAndSex(@Param("name") String name,
@Param("sex") Integer sex);配置信息:
<select id="queryUserByNameAndSex" resultType="com.webcode.pojo.User">
<!--
public List<User> queryUserByNameAndSex(@Param("name") String name,
@Param("sex") Integer sex);
当我们在方法的参数上使用了@Param注解给参数进行全名之后,我们可以在配置的sql语句中的占位符里写中参数的名
-->
select id,last_name lastName,sex from t_user where last_name = #{name} and sex = #{sex}
</select>3、传递一个Map对象作为参数
方法代码:
/**
* Map<String, Object> param,我们希望在Map中放name的值和sex的值,来进行查询
*/
public List<User> queryUserByMap(Map<String, Object> param);
配置信息:
<select id="queryUserByMap" resultType="com.webcode.pojo.User">
<!--
当参数是Map类型的时候,sql语句中的参数名必须和map的key一致
map.put("name",xxx);
map.put("sex",xxx);
-->
select id,last_name lastName,sex from t_user where last_name = #{name} and sex = #{sex}
</select>4、一个JavaBean数据类型
方法代码:
/**
* 我们希望使用user对象的lastName属性和sex属性,来进行查询
*/
public List<User> queryUserByUser(User user);配置信息:
<select id="queryUserByUser" resultType="com.webcode.pojo.User">
<!-- 当传递的参数是javaBean对象的时候,在sql语句的配置的占位符中,使用属性名 -->
select id,last_name lastName,sex from t_user where last_name = #{lastName} and sex = #{sex}
</select>5、多个Pojo数据类型
方法代码:
/**
* 我们希望使用第一个user对象的lastName属性和第二个user对象的sex属性,来进行查询
*/
public List<User> queryUserByUsers(User name,User sex);配置信息:
<select id="queryUserByUsers" resultType="com.webcode.pojo.User">
<!--
如果参数是多个javaBean的时候,
第一个javaBean是param1,第二个javaBean是param2.以此类推。
但我们使用的只是javaBean的属性。#{param1.属性名} 就表示使用第一个javaBean的某个属性的值
-->
select id,last_name lastName,sex from t_user where last_name = #{param1.lastName} and sex = #{param2.sex}
</select>6、模糊查询
需求:现在要根据用户名查询用户对象。 也就是希望查询如下: select * from t_user where last_name like '%张%'
方法代码:
/**
* 需求:现在要根据用户名查询用户对象。 也就是希望查询如下:<br/>
* select * from t_user where last_name like '%张%'
*/
public List<User> queryUsersByNameLike(String lastName);
7、#{}和${}的区别
#{} 是占位符
${} 是做字符串原样输出,然后和配置的sql语句做字符串拼接。

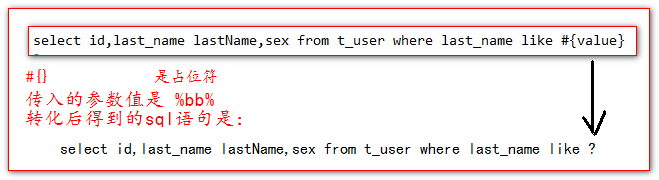
8、MySQL的字符串拼接,concat函数实现。

<select id="queryUsersByNameLike" resultType="com.webcode.pojo.User">
<!--
#{} 是占位符
${} 是字符串原样输出,然后做字符串拼接(有sql注入的风险)
concat 是mysql提供的字符串拼接函数。
-->
select id,last_name lastName,sex from t_user where last_name like concat('%',#{lastName},'%')
</select>二、自定义结果集<resultMap></resultMap>
1、<resultMap>的作用。
ResultMap标签可以给那些查询出来的结果要封装成为的Bean对象。是复杂bean对象的情况。
原来我们查询出来的结果,封装的对象里面的属性都是普通的属性。不包含子的javaBean对象。也不包含Bean对象的集合。那种叫普通的javabean。
那些Bean对象中又包含了子的Bean对象的情况,或者是Bean对象中又包含的bean对象集合的情况,叫复杂的Bean对象。
这种情况,只能使用ResultMap标签来将结果集转换成为复杂的Bean对象。而简单的不需要。简单的Bean对象,只需要使用ResultType属性即可。
2、创建一对一数据库表
## 一对一数据表
## 创建锁表
create table t_lock(
`id` int primary key auto_increment,
`name` varchar(50)
);
## 创建钥匙表
create table t_key(
`id` int primary key auto_increment,
`name` varchar(50),
`lock_id` int ,
foreign key(`lock_id`) references t_lock(`id`)
);
## 插入初始化数据
insert into t_lock(`name`) values('阿里巴巴');
insert into t_lock(`name`) values('华为');
insert into t_lock(`name`) values('联想');
insert into t_key(`name`,`lock_id`) values('马云',1);
insert into t_key(`name`,`lock_id`) values('任正非',2);
insert into t_key(`name`,`lock_id`) values('柳传志',3);3、创建实体对象
public class Lock {
private Integer id;
private String name;
public class Key {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Lock lock;4、一对一级联属性使用
Mapper接口的代码:
public interface KeyMapper {
public Key queryKeyByIdForSample(Integer id);
}KeyMapper配置文件的内容:
<!--
resultMap可以自定义结果集
type属性设置你要封装成为什么类型返回
id属性给resultMap集合集起一个唯一的标识
-->
<resultMap type="com.webcode.pojo.Key" id="queryKeyByIdForSample_resultMap">
<!-- id标签负责把数据库的主键列。转到对象的id属性中
column是列名
property是属性名
把列名的值,注入到property属性指向的属性中
-->
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<!-- 非主键列使用result标签 -->
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<!--
级联映射
一级一级的关联
-->
<result column="lock_id" property="lock.id"/>
<result column="lock_name" property="lock.name"/>
</resultMap>
<!-- public Key queryKeyByIdForSample(Integer id); -->
<select id="queryKeyByIdForSample" resultMap="queryKeyByIdForSample_resultMap">
select
t_key.* ,t_lock.name lock_name
from
t_key left join t_lock
on
t_key.lock_id = t_lock.id
where
t_key.id = #{id}
</select>4.2、<association /> 嵌套结果集映射配置
<resultMap type="com.webcode.pojo.Key" id="queryKeyByIdForSample_association_resultMap">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<!-- 非主键列使用result标签 -->
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<!-- association标签可以把查询的结果映射成为一个子对象
property="lock" 你要映射哪个子对象
javaType 是说明你要映射出来的子对象是什么类型
-->
<association property="lock" javaType="com.webcode.pojo.Lock">
<!-- id给主键进行配置 -->
<id column="lock_id" property="id"/>
<!-- result给非主键列进行配置 -->
<result column="lock_name" property="name"/>
</association>
</resultMap>
<!-- public Key queryKeyByIdForSample(Integer id); -->
<select id="queryKeyByIdForSample" resultMap="queryKeyByIdForSample_association_resultMap">
select
t_key.* ,t_lock.name lock_name
from
t_key left join t_lock
on
t_key.lock_id = t_lock.id
where
t_key.id = #{id}
</select>4.3、<association /> 定义分步(立即)查询
KeyMapper接口:
public interface KeyMapper {
// 分两次查,只查key
public Key queryKeyByIdForTwoStep(Integer id);
}LockMapper接口:
public interface LockMapper {
// 只查锁
public Lock queryLockById(Integer id);
}LockMapper配置信息:
<mapper namespace="com.webcode.mapper.LockMapper">
<!-- public Lock queryLockById(Integer id);
第二次查,只查锁的情况
-->
<select id="queryLockById" resultType="com.webcode.pojo.Lock">
select id,name from t_lock where id = #{id}
</select>
</mapper>KeyMapper的配置信息:
<resultMap type="com.webcode.pojo.Key" id="queryKeyByIdForTwoStep_resultMap">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<!--
association需要配置当前的这个子对象是使用一次查询得到
property="lock" 表示当前要配置哪个子对象
select表示你要使用哪个查询来得到这个子对象(需要一个参数)
column表示你要将原查询结果的哪个列做为参数传递给下一个查询使用。
-->
<association property="lock" column="lock_id"
select="com.webcode.mapper.LockMapper.queryLockById"/>
</resultMap>
<!-- 分两次查,只查key
public Key queryKeyByIdForTwoStep(Integer id); -->
<select id="queryKeyByIdForTwoStep" resultMap="queryKeyByIdForTwoStep_resultMap">
select id,name,lock_id from t_key where id = #{id}
</select>5、延迟加载
延迟加载在一定程序上可以减少很多没有必要的查询。给数据库服务器提升性能上的优化。
要启用延迟加载,需要在mybatis-config.xml配置文件中,添加如下两个全局的settings配置。
<!-- 打开延迟加载的开关 -->
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true" />
<!-- 将积极加载改为消极加载 按需加载 -->
<setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/> 懒加载还需要同时引入两个jar包(注意: 3.2.8版本需要导以下两个包)


5.2、延迟加载的一对一使用示例
<settings>
<!-- 自动开启驼峰命名 -->
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true" />
<!-- 打开延迟加载的开关 -->
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true" />
<!-- 将积极加载改为消极加载 按需加载 -->
<setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false" />
</settings>三、多对一、一对多的使用示例
1、创建一对多数据库
## 一对多数据表
## 创建班级表
create table t_clazz(
`id` int primary key auto_increment,
`name` varchar(50)
);
## 插入班级信息
insert into t_clazz(`name`) values('javaEE20170228');
insert into t_clazz(`name`) values('javaEE20170325');
insert into t_clazz(`name`) values('javaEE20170420');
insert into t_clazz(`name`) values('javaEE20170515');
## 创建学生表
create table t_student(
`id` int primary key auto_increment,
`name` varchar(50),
`clazz_id` int,
foreign key(`clazz_id`) references t_clazz(`id`)
);
## 插入班级信息
insert into t_student(`name`,`clazz_id`) values('stu0228_1',1);
insert into t_student(`name`,`clazz_id`) values('stu0228_2',1);
insert into t_student(`name`,`clazz_id`) values('stu0228_3',1);
insert into t_student(`name`,`clazz_id`) values('stu0325_1',2);
insert into t_student(`name`,`clazz_id`) values('stu0325_2',2);
insert into t_student(`name`,`clazz_id`) values('stu0420_1',3);2、<collection/> 一对多,立即加载
public class Student {
private Integer id;
private String name;public class Clazz {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private List<Student> stus;ClazzMapper接口的代码:
public interface ClazzMapper {
// 一次全部查询出来
public Clazz queryClazzByIdForSimple(Integer id);
}ClazzMapper配置信息:
<resultMap type="com.webcode.pojo.Clazz" id="queryClazzByIdForSimple_resultMap">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<!--
collection标签用来映射子集合=====>>>>private List<Student> stus;
property属性你要映射哪个属性
ofType属性配置集合中每个元素的具体类型
-->
<collection property="stus" ofType="com.webcode.pojo.Student">
<!-- id标签用来配置主键列,可以去重 -->
<id column="stu_id" property="id"/>
<result column="stu_name" property="name"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<!-- public Clazz queryClazzByIdForSimple(Integer id); -->
<select id="queryClazzByIdForSimple" resultMap="queryClazzByIdForSimple_resultMap">
select
t_clazz.*,t_student.id stu_id,t_student.name stu_name,t_student.clazz_id
from
t_clazz left join t_student
on
t_clazz.id = t_student.clazz_id
where
t_clazz.id = #{id}
</select>3、一对多,分步查询赖加载
ClazzMapper接口方法:
public interface ClazzMapper {
// 分两次查,这边只查班级
public Clazz queryClazzByIdForTwoStep(Integer id);
}StudentMapper接口方法:
public interface StudentMapper {
// 只查学生,
public List<Student> queryStudentByClazzId(Integer clazzId);
}StudentMaper的配置内容:
<!-- public List<Student> queryStudentByClazzId(Integer clazzId); -->
<select id="queryStudentByClazzId" resultType="com.webcode.pojo.Student">
select id,name from t_student where clazz_id = #{clazzId}
</select>ClazzMapper的配置内容:
<resultMap type="com.webcode.pojo.Clazz" id="queryClazzByIdForTwoStep_resultMap">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<!--
collection映射子的集合属性
property="stus" 设置当前要配置(封装)哪个集合
select属性配置使用哪个查询得到这个集合
column属性将某个列做为查询语句的参数使用
-->
<collection property="stus" column="id"
select="com.webcode.mapper.StudentMapper.queryStudentByClazzId"/>
</resultMap>
<!-- public Clazz queryClazzByIdForTwoStep(Integer id); -->
<select id="queryClazzByIdForTwoStep" resultMap="queryClazzByIdForTwoStep_resultMap">
select id,name from t_clazz where id = #{id}
</select>4、双向关联
StudentMapper接口
public interface StudentMapper {
// 按班级id查学生。还可以关联查班级
public List<Student> queryStudentsByClazzIdForTwoStep(Integer clazzId);
}StudentMapper的配置:
<resultMap type="com.webcode.pojo.Student" id="queryStudentsByClazzIdForTwoStep_resultMap">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<!--
association用来处理子对象
property属性配置要处理哪个子对象
select属性配置用哪个查询得到这个子对象
column属性将哪个列做为查询的参数使用
-->
<association property="clazz" column="clazz_id"
select="com.webcode.mapper.ClazzMapper.queryClazzByIdForTwoStep"/>
</resultMap>
<!-- public List<Student> queryStudentsByClazzIdForTwoStep(Integer clazzId); -->
<select id="queryStudentsByClazzIdForTwoStep"
resultMap="queryStudentsByClazzIdForTwoStep_resultMap">
select id,name,clazz_id from t_student where clazz_id = #{clazzId}
</select>ClazzMapper的配置信息修改:
<resultMap type="com.webcode.pojo.Clazz" id="queryClazzByIdForTwoStep_resultMap">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<!--
collection映射子的集合属性
property="stus" 设置当前要配置(封装)哪个集合
select属性配置使用哪个查询得到这个集合
column属性将某个列做为查询语句的参数使用
-->
<collection property="stus" column="id"
select="com.webcode.mapper.StudentMapper.queryStudentsByClazzIdForTwoStep"/>
</resultMap>
<!-- public Clazz queryClazzByIdForTwoStep(Integer id); -->
<select id="queryClazzByIdForTwoStep" resultMap="queryClazzByIdForTwoStep_resultMap">
select id,name from t_clazz where id = #{id}
</select>测试:
@Test
public void testQueryClazzByIdForTwoStep() {
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try {
ClazzMapper mapper = session.getMapper(ClazzMapper.class);
Clazz clazz = mapper.queryClazzByIdForTwoStep(1);
session.clearCache();//清缓存,可以看到后面再次关联班级时的查询
System.out.println(clazz.getName());
List<Student> stus = clazz.getStus();
for (Student student : stus) {
session.clearCache();//清缓存,可以看到后面再次关联班级时的查询
System.out.println( "学生姓名:" + student.getName() );
System.out.println( "学生所在班级名称:" + student.getClazz().getName() );
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
session.close();
}
}注意:双向关联常见问题,就是死循环:
解决方法一:不要调用任何一方的toString方法
解决方法二:最后一次的查询使用resultType,而不是使用ResultMap