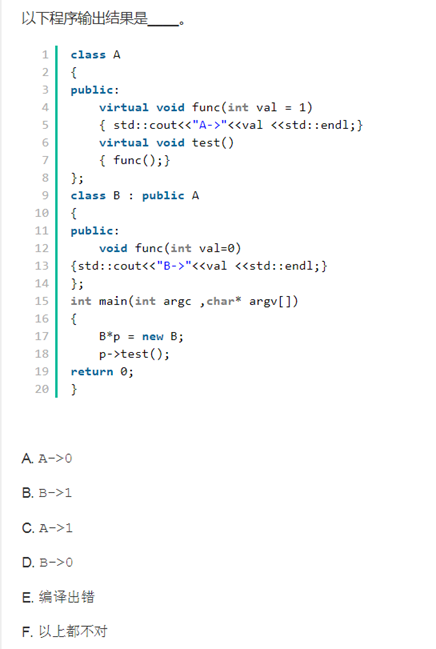
答案选择b
#include<iostream> using namespace std; class Father { public: Father(int a) { this->f = a; cout << "我是父类构造函数 f:" << a<< endl;; } ~Father() { cout << "我是父类析构函数 "; } void print() { cout << "我是父类的函数 f " << f << endl; } public: int f; protected: }; class Child: public Father { public: Child(int b):Father(10) { c = b; cout << "我是子类构造函数c :"<< b<< endl; } ~Child() { cout << "我是子类析构函数 "; } void print() { cout << "我是子类的函数c : "<< c << endl; } public: int c; protected: }; int main() { Father f1(20); //调用父类的构造函数 Child c1(30);//先调用 父类的构造函数 再调用子类的构造函数。 cout << endl; Father *f2; cout << endl; f2 = &c1; f2->print(); //显示调用子类的函数 cout << " 我是漂亮的分割线2----------------------" << endl; system("pause"); }

这里面就涉及静态绑定和动态绑定的过程。