一、MyBatis插件
插件是一种常见的扩展方式,大多数开源框架也都支持用户通过添加自定义插件的方式来扩展或者改变原有的功能,MyBatis中也提供的有插件,虽然叫插件,但是实际上是通过拦截器(Interceptor)实现的,在MyBatis的插件模块中涉及到责任链模式和JDK动态代理。
1. 自定义插件
首先我们来看下一个自定义的插件我们要如何来实现。https://mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/configuration.html#plugins
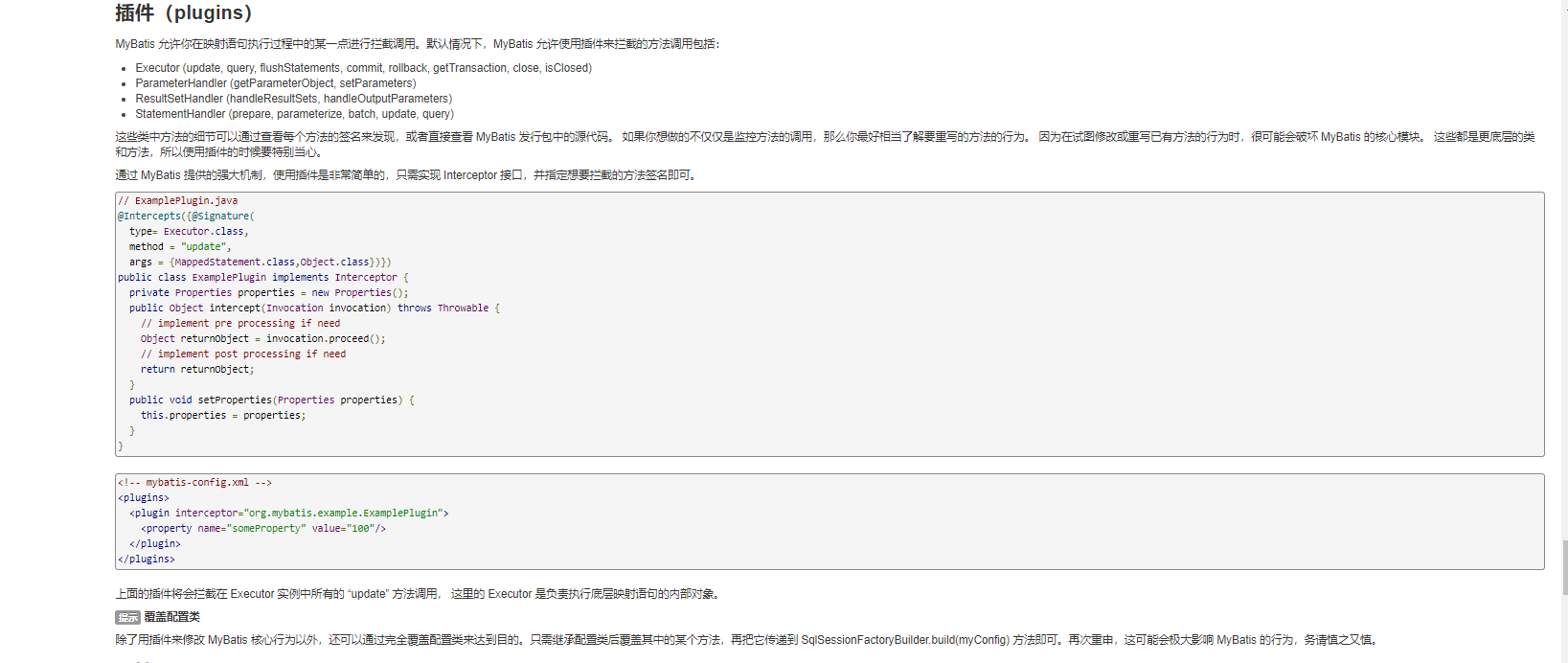
1.1 创建Interceptor实现类
创建的拦截器必须要实现Interceptor接口,Interceptor接口的定义为
public interface Interceptor { // 执行拦截逻辑的方法 111 Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable; // 决定是否触发 intercept()方法 default Object plugin(Object target) { return Plugin.wrap(target, this); } // 根据配置 初始化 Intercept 对象 default void setProperties(Properties properties) { // NOP } }
在MyBatis中Interceptor允许拦截的内容是
- Executor (update, query, flushStatements, commit, rollback, getTransaction, close, isClosed)
- ParameterHandler (getParameterObject, setParameters)
- ResultSetHandler (handleResultSets, handleOutputParameters)
- StatementHandler (prepare, parameterize, batch, update, query)
自己创建一个拦截Executor中的query和close的方法
/** * 自定义的拦截器 * @Signature 注解就可以表示一个方法签名, 唯一确定一个方法 */ @Intercepts({ @Signature( type = Executor.class // 需要拦截的类型 ,method = "query" // 需要拦截的方法 // args 中指定 被拦截方法的 参数列表 ,args={MappedStatement.class,Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class} ), @Signature( type = Executor.class ,method = "close" ,args = {boolean.class} ) }) public class FirstInterceptor implements Interceptor { private int testProp; /** * 执行拦截逻辑的方法 * @param invocation * @return * @throws Throwable */ public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable { System.out.println("FirtInterceptor 拦截之前 ...."); Object obj = invocation.proceed(); System.out.println("FirtInterceptor 拦截之后 ...."); return obj; } /** * 决定是否触发 intercept方法 * @param target * @return */ public Object plugin(Object target) { return Plugin.wrap(target,this); } public void setProperties(Properties properties) { System.out.println("---->"+properties.get("testProp")); } public int getTestProp() { return testProp; } public void setTestProp(int testProp) { this.testProp = testProp; } }
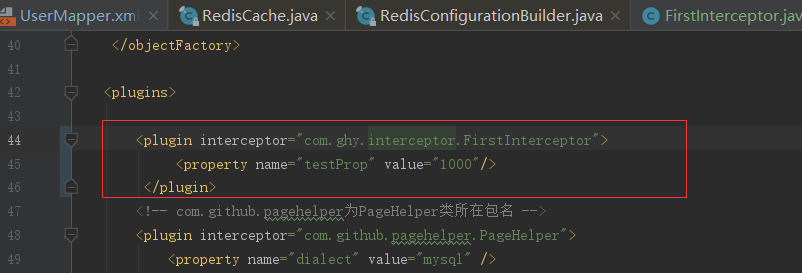
1.2 配置拦截器
创建好自定义的拦截器后,需要在全局配置文件中添加自定义插件的注册
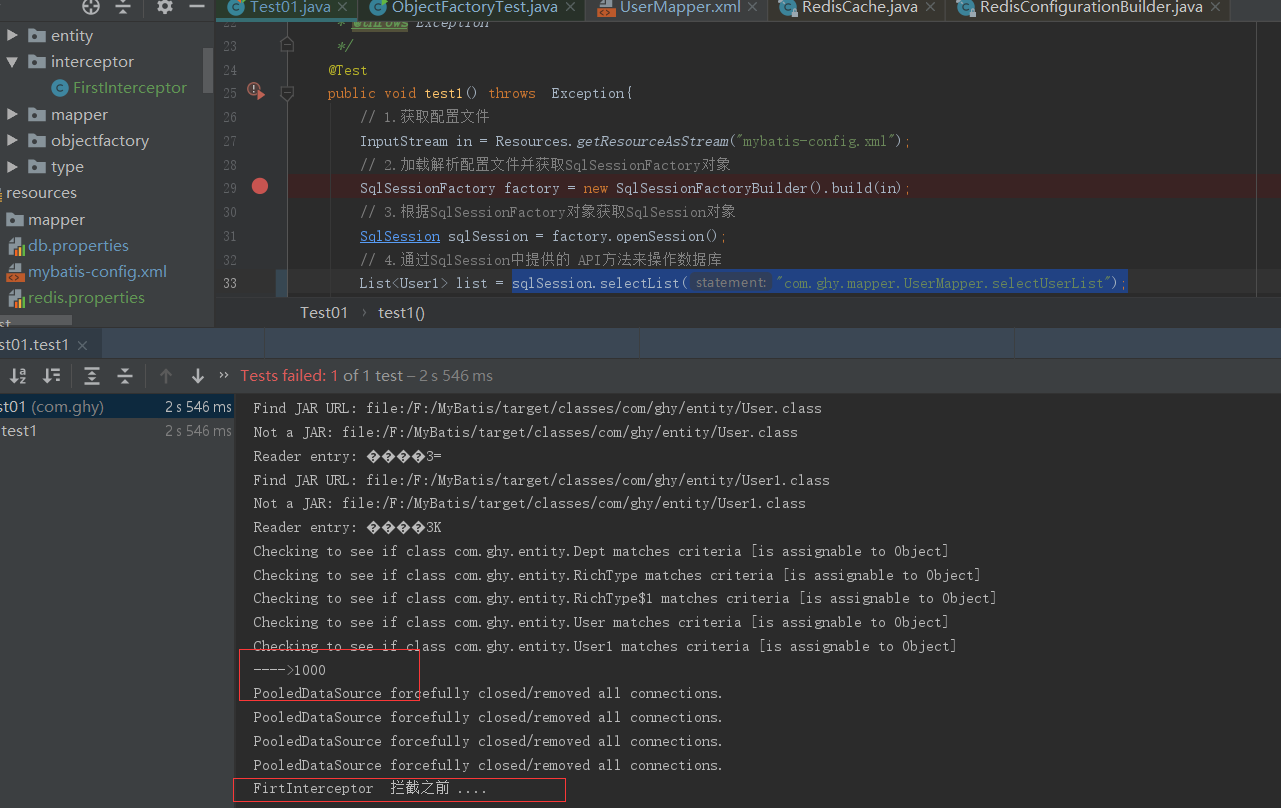
然后执行测试类中代码就 可以看到日志信息
2. 插件实现原理
自定义插件的步骤还是比较简单的,接下来就是分析下插件的实现原理
2.1 初始化操作
首先看下在全局配置文件加载解析的时候做了什么操作。解析配置文件的步骤前面源码跟了好多次就不再看了,直接从SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession();这里开始
@Override public SqlSession openSession() { return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false); }
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) { //事务对象 Transaction tx = null; try { final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment(); // 获取事务工厂 final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment); // 创建事务 tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit); // 根据事务工厂和默认的执行器类型,创建执行器 >>执行SQL语句操作 final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType); return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit); } catch (Exception e) { closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close() throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); } }
还是从他的执行器中找
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) { executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType; executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType; Executor executor; if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) { executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction); } else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {//针对Statement做缓存 executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction); } else { // 默认 SimpleExecutor,每一次只是SQL操作都创建一个新的Statement对象 executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction); } // 二级缓存开关,settings 中的 cacheEnabled 默认是 true if (cacheEnabled) { executor = new CachingExecutor(executor); } // 植入插件的逻辑,至此,四大对象已经全部拦截完毕;这里面是一个拦截器链 executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor); return executor; }
从上面代码可以看到插件的入口
public Object pluginAll(Object target) { for (Interceptor interceptor : interceptors) { // 获取拦截器链中的所有拦截器 target = interceptor.plugin(target); // 创建对应的拦截器的代理对象 } return target; } public void addInterceptor(Interceptor interceptor) { interceptors.add(interceptor); } public List<Interceptor> getInterceptors() { return Collections.unmodifiableList(interceptors); } }
从上面可以看到他是对interceptors进行解析循环,至于这个interceptors是怎么来的那还是得看SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(in);这里面的逻辑
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream) { return build(inputStream, null, null); }
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) { try { // 用于解析 mybatis-config.xml,同时创建了 Configuration 对象 >> XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties); // 解析XML,最终返回一个 DefaultSqlSessionFactory >> return build(parser.parse()); } catch (Exception e) { throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); try { inputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error. } } }
看他的解析步骤
public Configuration parse() { //检查是否已经解析过了 if (parsed) { throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once."); } parsed = true; // XPathParser,dom 和 SAX 都有用到 >> parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration")); return configuration; }
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) { try { //issue #117 read properties first // 对于全局配置文件各种标签的解析 propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties")); // 解析 settings 标签 Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings")); // 读取文件 loadCustomVfs(settings); // 日志设置 loadCustomLogImpl(settings); // 类型别名 typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases")); // 插件 pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins")); // 用于创建对象 objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory")); // 用于对对象进行加工 objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory")); // 反射工具箱 reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory")); // settings 子标签赋值,默认值就是在这里提供的 >> settingsElement(settings); // read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631 // 创建了数据源 >> environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments")); //解析databaseIdProvider标签,生成DatabaseIdProvider对象(用来支持不同厂商的数据库)。 databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider")); typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers")); // 解析引用的Mapper映射器 mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers")); } catch (Exception e) { throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e); } }
可以看到pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));的插件解析操作
private void pluginElement(XNode parent) throws Exception { if (parent != null) { for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) { // 获取<plugin> 节点的 interceptor 属性的值 String interceptor = child.getStringAttribute("interceptor"); // 获取<plugin> 下的所有的properties子节点 Properties properties = child.getChildrenAsProperties(); // 获取 Interceptor 对象 Interceptor interceptorInstance = (Interceptor) resolveClass(interceptor).getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance(); // 设置 interceptor的 属性 interceptorInstance.setProperties(properties); // Configuration中记录 Interceptor configuration.addInterceptor(interceptorInstance); } } }
可以看到对interceptor的解析操作,至于这interceptor的位置就是前面配置的配置
<plugin interceptor="com.ghy.interceptor.FirstInterceptor"> <property name="testProp" value="1000"/> </plugin>
这样一来就明白了自定义的插件是怎么在源码中读取的,pluginElement就是这样通过循环读取到配置信息然后通过反射获取Interceptor对象最后加到configuration中去
public void addInterceptor(Interceptor interceptor) { interceptorChain.addInterceptor(interceptor); }

而他保存的addInterceptor就到了下面的代码中去了
public void addInterceptor(Interceptor interceptor) { interceptors.add(interceptor); }
// 保存所有的 Interceptor 也就我所有的插件是保存在 Interceptors 这个List集合中的 private final List<Interceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<>();
这样一来,整个链路就通了;这个过程其实就是系统启动时把我们自定义的插件配置添加到了集合中去;
2.2 如何创建代理对象
初始化过程看完了接下来就是看代理对象的创建了,在解析的时候创建了对应的Interceptor对象,并保存在了InterceptorChain中,那么这个拦截器是如何和对应的目标对象进行关联的呢?首先拦截器可以拦截的对象是Executor,ParameterHandler,ResultSetHandler,StatementHandler.那么我们来看下这四个对象在创建的时候又什么要注意的
2.2.1 Executor
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) { executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType; executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType; Executor executor; if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) { executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction); } else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {//针对Statement做缓存 executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction); } else { // 默认 SimpleExecutor,每一次只是SQL操作都创建一个新的Statement对象 executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction); } // 二级缓存开关,settings 中的 cacheEnabled 默认是 true if (cacheEnabled) { executor = new CachingExecutor(executor); } // 植入插件的逻辑,至此,四大对象已经全部拦截完毕;这里面是一个拦截器链 executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor); return executor; }
可以看到Executor在装饰完二级缓存后会通过pluginAll来创建Executor的代理对象
public Object pluginAll(Object target) { for (Interceptor interceptor : interceptors) { // 获取拦截器链中的所有拦截器 target = interceptor.plugin(target); // 创建对应的拦截器的代理对象 } return target; }
进入plugin方法中,我们会进入到
// 决定是否触发 intercept()方法 default Object plugin(Object target) { return Plugin.wrap(target, this); }
然后进入到MyBatis给我们提供的Plugin工具类的实现 wrap方法中。
/** * 创建目标对象的代理对象 * 目标对象 Executor ParameterHandler ResultSetHandler StatementHandler * @param target 目标对象 * @param interceptor 拦截器 * @return */ public static Object wrap(Object target, Interceptor interceptor) { // 获取用户自定义 Interceptor中@Signature注解的信息 // getSignatureMap 负责处理@Signature 注解 Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = getSignatureMap(interceptor); // 获取目标类型 Class<?> type = target.getClass(); // 获取目标类型 实现的所有的接口 Class<?>[] interfaces = getAllInterfaces(type, signatureMap); // 如果目标类型有实现的接口 就创建代理对象 if (interfaces.length > 0) { return Proxy.newProxyInstance( type.getClassLoader(), interfaces, new Plugin(target, interceptor, signatureMap)); } // 否则原封不动的返回目标对象 return target; }
Plugin中的各个方法的作用
public class Plugin implements InvocationHandler { private final Object target; // 目标对象 private final Interceptor interceptor; // 拦截器 private final Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap; // 记录 @Signature 注解的信息 private Plugin(Object target, Interceptor interceptor, Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap) { this.target = target; this.interceptor = interceptor; this.signatureMap = signatureMap; } /** * 创建目标对象的代理对象 * 目标对象 Executor ParameterHandler ResultSetHandler StatementHandler * @param target 目标对象 * @param interceptor 拦截器 * @return */ public static Object wrap(Object target, Interceptor interceptor) { // 获取用户自定义 Interceptor中@Signature注解的信息 // getSignatureMap 负责处理@Signature 注解 Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = getSignatureMap(interceptor); // 获取目标类型 Class<?> type = target.getClass(); // 获取目标类型 实现的所有的接口 Class<?>[] interfaces = getAllInterfaces(type, signatureMap); // 如果目标类型有实现的接口 就创建代理对象 if (interfaces.length > 0) { return Proxy.newProxyInstance( type.getClassLoader(), interfaces, new Plugin(target, interceptor, signatureMap)); } // 否则原封不动的返回目标对象 return target; } /** * 代理对象方法被调用时执行的代码 * @param proxy * @param method * @param args * @return * @throws Throwable */ @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { try { // 获取当前方法所在类或接口中,可被当前Interceptor拦截的方法 Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.get(method.getDeclaringClass()); if (methods != null && methods.contains(method)) { // 当前调用的方法需要被拦截 执行拦截操作 return interceptor.intercept(new Invocation(target, method, args)); } // 不需要拦截 则调用 目标对象中的方法 return method.invoke(target, args); } catch (Exception e) { throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(e); } } private static Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> getSignatureMap(Interceptor interceptor) { Intercepts interceptsAnnotation = interceptor.getClass().getAnnotation(Intercepts.class); // issue #251 if (interceptsAnnotation == null) { throw new PluginException("No @Intercepts annotation was found in interceptor " + interceptor.getClass().getName()); } Signature[] sigs = interceptsAnnotation.value(); Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = new HashMap<>(); for (Signature sig : sigs) { Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.computeIfAbsent(sig.type(), k -> new HashSet<>()); try { Method method = sig.type().getMethod(sig.method(), sig.args()); methods.add(method); } catch (NoSuchMethodException e) { throw new PluginException("Could not find method on " + sig.type() + " named " + sig.method() + ". Cause: " + e, e); } } return signatureMap; } private static Class<?>[] getAllInterfaces(Class<?> type, Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap) { Set<Class<?>> interfaces = new HashSet<>(); while (type != null) { for (Class<?> c : type.getInterfaces()) { if (signatureMap.containsKey(c)) { interfaces.add(c); } } type = type.getSuperclass(); } return interfaces.toArray(new Class<?>[interfaces.size()]); } }
这一段搞通后其实就可以看拦截的逻辑了,也就是执行sqlSession.selectList("com.ghy.mapper.UserMapper.selectUserList");时做了啥
@Override public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement) { return this.selectList(statement, null); }
@Override public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) { try { MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement); // 如果 cacheEnabled = true(默认),Executor会被 CachingExecutor装饰 return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER); } catch (Exception e) { throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); } }
当调用executor.query方法时其实就满足了拦截的条件了,这个对象中的参数完全满足在自定义拦截中定义的参数类型,所以在调用这个方法时就会被拦截调用如下方法
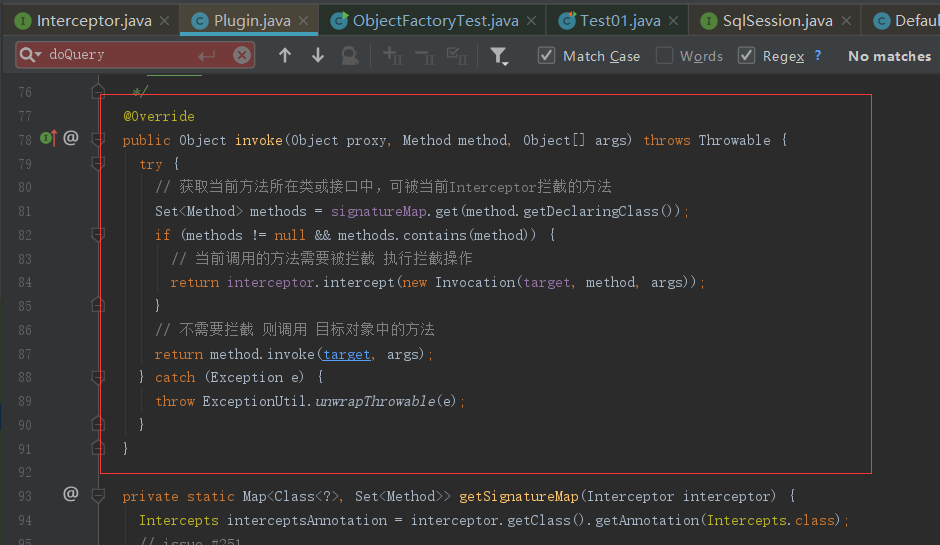
就走进了我们自己写的逻辑中来了
/** * 执行拦截逻辑的方法 * @param invocation * @return * @throws Throwable */ @Override public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable { System.out.println("FirtInterceptor 拦截之前 ...."); Object obj = invocation.proceed(); System.out.println("FirtInterceptor 拦截之后 ...."); return obj; }
2.2.2 StatementHandler

在定义搞明白后,接下来要搞的就是官网上说的另外三个插件的植入在哪;回退到
@Override public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) { try { MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement); // 如果 cacheEnabled = true(默认),Executor会被 CachingExecutor装饰 return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER); } catch (Exception e) { throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); } }
@Override public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException { BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter); // 一级缓存和二级缓存的CacheKey是同一个 CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql); return query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); }
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") @Override public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { // 异常体系之 ErrorContext ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId()); if (closed) { throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed."); } if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) { // flushCache="true"时,即使是查询,也清空一级缓存 clearLocalCache(); } List<E> list; try { // 防止递归查询重复处理缓存 queryStack++; // 查询一级缓存 // ResultHandler 和 ResultSetHandler的区别 list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null; if (list != null) { //缓存中有数据 handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql); } else { // 真正的查询流程 list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); } } finally { queryStack--; } if (queryStack == 0) { for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) { deferredLoad.load(); } // issue #601 deferredLoads.clear(); if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) { // issue #482 clearLocalCache(); } } return list; }
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { List<E> list; // 先占位 localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER); try { // 三种 Executor 的区别,看doUpdate // 默认Simple list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); } finally { // 移除占位符 localCache.removeObject(key); } // 写入一级缓存 localCache.putObject(key, list); if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) { localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter); } return list; }
进入数据库查询
@Override public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { Statement stmt = null; try { Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration(); // 注意,已经来到SQL处理的关键对象 StatementHandler >> StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); // 获取一个 Statement对象 stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog()); // 执行查询 return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler); } finally { // 用完就关闭 closeStatement(stmt); } }
在进入newStatementHandler方法
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) { StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); // 植入插件逻辑(返回代理对象) statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler); return statementHandler; }
可以看到statementHandler的代理对象
2.2.3 ParameterHandler
这个在上面步骤的RoutingStatementHandler方法中
public RoutingStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) { // StatementType 是怎么来的? 增删改查标签中的 statementType="PREPARED",默认值 PREPARED switch (ms.getStatementType()) { case STATEMENT: delegate = new SimpleStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); break; case PREPARED: // 创建 StatementHandler 的时候做了什么? >> delegate = new PreparedStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); break; case CALLABLE: delegate = new CallableStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); break; default: throw new ExecutorException("Unknown statement type: " + ms.getStatementType()); } }
然后随便选择一个分支进入,比如PreparedStatementHandler
public class PreparedStatementHandler extends BaseStatementHandler { public PreparedStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) { super(executor, mappedStatement, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); } @Override public int update(Statement statement) throws SQLException { PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement; ps.execute(); int rows = ps.getUpdateCount(); Object parameterObject = boundSql.getParameterObject(); KeyGenerator keyGenerator = mappedStatement.getKeyGenerator(); keyGenerator.processAfter(executor, mappedStatement, ps, parameterObject); return rows; } @Override public void batch(Statement statement) throws SQLException { PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement; ps.addBatch(); } @Override public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException { PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement; // 到了JDBC的流程 ps.execute(); // 处理结果集 return resultSetHandler.handleResultSets(ps); } @Override public <E> Cursor<E> queryCursor(Statement statement) throws SQLException { PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement; ps.execute(); return resultSetHandler.handleCursorResultSets(ps); } @Override protected Statement instantiateStatement(Connection connection) throws SQLException { String sql = boundSql.getSql(); if (mappedStatement.getKeyGenerator() instanceof Jdbc3KeyGenerator) { String[] keyColumnNames = mappedStatement.getKeyColumns(); if (keyColumnNames == null) { return connection.prepareStatement(sql, PreparedStatement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS); } else { // 在执行 prepareStatement 方法的时候会进入进入到ConnectionLogger的invoker方法中 return connection.prepareStatement(sql, keyColumnNames); } } else if (mappedStatement.getResultSetType() == ResultSetType.DEFAULT) { return connection.prepareStatement(sql); } else { return connection.prepareStatement(sql, mappedStatement.getResultSetType().getValue(), ResultSet.CONCUR_READ_ONLY); } } @Override public void parameterize(Statement statement) throws SQLException { parameterHandler.setParameters((PreparedStatement) statement); } }
public abstract class BaseStatementHandler implements StatementHandler { protected final Configuration configuration; protected final ObjectFactory objectFactory; protected final TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry; protected final ResultSetHandler resultSetHandler; protected final ParameterHandler parameterHandler; protected final Executor executor; protected final MappedStatement mappedStatement; protected final RowBounds rowBounds; protected BoundSql boundSql; protected BaseStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) { this.configuration = mappedStatement.getConfiguration(); this.executor = executor; this.mappedStatement = mappedStatement; this.rowBounds = rowBounds; this.typeHandlerRegistry = configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry(); this.objectFactory = configuration.getObjectFactory(); if (boundSql == null) { // issue #435, get the key before calculating the statement generateKeys(parameterObject); boundSql = mappedStatement.getBoundSql(parameterObject); } this.boundSql = boundSql; // 创建了四大对象的其它两大对象 >> // 创建这两大对象的时候分别做了什么? this.parameterHandler = configuration.newParameterHandler(mappedStatement, parameterObject, boundSql); this.resultSetHandler = configuration.newResultSetHandler(executor, mappedStatement, rowBounds, parameterHandler, resultHandler, boundSql); } @Override public BoundSql getBoundSql() { return boundSql; } @Override public ParameterHandler getParameterHandler() { return parameterHandler; } @Override public Statement prepare(Connection connection, Integer transactionTimeout) throws SQLException { ErrorContext.instance().sql(boundSql.getSql()); Statement statement = null; try { statement = instantiateStatement(connection); setStatementTimeout(statement, transactionTimeout); setFetchSize(statement); return statement; } catch (SQLException e) { closeStatement(statement); throw e; } catch (Exception e) { closeStatement(statement); throw new ExecutorException("Error preparing statement. Cause: " + e, e); } } protected abstract Statement instantiateStatement(Connection connection) throws SQLException; protected void setStatementTimeout(Statement stmt, Integer transactionTimeout) throws SQLException { Integer queryTimeout = null; if (mappedStatement.getTimeout() != null) { queryTimeout = mappedStatement.getTimeout(); } else if (configuration.getDefaultStatementTimeout() != null) { queryTimeout = configuration.getDefaultStatementTimeout(); } if (queryTimeout != null) { stmt.setQueryTimeout(queryTimeout); } StatementUtil.applyTransactionTimeout(stmt, queryTimeout, transactionTimeout); } protected void setFetchSize(Statement stmt) throws SQLException { Integer fetchSize = mappedStatement.getFetchSize(); if (fetchSize != null) { stmt.setFetchSize(fetchSize); return; } Integer defaultFetchSize = configuration.getDefaultFetchSize(); if (defaultFetchSize != null) { stmt.setFetchSize(defaultFetchSize); } } protected void closeStatement(Statement statement) { try { if (statement != null) { statement.close(); } } catch (SQLException e) { //ignore } } protected void generateKeys(Object parameter) { KeyGenerator keyGenerator = mappedStatement.getKeyGenerator(); ErrorContext.instance().store(); keyGenerator.processBefore(executor, mappedStatement, null, parameter); ErrorContext.instance().recall(); }
在newParameterHandler的步骤可以发现代理对象的创建
public ParameterHandler newParameterHandler(MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, BoundSql boundSql) { ParameterHandler parameterHandler = mappedStatement.getLang().createParameterHandler(mappedStatement, parameterObject, boundSql); // 植入插件逻辑(返回代理对象) parameterHandler = (ParameterHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(parameterHandler); return parameterHandler; }
2.2.4 ResultSetHandler
在上面的newResultSetHandler()方法中,也可以看到ResultSetHander的代理对象
public ResultSetHandler newResultSetHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, RowBounds rowBounds, ParameterHandler parameterHandler, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) { ResultSetHandler resultSetHandler = new DefaultResultSetHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterHandler, resultHandler, boundSql, rowBounds); // 植入插件逻辑(返回代理对象) resultSetHandler = (ResultSetHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(resultSetHandler); return resultSetHandler; }
2.3 多拦截器
如果我们有多个自定义的拦截器,那么他的执行流程是怎么样的呢?比如我们创建了两个Interceptor 都是用来拦截 Executor 的query方法,一个是用来执行逻辑A 一个是用来执行逻辑B的
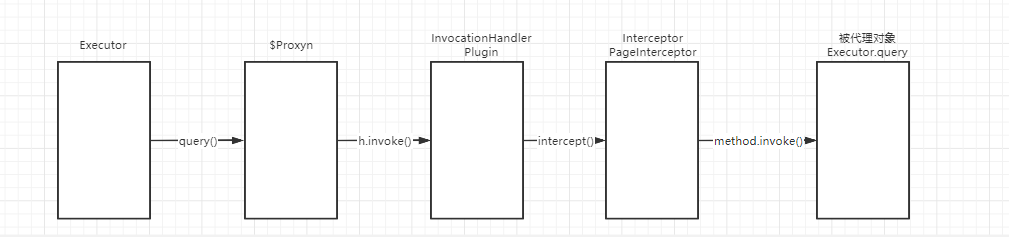
如果说对象被代理了多次,这里会继续调用下一个插件的逻辑,再走一次Plugin的invoke()方法。这里需要关注一下有多个插件的时候的运行顺序。配置的顺序和执行的顺序是相反的。InterceptorChain的List是按照插件从上往下的顺序解析、添加的。而创建代理的时候也是按照list的顺序代理。执行的时候当然是从最后代理的对象开始。
| 对象 | 作用 |
| Interceptor | 自定义插件需要实现接口,实现4个方法 |
| InterceptChain | 配置的插件解析后会保存在Configuration的InterceptChain中 |
| Plugin | 触发管理类,还可以用来创建代理对象 |
| Invocation | 对被代理类进行包装,可以调用proceed()调用到被拦截的方法 |
3. PageHelper分析
Mybatis的插件使用中分页插件PageHelper应该是我们使用到的比较多的插件应用。先来看下PageHelper的应用
3.1 PageHelper的应用
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.pagehelper</groupId>
<artifactId>pagehelper</artifactId>
<version>4.1.6</version>
</dependency>
在全局配置文件中注册
<plugin interceptor="com.github.pagehelper.PageHelper"> <property name="dialect" value="mysql" /> <!-- 该参数默认为false --> <!-- 设置为true时,会将RowBounds第一个参数offset当成pageNum页码使用 --> <!-- 和startPage中的pageNum效果一样 --> <property name="offsetAsPageNum" value="true" /> <!-- 该参数默认为false --> <!-- 设置为true时,使用RowBounds分页会进行count查询 --> <property name="rowBoundsWithCount" value="true" /> <!-- 设置为true时,如果pageSize=0或者RowBounds.limit = 0就会查询出全部的结果 --> <!-- (相当于没有执行分页查询,但是返回结果仍然是Page类型) --> <property name="pageSizeZero" value="true" /> <!-- 3.3.0版本可用 - 分页参数合理化,默认false禁用 --> <!-- 启用合理化时,如果pageNum<1会查询第一页,如果pageNum>pages会查询最后一页 --> <!-- 禁用合理化时,如果pageNum<1或pageNum>pages会返回空数据 --> <property name="reasonable" value="false" /> <!-- 3.5.0版本可用 - 为了支持startPage(Object params)方法 --> <!-- 增加了一个`params`参数来配置参数映射,用于从Map或ServletRequest中取值 --> <!-- 可以配置pageNum,pageSize,count,pageSizeZero,reasonable,不配置映射的用默认值 --> <!-- 不理解该含义的前提下,不要随便复制该配置 --> <property name="params" value="pageNum=start;pageSize=limit;" /> <!-- always总是返回PageInfo类型,check检查返回类型是否为PageInfo,none返回Page --> <property name="returnPageInfo" value="check" /> </plugin>
然后就是分页查询操作

通过MyBatis的分页插件的使用,在执行操作之前设置了一句PageHelper.startPage(1,5); 并没有做其他操作,也就是没有改变任何其他的业务代码。这就是它的优点,那么再来看下他的实现原理
3.2 实现原理剖析
在PageHelper中,肯定有提供Interceptor的实现类,通过源码可以发现是PageHelper,而且我们也可以看到在该方法头部添加的注解,声明了该拦截器拦截的是Executor的query方法
然后当我们要执行查询操作的时候,我们知道 Executor.query() 方法的执行本质上是执行 Executor的代理对象的方法,前面有说过。先来看下Plugin中的invoke方法
@Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { try { // 获取当前方法所在类或接口中,可被当前Interceptor拦截的方法 Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.get(method.getDeclaringClass()); if (methods != null && methods.contains(method)) { // 当前调用的方法需要被拦截 执行拦截操作 return interceptor.intercept(new Invocation(target, method, args)); } // 不需要拦截 则调用 目标对象中的方法 return method.invoke(target, args); } catch (Exception e) { throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(e); } }
interceptor.intercept(new Invocation(target, method, args));方法的执行会进入到 PageHelper的intercept方法中
/** * Mybatis拦截器方法 * * @param invocation 拦截器入参 * @return 返回执行结果 * @throws Throwable 抛出异常 */ public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable { if (autoRuntimeDialect) { SqlUtil sqlUtil = getSqlUtil(invocation); return sqlUtil.processPage(invocation); } else { if (autoDialect) { initSqlUtil(invocation); } return sqlUtil.processPage(invocation); } }
在interceptor方法中首先会获取一个SqlUtils对象;SqlUtil:数据库类型专用sql工具类,一个数据库url对应一个SqlUtil实例,SqlUtil内有一个Pars对象,如果是mysql,它是MysqlParser,如果是oracle,它是OracleParser,这个Parser对象是SqlUtil不同实例的主要存在价值。执行count查询、设置Parser对象、执行分页查询、保存Page分页对象等功能,均由SqlUtil来完成。
/** * 初始化sqlUtil * * @param invocation */ public synchronized void initSqlUtil(Invocation invocation) { if (this.sqlUtil == null) { this.sqlUtil = getSqlUtil(invocation); if (!autoRuntimeDialect) { properties = null; sqlUtilConfig = null; } autoDialect = false; } }
/** * 根据datasource创建对应的sqlUtil * * @param invocation */ public SqlUtil getSqlUtil(Invocation invocation) { MappedStatement ms = (MappedStatement) invocation.getArgs()[0]; //改为对dataSource做缓存 DataSource dataSource = ms.getConfiguration().getEnvironment().getDataSource(); String url = getUrl(dataSource); if (urlSqlUtilMap.containsKey(url)) { return urlSqlUtilMap.get(url); } try { lock.lock(); if (urlSqlUtilMap.containsKey(url)) { return urlSqlUtilMap.get(url); } if (StringUtil.isEmpty(url)) { throw new RuntimeException("无法自动获取jdbcUrl,请在分页插件中配置dialect参数!"); } String dialect = Dialect.fromJdbcUrl(url); if (dialect == null) { throw new RuntimeException("无法自动获取数据库类型,请通过dialect参数指定!"); } SqlUtil sqlUtil = new SqlUtil(dialect); if (this.properties != null) { sqlUtil.setProperties(properties); } else if (this.sqlUtilConfig != null) { sqlUtil.setSqlUtilConfig(this.sqlUtilConfig); } urlSqlUtilMap.put(url, sqlUtil); return sqlUtil; } finally { lock.unlock(); } }
/** * 构造方法 * * @param strDialect */ public SqlUtil(String strDialect) { if (strDialect == null || "".equals(strDialect)) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Mybatis分页插件无法获取dialect参数!"); } Exception exception = null; try { Dialect dialect = Dialect.of(strDialect); parser = AbstractParser.newParser(dialect); } catch (Exception e) { exception = e; //异常的时候尝试反射,允许自己写实现类传递进来 try { Class<?> parserClass = Class.forName(strDialect); if (Parser.class.isAssignableFrom(parserClass)) { parser = (Parser) parserClass.newInstance(); } } catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) { exception = ex; } catch (InstantiationException ex) { exception = ex; } catch (IllegalAccessException ex) { exception = ex; } } if (parser == null) { throw new RuntimeException(exception); } }
public static Parser newParser(Dialect dialect) { Parser parser = null; switch (dialect) { case mysql: case mariadb: case sqlite: parser = new MysqlParser(); break; case oracle: parser = new OracleParser(); break; case hsqldb: parser = new HsqldbParser(); break; case sqlserver: parser = new SqlServerParser(); break; case sqlserver2012: parser = new SqlServer2012Dialect(); break; case db2: parser = new Db2Parser(); break; case postgresql: parser = new PostgreSQLParser(); break; case informix: parser = new InformixParser(); break; case h2: parser = new H2Parser(); break; default: throw new RuntimeException("分页插件" + dialect + "方言错误!"); } return parser; }
我们可以看到不同的数据库方言,创建了对应的解析器。然后再回到前面的interceptor方法中继续,查看sqlUtil.processPage(invocation);方法
/** * Mybatis拦截器方法,这一步嵌套为了在出现异常时也可以清空Threadlocal * * @param invocation 拦截器入参 * @return 返回执行结果 * @throws Throwable 抛出异常 */ public Object processPage(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable { try { Object result = _processPage(invocation); return result; } finally { clearLocalPage(); } }
/** * Mybatis拦截器方法 * * @param invocation 拦截器入参 * @return 返回执行结果 * @throws Throwable 抛出异常 */ private Object _processPage(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable { final Object[] args = invocation.getArgs(); Page page = null; //支持方法参数时,会先尝试获取Page if (supportMethodsArguments) { page = getPage(args); } //分页信息 RowBounds rowBounds = (RowBounds) args[2]; //支持方法参数时,如果page == null就说明没有分页条件,不需要分页查询 if ((supportMethodsArguments && page == null) //当不支持分页参数时,判断LocalPage和RowBounds判断是否需要分页 || (!supportMethodsArguments && SqlUtil.getLocalPage() == null && rowBounds == RowBounds.DEFAULT)) { return invocation.proceed(); } else { //不支持分页参数时,page==null,这里需要获取 if (!supportMethodsArguments && page == null) { page = getPage(args); } return doProcessPage(invocation, page, args); } }
/** * Mybatis拦截器方法 * * @param invocation 拦截器入参 * @return 返回执行结果 * @throws Throwable 抛出异常 */ private Page doProcessPage(Invocation invocation, Page page, Object[] args) throws Throwable { //保存RowBounds状态 RowBounds rowBounds = (RowBounds) args[2]; //获取原始的ms MappedStatement ms = (MappedStatement) args[0]; //判断并处理为PageSqlSource if (!isPageSqlSource(ms)) { processMappedStatement(ms); } //设置当前的parser,后面每次使用前都会set,ThreadLocal的值不会产生不良影响 ((PageSqlSource)ms.getSqlSource()).setParser(parser); try { //忽略RowBounds-否则会进行Mybatis自带的内存分页 args[2] = RowBounds.DEFAULT; //如果只进行排序 或 pageSizeZero的判断 if (isQueryOnly(page)) { return doQueryOnly(page, invocation); } //简单的通过total的值来判断是否进行count查询 if (page.isCount()) { page.setCountSignal(Boolean.TRUE); //替换MS args[0] = msCountMap.get(ms.getId()); //查询总数 Object result = invocation.proceed(); //还原ms args[0] = ms; //设置总数 page.setTotal((Integer) ((List) result).get(0)); if (page.getTotal() == 0) { return page; } } else { page.setTotal(-1l); } //pageSize>0的时候执行分页查询,pageSize<=0的时候不执行相当于可能只返回了一个count if (page.getPageSize() > 0 && ((rowBounds == RowBounds.DEFAULT && page.getPageNum() > 0) || rowBounds != RowBounds.DEFAULT)) { //将参数中的MappedStatement替换为新的qs page.setCountSignal(null); BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(args[1]); args[1] = parser.setPageParameter(ms, args[1], boundSql, page); page.setCountSignal(Boolean.FALSE); //执行分页查询 Object result = invocation.proceed(); //得到处理结果 page.addAll((List) result); } } finally { ((PageSqlSource)ms.getSqlSource()).removeParser(); } //返回结果 return page; }
invocation.proceed();方法会进入 CachingExecutor中的query方法
@Override public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException { // 获取SQL BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject); // 创建CacheKey:什么样的SQL是同一条SQL? >> CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql); return query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); }
ms.getBoundSql方法中会完成分页SQL的绑定
@Override public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) { Boolean count = getCount(); if (count == null) { return getDefaultBoundSql(parameterObject); } else if (count) { return getCountBoundSql(parameterObject); } else { return getPageBoundSql(parameterObject); } } }
然后进入getPageBoundSql获取分页的SQL语句,在这个方法中也可以发现查询总的记录数的SQL生成;想看可以debugger看一下就明白了
@Override protected BoundSql getPageBoundSql(Object parameterObject) { String tempSql = sql; String orderBy = PageHelper.getOrderBy(); if (orderBy != null) { tempSql = OrderByParser.converToOrderBySql(sql, orderBy); } tempSql = localParser.get().getPageSql(tempSql); return new BoundSql(configuration, tempSql, localParser.get().getPageParameterMapping(configuration, original.getBoundSql(parameterObject)), parameterObject); }
@Override
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
// 如果 cacheEnabled = true(默认),Executor会被 CachingExecutor装饰
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}