前文回顾:
1 插件学习篇
4 SWT编程须知
前面几篇都提到了SWT的布局,布局系统也为规整的UI提供了保障。那么如何设计一个布局呢?
Eclipse的布局机制,提供了两个对象概念,Layout(描述内部布局方式)以及GridData(描述本身布局方式)。
什么是Layout?
首先说一下Layout,layout定义了一个空间内部的布局格式。比如我们把箱子作为一个整体,那么箱子内部该怎么去设计,怎么放置东西进去,就需要用layout来指定。

而常用的布局方式,就包括FillLayout,gridLayout,RowLayout,以及FormLayout。
下面就针对这几种布局进行一下介绍:
Filllayout
也叫做填充布局,它会让里面的子空间以填充的方式进行布局。
比如我们采用如下的设计方式:
FillLayout layout = new FillLayout(); shell.setLayout(layout); for(int i=0;i<10;i++){ Button button = new Button(shell,SWT.PUSH); button.setText("Button"+i); }
正常的布局是这样的:
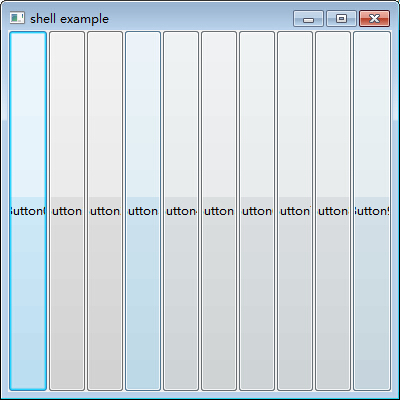
经过拉伸就变成了这样:

RowLayout
也叫行布局,它会让内部的子空间以行为单位进行排列,遇到边界时,自动换成下一行。
RowLayout layout = new RowLayout(); shell.setLayout(layout); for(int i=0;i<10;i++){ Button button = new Button(shell,SWT.PUSH); Image img = new Image(null,"icons\ok.png"); button.setImage(img); button.setText("Button"+i); }
得到的结果是这样的:

当压缩边界的时候,会自动换行

GridLayout
也叫做网格布局,它以规定网格的形式,指定每一行有多少列,元素会以每列几个的方式进行排列,超出的部分挤到下一行。
GridLayout layout = new GridLayout(); layout.numColumns = 3; shell.setLayout(layout); for(int i=0;i<10;i++){ Button button = new Button(shell,SWT.PUSH); Image img = new Image(null,"icons\ok.png"); button.setImage(img); button.setText("Button"+i); }
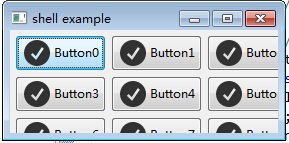
当指定每行有3个子控件时,无论怎么改变窗口的大小,都不会改变排列的方式

当改变窗口大小时,不会发生变化
FormLayout
感觉这个是最难使用的了,它会以一个Form表单的形式提供布局。先看一下使用方式吧:
FormLayout layout = new FormLayout(); shell.setLayout(layout); Button cancelButton = new Button(shell,SWT.PUSH); cancelButton.setText("Cancel"); FormData formData1 = new FormData(); formData1.right = new FormAttachment(100,-5); //第一个数字式百分比,也就是说 【宽度-5】 formData1.bottom = new FormAttachment(100,-5); //第一个数字式百分比,也就是说 【高度-5】 cancelButton.setLayoutData(formData1); Button okButton = new Button(shell,SWT.PUSH); okButton.setText("OK"); FormData formData2 = new FormData(); formData2.right = new FormAttachment(100,-60); formData2.bottom = new FormAttachment(100,-5); okButton.setLayoutData(formData2); Text text = new Text(shell,SWT.MULTI | SWT.BORDER | SWT.V_SCROLL | SWT.H_SCROLL); FormData formData3 = new FormData(); formData3.top = new FormAttachment(0,5); formData3.bottom = new FormAttachment(cancelButton,-5);//底部距离 【底部控件-5个像素】 formData3.left = new FormAttachment(0,5); formData3.right = new FormAttachment(100,-5); text.setLayoutData(formData3); Color color = new Color(null,255,0,0); text.setForeground(color);
可以看到他提供了一个FormData的布局方式,通过FormAttachment实现,这个类需要两个参数,第一个是宽度(left或者right)或者高度(top或者bottom)的百分比,第二个参数是它相对加上的值。如果是负数,就是减去的像素值。而且提供Control类型的参数,也就是控件类型的参数。如果第一个参数指定一个控件,比如上面指定的那个bottom,那么他会自动获取这个控件对应的高度,在进行加减。
这样就保证了,某些控件的相对位置保持不变。
下面看一下效果:

拉伸后编程

什么是GridData呢?又该如何使用呢?
下面介绍一下GridData,这个也是一个重量级的参数:
这个参数用于指定目标如何摆放,它描述了以表格为单位的布局。
它描述了空间本身的一个布局摆放的方式:

并且搭配之前的GridLayout布局,通过每行有几列的方式,控制布局。先看一下都有什么参数,以及参数描述的意义:
GridData griddata = new GridData(SWT.FILL,SWT.FILL,false,false,1,1); 一般都是上面这样的参数格式: 第一个参数:水平方向如何对齐 第二个参数:竖直方向如何对齐 第三个参数:是否占用水平的剩余空间 第四个参数:是否占用竖直的剩余空间 第五个参数:水平的列数 第六个参数:竖直的行数
这样一来,举个例子就简单了。
比如我们指定了一个表格是三行三列的,那么通过设定
第一个控件参数是(SWT.FILL,SWT.FILL,false,false,1,1); 第二个参数是(SWT,SWT,false,false,1,2); 第三个参数是(SWT.FILL_BOTH); 第四个得到如下的布局:(SWT.FILL,SWT.FILL,false,false,1,1);
这样我们得到如下的布局:

感觉上面的图顿时拉低了文章的档次,凑合看吧。可以看到第二个控件,通过指定真的占用了两列。
但是第三个的FILL_BOTH并没有按照预期占用了剩余的所有控件,这就说明,填充布局还是不会垮行到下一列的布局的。
另外添加两个小知识,就是使用颜色以及图片。
颜色通常使用RGB来指定:
Color color = new Color(null,255,0,0); text.setForeground(color);
颜色的第一参数是Device,可以填写为null;
而图片也图普通的控件一样,需要指定一个ImgData来指定图片的URL即可:
Image img = new Image(null,"icons\ok.png"); button.setImage(img);
下面是这个例子所用到的代码:

package com.xingoo.plugin.swttest.test; import org.eclipse.swt.SWT; import org.eclipse.swt.graphics.Color; import org.eclipse.swt.graphics.Image; import org.eclipse.swt.layout.FillLayout; import org.eclipse.swt.layout.FormAttachment; import org.eclipse.swt.layout.FormData; import org.eclipse.swt.layout.FormLayout; import org.eclipse.swt.layout.GridData; import org.eclipse.swt.layout.GridLayout; import org.eclipse.swt.layout.RowLayout; import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Button; import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Shell; import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Text; import com.xingoo.plugin.swttest.Abstract.AbstractExample; public class LayoutTest extends AbstractExample{ public static void main(String[] args) { new LayoutTest().run(); } public void todo(Shell shell) { ////////////////////////////////////////////////////// //FillLayout ////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // FillLayout layout = new FillLayout(); // shell.setLayout(layout); // for(int i=0;i<10;i++){ // Button button = new Button(shell,SWT.PUSH); // button.setText("Button"+i); // //// Image img = new Image(null,"icons\ok.png"); //// button.setImage(img); // } ////////////////////////////////////////////////////// //RowLayout ////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // RowLayout layout = new RowLayout(); // shell.setLayout(layout); // for(int i=0;i<10;i++){ // Button button = new Button(shell,SWT.PUSH); // Image img = new Image(null,"icons\ok.png"); // button.setImage(img); // button.setText("Button"+i); // } ////////////////////////////////////////////////////// //GridLayout ////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // GridLayout layout = new GridLayout(); // layout.numColumns = 3; // shell.setLayout(layout); // for(int i=0;i<10;i++){ // Button button = new Button(shell,SWT.PUSH); // Image img = new Image(null,"icons\ok.png"); // button.setImage(img); // button.setText("Button"+i); // } GridLayout layout = new GridLayout(); layout.numColumns = 3; shell.setLayout(layout); Button btn1 = new Button(shell,SWT.PUSH); GridData gd1 = new GridData(SWT.FILL,SWT.FILL,false,false,1,1); gd1.widthHint = 100; gd1.heightHint = 100; btn1.setLayoutData(gd1); Button btn2 = new Button(shell,SWT.PUSH); GridData gd2 = new GridData(SWT.FILL,SWT.FILL,false,false,1,2); gd2.widthHint = 100; gd2.heightHint = 100; btn2.setLayoutData(gd2); Button btn3 = new Button(shell,SWT.PUSH); GridData gd3 = new GridData(GridData.FILL_BOTH); // gd3.widthHint = 100; // gd3.heightHint = 100; btn3.setLayoutData(gd3); Button btn4 = new Button(shell,SWT.PUSH); GridData gd4 = new GridData(SWT.FILL,SWT.FILL,false,false,1,1); gd4.widthHint = 100; gd4.heightHint = 100; btn4.setLayoutData(gd4); ////////////////////////////////////////////////////// //FormLayout ////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // FormLayout layout = new FormLayout(); // shell.setLayout(layout); // // Button cancelButton = new Button(shell,SWT.PUSH); // cancelButton.setText("Cancel"); // FormData formData1 = new FormData(); // formData1.right = new FormAttachment(100,-5); //第一个数字式百分比,也就是说 【宽度-5】 // formData1.bottom = new FormAttachment(100,-5); //第一个数字式百分比,也就是说 【高度-5】 // cancelButton.setLayoutData(formData1); // // Button okButton = new Button(shell,SWT.PUSH); // okButton.setText("OK"); // FormData formData2 = new FormData(); // formData2.right = new FormAttachment(100,-60); // formData2.bottom = new FormAttachment(100,-5); // okButton.setLayoutData(formData2); // // Text text = new Text(shell,SWT.MULTI | SWT.BORDER | SWT.V_SCROLL | SWT.H_SCROLL); // FormData formData3 = new FormData(); // formData3.top = new FormAttachment(0,5); // formData3.bottom = new FormAttachment(cancelButton,-5);//底部距离 【底部控件-5个像素】 // formData3.left = new FormAttachment(0,5); // formData3.right = new FormAttachment(100,-5); // text.setLayoutData(formData3); // Color color = new Color(null,255,0,0); // text.setForeground(color); } }
当然,最好是参考前几篇例子,可以真正体会到布局的妙处!
