共有7897张图像,其中训练集5897张,测试集2000张图像,每幅图像的大小为32*32*3
数据集:
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1hnBhDg6XJW7m_bmqA-tNXw
提取码:appn
# 导入依赖包 import sys import numpy as np # import lr_utils import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import paddle import paddle.fluid as fluid %matplotlib inline
# 加载数据, 并展示一张,由于数据图片较小,所以显示出来比较模糊 train_set_x_orig=np.load("/home/aistudio/data/data1589/traindata.npy") train_set_y=np.load("/home/aistudio/data/data1589/trainlabel.npy") test_set_x_orig=np.load("/home/aistudio/data/data1589/testdata.npy") test_set_y=np.load("/home/aistudio/data/data1589/testlabel.npy") plt.imshow(train_set_x_orig[2]) plt.show()
# 输出数据集的信息 m_train=train_set_x_orig.shape[0] m_test=test_set_x_orig.shape[0] num_px=train_set_x_orig.shape[1] print ("训练样本数: m_train = " + str(m_train)) print ("测试样本数: m_test = " + str(m_test)) print ("图片高度/宽度: num_px = " + str(num_px)) print ("图片大小: (" + str(num_px) + ", " + str(num_px) + ", 3)") print ("train_set_x shape: " + str(train_set_x_orig.shape)) print ("train_set_y shape: " + str(train_set_y.shape)) print ("test_set_x shape: " + str(test_set_x_orig.shape)) print ("test_set_y shape: " + str(test_set_y.shape))
训练样本数: m_train = 5897 测试样本数: m_test = 2000 图片高度/宽度: num_px = 32 图片大小: (32, 32, 3) train_set_x shape: (5897, 32, 32, 3) train_set_y shape: (5897, 1) test_set_x shape: (2000, 32, 32, 3) test_set_y shape: (2000, 1)
###因为paddlepaddle认识的数据是3*l*h的,所以需要进行数据格式转换 train_set_x = np.array(train_set_x_orig).reshape(m_train, 3, num_px, num_px).astype(np.float32) train_set_y = np.array(train_set_y).reshape(m_train, 1).astype(np.float32) test_set_x = np.array(test_set_x_orig).reshape(m_test, 3, num_px, num_px).astype(np.float32) test_set_y = np.array(test_set_y).reshape(m_test, 1).astype(np.float32)
#归一化 train_set_x=train_set_x/ 255.0 * 2.0 - 1.0 test_set_x=test_set_x/ 255.0 * 2.0 - 1.0
# 读取训练数据或测试数据 def read_data(train_set_x,train_set_y,buffer_size): def reader(): for i in range(buffer_size): yield train_set_x[i,:], int(train_set_y[i]) return reader
def convolutional_neural_network(): """ 定义卷积神经网络分类器: 输入的二维图像,经过两个卷积-池化层,使用以softmax为激活函数的全连接层作为输出层 Args: img -- 输入的原始图像数据 Return: predict -- 分类的结果 """ img = fluid.layers.data( name='img', shape =[3,32,32],dtype = 'float32') #第一个卷积层 # hidden = fluid.nets.simple_img_conv_pool(input, num_filters, filter_size, pool_size, pool_stride, pool_padding=0) hidden=fluid.nets.simple_img_conv_pool( input=img, num_filters=64, filter_size=10, pool_size=5, pool_stride=1, pool_padding=0 ) #第二个卷积层 h2=fluid.nets.simple_img_conv_pool( input=hidden, num_filters=128, filter_size=3, pool_size=2, pool_stride=1, pool_padding=0 ) # predict = fluid.layers.fc(h2,size=1,act='sigmoid') predict = fluid.layers.fc(h2,size=2,act='softmax') #predict=fluid.layers.dropout(x=predict, dropout_prob=0.5) return predict
# 设置训练场所 use_cuda = True place = fluid.CUDAPlace(0) if use_cuda else fluid.CPUPlace()
#配置网络结构 def train_func(): label = fluid.layers.data(name='label', shape = [1],dtype = 'int64') #predict = convolutional_neural_network() predict=convolutional_neural_network() # 损失函数,cross_entropy 函数内部使用交叉熵损失函数 cost = fluid.layers.cross_entropy(input=predict, label=label) avg_cost = fluid.layers.mean(cost) return avg_cost
def optimizer_func(): # 创建Momentum优化器,并设置学习率(learning_rate)、动量(momentum) optimizer=fluid.optimizer.Momentum(learning_rate=0.001,momentum=0.5) #使用Adam算法进行优化, learning_rate 是学习率(它的大小与网络的训练收敛速度有关系) #optimizer = fluid.optimizer.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=0.001) return optimizer
feed_order = ['img', 'label'] #数据格式 params_dirname = "./DNN_model" #模型保存路径
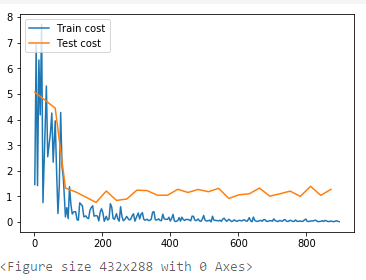
# 事件处理函数 from paddle.utils.plot import Ploter from paddle.fluid.contrib.trainer import EndStepEvent train_title = "Train cost" test_title = "Test cost" plot_cost = Ploter(train_title, test_title) step = 0 def event_handler_plot(event): global step if isinstance(event, EndStepEvent): if event.step % 2 == 0: # 若干个batch,记录cost if event.metrics[0] < 10: plot_cost.append(train_title, step, event.metrics[0]) plot_cost.plot() if event.step % 20 == 0: # 若干个batch,记录cost test_metrics = trainer.test( reader=test_reader, feed_order=feed_order) if test_metrics[0] < 10: plot_cost.append(test_title, step, test_metrics[0]) plot_cost.plot() # if test_metrics[0] < 1.0: # # 如果准确率达到阈值,则停止训练 # print('loss is less than 10.0, stop') # trainer.stop() # 将参数存储,用于预测使用 if params_dirname is not None: trainer.save_params(params_dirname ) step += 1
#训练所用到的具体数据 BATCH_SIZE=16 # 设置训练reader train_reader = paddle.batch( paddle.reader.shuffle( read_data(train_set_x,train_set_y,buffer_size=209), buf_size=50), batch_size=BATCH_SIZE) # 设置测试reader test_reader = paddle.batch( paddle.reader.shuffle( read_data(test_set_x,test_set_y,buffer_size=50), buf_size=20), batch_size=BATCH_SIZE)
#创建训练器 from paddle.fluid.contrib.trainer import Trainer trainer= Trainer( train_func= train_func, place= place, optimizer_func= optimizer_func )
#开始训练 trainer.train( reader=train_reader, num_epochs=30, event_handler=event_handler_plot, feed_order= feed_order )
from paddle.fluid.contrib.inferencer import Inferencer inferencer = Inferencer( infer_func=convolutional_neural_network, param_path=params_dirname, place=place)
#取出一个 mini-batch for mini_batch in test_reader(): # 转化为 numpy 的 ndarray 结构,并且设置数据类型 test_x = np.array([data[0] for data in mini_batch]).astype("float32") test_y = np.array([data[1] for data in mini_batch]).astype("int64") # 真实进行预测 mini_batch_result = inferencer.infer({'img': test_x}) result=(mini_batch_result[0][:,-1]>0.5)+0 #True or False 转0/1,直接后面+0即可 # 打印预测结果 # mini_batch_result = np.argsort(mini_batch_result) #找出可能性最大的列标,升序排列, ###经过分析,这是多分类问题会用到的函数,找出概率值最大的下标 # mini_batch_result = mini_batch_result[0][:, -1] #把这些列标拿出来 print('预测结果:%s'%result) # 打印真实结果 label = np.array(test_y) # 转化为 label print('真实结果:%s'%label) break
# 查看百分比 def right_ratio(right_counter, total): ratio = float(right_counter)/total return ratio
# 评估函数 data_set 是一个reader def evl(data_set): total = 0 #操作的元素的总数 right_counter = 0 #正确的元素 pass_num = 0 # print(liruoyi) for mini_batch in data_set(): pass_num += 1 #预测 test_x = np.array([data[0] for data in mini_batch]).astype("float32") test_y = np.array([data[1] for data in mini_batch]).astype("int64") mini_batch_result = inferencer.infer({'img': test_x}) mini_batch_result=(mini_batch_result[0][:,-1]>0.5)+0 #True or False 转0/1,直接后面+0即可 #预测的结果 # mini_batch_result = np.argsort(mini_batch_result) #找出可能性最大的列标,升序排列 # mini_batch_result = mini_batch_result[0][:, -1]+0 #把这些列标拿出来 #print('预测结果:%s'%result) label = np.array(test_y) # 转化为 label # print('真实结果:%s'%label) #计数 label_len = len(label) total += label_len for i in range(label_len): if mini_batch_result[i] == label[i]: right_counter += 1 ratio = right_ratio(right_counter, total) return ratio
ratio = evl(train_reader) print('训练数据的正确率 %0.2f%%'%(ratio*100)) ratio = evl(test_reader) print('预测数据的正确率 %0.2f%%'%(ratio*100))