1.. 整型哈希函数的设计
-
小范围正整数直接使用
-
小范围负整数整体进行偏移
-
大整数,通常做法是"模一个素数"
2.. 浮点型哈希函数的设计
-
转成整型进行处理
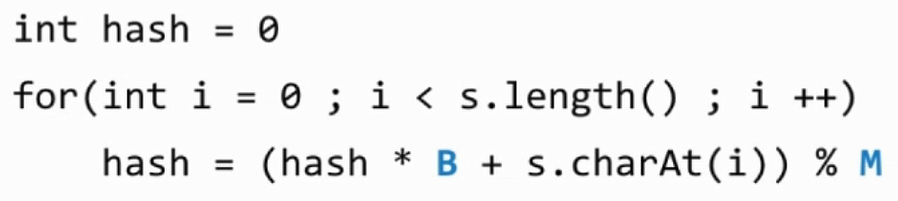
3.. 字符串哈希函数的设计
- 转成整型进行处理
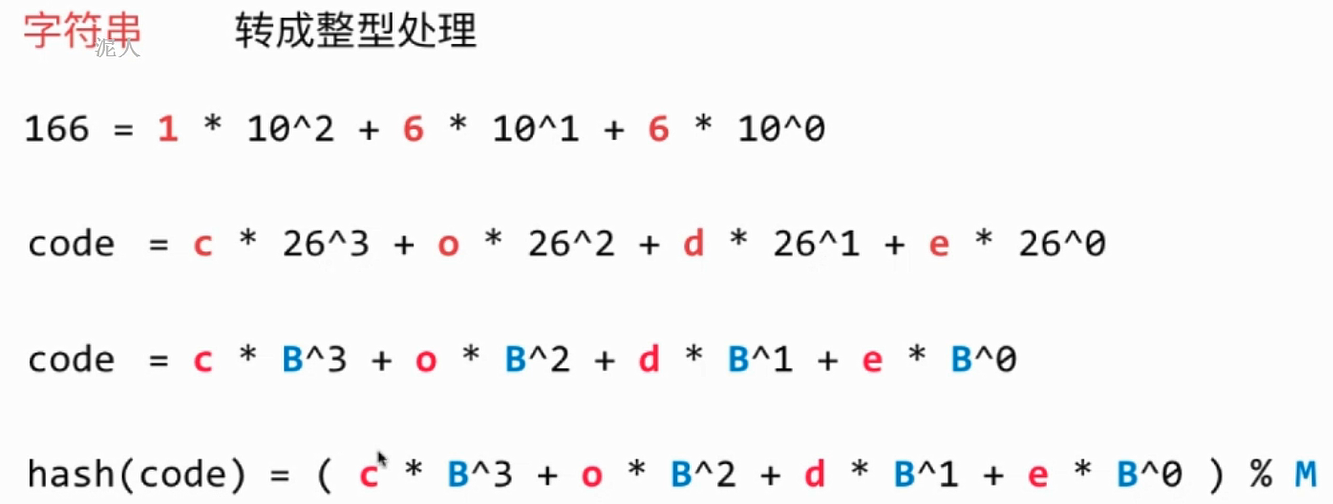
- 简单变形优化

- 防止整型溢出优化

- 具体代码实现
4.. 复合类型哈希函数的设计
- 转成整型进行处理
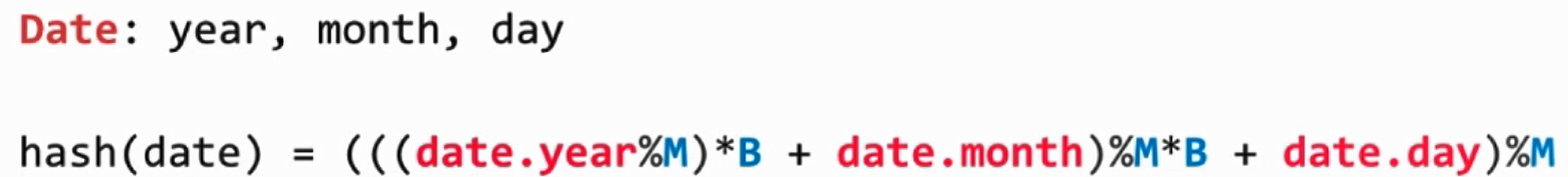
5.. 哈希函数的设计原则
6.. 哈希冲突的处理
- 链地址法

- 开放地址法之线性探测

-
开放地址法之平方探测

- 开放地址法之二次哈希

7.. 哈希表的动态空间处理
8.. 实现哈希表的业务逻辑
-
import java.util.TreeMap; public class HashTable<K, V> { private final int[] capacity = {53, 97, 193, 389, 769, 1543, 3079, 6151, 12289, 24593, 49157, 98317, 196613, 393241, 786433, 1572869, 3145739, 6291469, 12582917, 25165843, 50331653, 100663319, 201326611, 402653189, 805306457, 1610612741}; private static final int upperTol = 10; private static final int lowerTol = 2; private int capacityIndex = 0; private TreeMap<K, V>[] hashTable; private int M; private int size; public HashTable() { this.M = capacity[capacityIndex]; this.size = 0; hashTable = new TreeMap[M]; for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) { hashTable[i] = new TreeMap<>(); } } private int hash(K key) { return key.hashCode() & 0x7fffffff % M; } public void add(K key, V value) { TreeMap<K, V> map = hashTable[hash(key)]; if (map.containsKey(key)) { map.put(key, value); } else { map.put(key, value); size++; if (size >= upperTol * M && capacityIndex + 1 < capacity.length) { capacityIndex++; resize(capacity[capacityIndex]); } } } public V remove(K key) { TreeMap<K, V> map = hashTable[hash(key)]; V ret = null; if (map.containsKey(key)) { ret = map.remove(key); size--; if (size < lowerTol * M && capacityIndex - 1 >= 0) { capacityIndex--; resize(capacity[capacityIndex]); } } return ret; } public void set(K key, V value) { TreeMap<K, V> map = hashTable[hash(key)]; if (!map.containsKey(key)) { throw new IllegalArgumentException(key + "doesn't exist."); } else { map.put(key, value); } } public boolean contains(K key) { return hashTable[hash(key)].containsKey(key); } public V get(K key) { return hashTable[hash(key)].get(key); } private void resize(int newM) { TreeMap<K, V>[] newHashTable = new TreeMap[newM]; for (int i = 0; i < newM; i++) { newHashTable[i] = new TreeMap<>(); } int oldM = M; M = newM; for (int i = 0; i < oldM; i++) { TreeMap<K, V> map = hashTable[i]; for (K key : map.keySet()) { newHashTable[hash(key)].put(key, map.get(key)); } } this.hashTable = newHashTable; } }

