一、二叉树与递归
二叉树具有天然的递归性。
关于递归函数的写法要明确的几个点:1.递归出去的条件(开头一个return (是递归出去条件) 结尾处return(是返回执行的结果)) 2.明确函数的实际意义(以便于后面可以直接按照含义来递归执行) 3.递归过程要执行的逻辑
1.以下简单的递归都是 1).递归出去的条件 + 2).明确函数的实际意义 就可以直接构建出递归函数来解决问题
104. Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
Given binary tree [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/
9 20
/
15 7
return its depth = 3.
代码如下:
class Solution { public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) { if(root == null) { return 0; } else{ return 1+ Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)); } } }
111. Minimum Depth of Binary Tree
Given a binary tree, find its minimum depth.
The minimum depth is the number of nodes along the shortest path from the root node down to the nearest leaf node.
Note: A leaf is a node with no children.
Example:
Given binary tree [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/
9 20
/
15 7
return its minimum depth = 2.
代码如下:
//为什么采用分治的思想而不是求数最大深度思想,因为可能为单链表(链表是特殊树)没法处理 class Solution { public int minDepth(TreeNode root) { if(root == null) return 0; int left = minDepth(root.left); int right = minDepth(root.right); return (left == 0 || right == 0) ? left + right + 1//为什么可以写成left + right + 1 : Math.min(left,right) + 1; //因为left 跟right 必有一个为0,所以.. } }
226. Invert Binary Tree
Invert a binary tree.
Example:
Input:
4 / 2 7 / / 1 3 6 9
Output:
4 / 7 2 / / 9 6 3 1
代码如下:
public class Solution { public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) { if(root == null) return null; //递归出口 TreeNode node = root.left; root.left = invertTree(root.right); root.right = invertTree(node); return root; //执行结果 } }
//还有另一种递归思想 root的左子树先反转 root的右子树也先反转, 后面再交换root的左右子树
100. Same Tree
Given two binary trees, write a function to check if they are the same or not.
Two binary trees are considered the same if they are structurally identical and the nodes have the same value.
Example 1:
Input: 1 1
/ /
2 3 2 3
[1,2,3], [1,2,3]
Output: true
代码如下:
class Solution { public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { if(p == null && q == null) return true; if(p == null || q == null) return false;//递归出去条件有两 if(p.val == q.val) return isSameTree(p.left, q.left) && isSameTree(p.right, q.right); return false; } }
101. Symmetric Tree
For example, this binary tree [1,2,2,3,4,4,3] is symmetric:
1 / 2 2 / / 3 4 4 3
代码如下:
class Solution { public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) { if(root==null) return true; return isMirror(root.left,root.right); } public boolean isMirror(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { if(p==null && q==null) return true; if(p==null || q==null) return false; return (p.val==q.val) && isMirror(p.left,q.right) && isMirror(p.right,q.left); } }
222. Count Complete Tree Nodes
Given a complete binary tree, count the number of nodes.
Note:
Definition of a complete binary tree from Wikipedia:
In a complete binary tree every level, except possibly the last, is completely filled, and all nodes in the last level are as far left as possible. It can have between 1 and 2hnodes inclusive at the last level h.
Example:
Input:
1
/
2 3
/ /
4 5 6
Output: 6
分析:
- 假如左子树高度等于右子树高度,则右子树为完全二叉树,左子树为满二叉树。
- 假如高度不等,则左字数为完全二叉树,右子树为满二叉树。
- 求高度的时候只往左子树来找。
代码如下:
class Solution { public int countNodes(TreeNode root) { int h = height(root); return h < 0 ? 0 : height(root.right) == h-1 ? (1 << h) + countNodes(root.right) : (1 << h-1) + countNodes(root.left); } int height(TreeNode root) { return root == null ? -1 : 1 + height(root.left); } }
//或者直接对任意二叉树用暴力解法 class Solution { public int countNodes(TreeNode* root) { return root ? (1 + countNodes(root->left) + countNodes(root->right)) : 0; } }
110. Balanced Binary Tree
Given a binary tree, determine if it is height-balanced.
For this problem, a height-balanced binary tree is defined as:
a binary tree in which the depth of the two subtrees of every node never differ by more than 1.
Example 1:
Given the following tree [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]:
3
/
9 20
/
15 7
Return true.
代码如下:
public class Solution { private boolean result = true; public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) { maxDepth(root); return result; } public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) return 0; int l = maxDepth(root.left); int r = maxDepth(root.right); if (Math.abs(l - r) > 1) result = false; return 1 + Math.max(l, r); } }
2. 递归终止条件存在陷阱的递归
112. Path Sum
Given a binary tree and a sum, determine if the tree has a root-to-leaf path such that adding up all the values along the path equals the given sum.
Note: A leaf is a node with no children.
Example:
Given the below binary tree and sum = 22,
5
/
4 8
/ /
11 13 4
/
7 2 1
return true, as there exist a root-to-leaf path 5->4->11->2 which sum is 22.
特殊情况 二叉树如下 sum = 5
5
8
/
13 4
代码如下:
public class Solution { public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) { if(root == null) return false; if(root.left == null && root.right == null && sum - root.val == 0) return true; //判断为叶子节点 return hasPathSum(root.left, sum - root.val) || hasPathSum(root.right, sum - root.val); } }
404. Sum of Left Leaves(跟上一题一样,判断是否为叶子节点)
Find the sum of all left leaves in a given binary tree.
Example:
3
/
9 20
/
15 7
There are two left leaves in the binary tree, with values 9 and 15 respectively. Return 24.
代码如下:
class Solution { public int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode root) { if(root == null) return 0; int ans = 0; if(root.left != null) { if(root.left.left == null && root.left.right == null) ans += root.left.val;//判断是否为叶子节点 else ans += sumOfLeftLeaves(root.left); } ans += sumOfLeftLeaves(root.right); return ans; } }
3.执行逻辑部分比较复杂的二叉树的递归
257. Binary Tree Paths
iven a binary tree, return all root-to-leaf paths.
Note: A leaf is a node with no children.
Example:
Input: 1 / 2 3 5 Output: ["1->2->5", "1->3"]
class Solution { public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) { List<String> answer = new ArrayList<String>(); if (root != null) searchBT(root, "", answer); return answer; } private void searchBT(TreeNode root, String path, List<String> answer) { if (root.left == null && root.right == null) answer.add(path + root.val); if (root.left != null) searchBT(root.left, path + root.val + "->", answer); if (root.right != null) searchBT(root.right, path + root.val + "->", answer); } }
113. Path Sum II
Given a binary tree and a sum, find all root-to-leaf paths where each path's sum equals the given sum.
Note: A leaf is a node with no children.
Example:
Given the below binary tree and sum = 22,
5
/
4 8
/ /
11 13 4
/ /
7 2 5 1
Return:
[ [5,4,11,2], [5,8,4,5] ]
代码如下:
class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int sum){ List<List<Integer>> result = new LinkedList<List<Integer>>(); List<Integer> currentResult = new LinkedList<Integer>(); pathSum(root,sum,currentResult,result); return result; } public void pathSum(TreeNode root, int sum, List<Integer> currentResult, List<List<Integer>> result) { if (root == null) return; currentResult.add(new Integer(root.val)); if (root.left == null && root.right == null && sum == root.val) { result.add(new LinkedList(currentResult)); currentResult.remove(currentResult.size() - 1);//don't forget to remove the last integer return; } else { pathSum(root.left, sum - root.val, currentResult, result); pathSum(root.right, sum - root.val, currentResult, result); } currentResult.remove(currentResult.size() - 1); } }
129. Sum Root to Leaf Numbers
Given a binary tree containing digits from 0-9 only, each root-to-leaf path could represent a number.
An example is the root-to-leaf path 1->2->3 which represents the number 123.
Find the total sum of all root-to-leaf numbers.
Note: A leaf is a node with no children.
Input: [4,9,0,5,1]
4
/
9 0
/
5 1
Output: 1026
Explanation:
The root-to-leaf path 4->9->5 represents the number 495.
The root-to-leaf path 4->9->1 represents the number 491.
The root-to-leaf path 4->0 represents the number 40.
Therefore, sum = 495 + 491 + 40 = 1026.
代码如下:
class Solution { public int sumNumbers(TreeNode root) { return sum(root, 0); } public int sum(TreeNode n, int s){ if (n == null) return 0; if (n.right == null && n.left == null) return s*10 + n.val; return sum(n.left, s*10 + n.val) + sum(n.right, s*10 + n.val); } }
其实以上递归出去的条件基本是 root = null, n.right == null && n.left == null (叶子节点) n.right == null || n.left == null
437. Path Sum III
You are given a binary tree in which each node contains an integer value.
Find the number of paths that sum to a given value.
The path does not need to start or end at the root or a leaf, but it must go downwards (traveling only from parent nodes to child nodes).
The tree has no more than 1,000 nodes and the values are in the range -1,000,000 to 1,000,000.
Example:
root = [10,5,-3,3,2,null,11,3,-2,null,1], sum = 8
10
/
5 -3
/
3 2 11
/
3 -2 1
Return 3. The paths that sum to 8 are:
1. 5 -> 3
2. 5 -> 2 -> 1
3. -3 -> 11
代码如下:
public class Solution { public int pathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) { if (root == null) return 0; return pathSumFrom(root, sum) + pathSum(root.left, sum) + pathSum(root.right, sum); } private int pathSumFrom(TreeNode node, int sum) { if (node == null) return 0; return (node.val == sum ? 1 : 0) + pathSumFrom(node.left, sum - node.val) + pathSumFrom(node.right, sum - node.val); } }
4.二分搜索树
235. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Search Tree
Given a binary search tree (BST), find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two given nodes in the BST.
According to the definition of LCA on Wikipedia: “The lowest common ancestor is defined between two nodes p and q as the lowest node in T that has both p and q as descendants (where we allow a node to be a descendant of itself).”
Given binary search tree: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5]
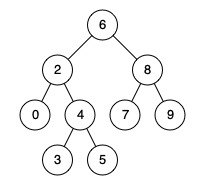
Example 1:
Input: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 8 Output: 6 Explanation: The LCA of nodes2and8is6.
代码如下:
class Solution { public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { while((root.val - p.val)*(root.val -q.val) > 0){ root = root.val > p.val ? root.left : root.right; } return root; } } //或者 public class Solution { public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { if(root.val > p.val && root.val > q.val){ return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q); }else if(root.val < p.val && root.val < q.val){ return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q); }else{ return root; } } }
98. Validate Binary Search Tree
Given a binary tree, determine if it is a valid binary search tree (BST).
Assume a BST is defined as follows:
- The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than the node's key.
- The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than the node's key.
- Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
Example 1:
2 / 1 3 Input: [2,1,3] Output: true
验证该树是否为二分搜索树
代码如下:
//可以中序遍历出来递增则是.....
//核心思想是左子树的最大值小于跟节点,右子树最小值大于跟节点 public class Solution { public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) { return isValidBST(root, Long.MIN_VALUE, Long.MAX_VALUE); } public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root, long minVal, long maxVal) { if (root == null) return true; if (root.val >= maxVal || root.val <= minVal) return false; return isValidBST(root.left, minVal, root.val) && isValidBST(root.right, root.val, maxVal); } //左子树的最大值就是跟节点 所以maxVal = root.val, }
108. Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree
Given an array where elements are sorted in ascending order, convert it to a height balanced BST.
For this problem, a height-balanced binary tree is defined as a binary tree in which the depth of the two subtrees of every node never differ by more than 1.
Example:
Given the sorted array: [-10,-3,0,5,9],
One possible answer is: [0,-3,9,-10,null,5], which represents the following height balanced BST:
0
/
-3 9
/ /
-10 5
分析:有序数组转为二叉树其实就是对二叉树进行中序遍历的逆过程
代码如下:
class Solution { public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] num) { if (num.length == 0) { return null; } TreeNode head = helper(num, 0, num.length - 1); return head; } public TreeNode helper(int[] num, int low, int high) { if (low > high) { // Done return null; } int mid = (low + high)/2; TreeNode node = new TreeNode(num[mid]); node.left = helper(num, low, mid-1); node.right = helper(num, mid+1 ,high); return node; } }
230. Kth Smallest Element in a BST
Given a binary search tree, write a function kthSmallest to find the kth smallest element in it.
Note:
You may assume k is always valid, 1 ≤ k ≤ BST's total elements.
Example 1:
Input: root = [3,1,4,null,2], k = 1 3 / 1 4 2 Output: 1
代码如下:
class Solution { public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) { Stack<TreeNode> st = new Stack<>(); while (root != null) { st.push(root); root = root.left; } while (k != 0) { TreeNode n = st.pop(); k--; if (k == 0) return n.val; TreeNode right = n.right; while (right != null) { st.push(right); right = right.left; } } return -1; // never hit if k is valid } }
236. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree
Given a binary tree, find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two given nodes in the tree.
According to the definition of LCA on Wikipedia: “The lowest common ancestor is defined between two nodes p and q as the lowest node in T that has both p and q as descendants (where we allow a node to be a descendant of itself).”
Given the following binary tree: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4]

Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1 Output: 3 Explanation: The LCA of nodes5and1is3.
分析:任意一颗二叉树的公共祖先
代码如下:
class Solution { public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { if(root == null || root == p || root ==q) return root; TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q); //查找pq是否在左子树 TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);// if(left == null){ return right; } if(right == null){ return left; } return root; } }