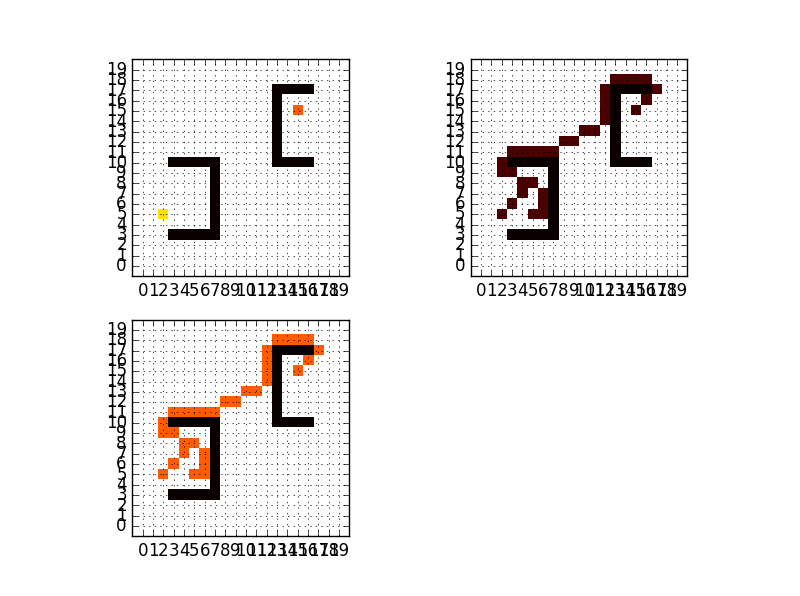
1 # 版本2,2018—04—09 2 # 所有节点的g值并没有初始化为无穷大 3 # 当两个子节点的f值一样时,程序选择最先搜索到的一个作为父节点加入closed 4 # 对相同数值的不同对待,导致不同版本的A*算法找到等长的不同路径 5 # 最后closed表中的节点很多,如何找出最优的一条路径 6 # 撞墙之后产生较多的节点会加入closed表,此时开始删除closed表中不合理的节点 7 8 9 import numpy 10 from pylab import * 11 import copy 12 13 # 定义一个含有障碍物的20×20的栅格地图 14 # 10表示可通行点 15 # 0表示障碍物 16 # 7表示起点 17 # 5表示终点 18 map_grid = numpy.full((20, 20), int(10), dtype=numpy.int8) 19 # print(map_grid) 20 map_grid[3, 3:8] = 0 21 map_grid[3:10, 7] = 0 22 map_grid[10, 3:8] = 0 23 map_grid[17, 13:17] = 0 24 map_grid[10:17, 13] = 0 25 map_grid[10, 13:17] = 0 26 map_grid[5, 2] = 7 27 map_grid[15, 15] = 5 28 # 画出定义的栅格地图 29 30 # plt.imshow(map_grid, cmap=plt.cm.hot, interpolation='nearest', vmin=0, vmax=10) 31 # plt.colorbar() 32 # xlim(-1, 20) # 设置x轴范围 33 # ylim(-1, 20) # 设置y轴范围 34 # my_x_ticks = numpy.arange(0, 20, 1) 35 # my_y_ticks = numpy.arange(0, 20, 1) 36 # plt.xticks(my_x_ticks) 37 # plt.yticks(my_y_ticks) 38 # plt.grid(True) 39 # plt.show() 40 41 42 class AStar(object): 43 """ 44 创建一个A*算法类 45 """ 46 47 def __init__(self): 48 """ 49 初始化 50 """ 51 self.f = 0 52 self.g = 0 53 self.last_point = numpy.array([]) # 上一个目标点不断取得更新 54 self.current_point = numpy.array([]) # 当前目标点不断取得更新 55 self.open = numpy.array([[], []]) # 先创建一个空的open表 56 self.closed = numpy.array([[], []]) # 先创建一个空的closed表 57 self.taboo = numpy.array([[], []]) # 创建一个禁忌表,用于放置不再搜索的点 58 self.start = numpy.array([5, 2]) # 起点坐标 59 self.goal = numpy.array([15, 15]) # 终点坐标 60 61 def h_value_tem(self, cur_p): 62 """ 63 计算拓展节点和终点的h值 64 :param cur_p:子搜索节点坐标 65 :return: 66 """ 67 h = (cur_p[0] - 15) ** 2 + (cur_p[1] - 15) ** 2 68 h = numpy.sqrt(h) # 计算h 69 return h 70 71 def g_value_tem(self, chl_p, cu_p): 72 """ 73 计算拓展节点和父节点的g值 74 其实也可以直接用1或者1.414代替 75 :param chl_p:子节点坐标 76 :param cu_p:父节点坐标,也就是self.current_point 77 :return:返回子节点到父节点的g值,但不是全局g值 78 """ 79 g1 = cu_p[0] - chl_p[0] 80 g2 = cu_p[1] - chl_p[1] 81 g = g1 ** 2 + g2 ** 2 82 g = numpy.sqrt(g) 83 return g 84 85 def f_value_tem(self, chl_p, cu_p): 86 """ 87 求出的是临时g值和h值的和,还需加上累计g值得到全局f值 88 :param chl_p: 父节点坐标 89 :param cu_p: 子节点坐标 90 :return: 91 """ 92 f = self.g_value_tem(chl_p, cu_p) + self.h_value_tem(cu_p) 93 return f 94 95 def min_f(self): 96 """ 97 找出open中f值最小的节点坐标,记录为current_point 98 :return:返回open表中最小值的位置索引和在map_grid中的坐标 99 对撞墙后的处理方式是,随机选择一个方向进行搜索 100 并且将open列表清零,不然一直是死循环 101 这种处理方式以后待改进!!! 102 """ 103 tem_f = [] # 创建一个记录f值的临时列表 104 for i in range(self.open.shape[1]): 105 # 计算拓展节点的全局f值 106 f_value = self.f_value_tem(self.current_point, self.open[:, i]) + self.g 107 tem_f.append(f_value) 108 index = tem_f.index(min(tem_f)) # 返回最小值索引 109 location = self.open[:, index] # 返回最小值坐标 110 print('打印位置索引和地图坐标:') 111 print(index, location) 112 return index, location 113 114 def child_point(self, x): 115 """ 116 拓展的子节点坐标 117 :param x: 父节点坐标 118 :return: 子节点存入open表,返回值是每一次拓展出的子节点数目,用于撞墙判断 119 当搜索的节点撞墙后,如果不加处理,会陷入死循环 120 """ 121 tem_open = numpy.array([[], []]) # 统计拓展节点的临时数组 122 tem_open_shape = 0 # 统计临时数组的长度 123 # 开始遍历周围8个节点 124 for j in range(-1, 2, 1): 125 for q in range(-1, 2, 1): 126 if j == 0 and q == 0: # 搜索到父节点去掉 127 continue 128 129 # print(map_grid[int(x[0] + j), int(x[1] + q)]) 130 if map_grid[int(x[0] + j), int(x[1] + q)] == 0: # 搜索到障碍物去掉 131 continue 132 if x[0] + j < 0 or x[0] + j > 19 or x[1] + q < 0 or x[1] + q > 19: # 搜索点出了边界去掉 133 continue 134 # 在open表中,则去掉搜索点 135 a = self.judge_location(x, j, q, self.open) 136 if a == 1: 137 continue 138 # 在closed表中,则去掉搜索点 139 b = self.judge_location(x, j, q, self.closed) 140 if b == 1: 141 continue 142 143 # 在taboo表中,则去掉搜索点 144 c = self.judge_location(x, j, q, self.taboo) 145 if c == 1: 146 continue 147 148 m = numpy.array([x[0] + j, x[1] + q]) 149 150 tem_open = numpy.c_[tem_open, m] # 151 152 tem_open_shape = tem_open.shape[1] # 求出tem_open的长度 153 154 self.open = numpy.c_[self.open, m] # 搜索出的子节点加入open 155 # print('打印第一次循环后的open:') 156 # print(self.open) 157 return tem_open_shape 158 159 def judge_location(self, x, j, q, list_co): 160 """ 161 判断拓展点是否在open表或者closed表中 162 :return: 163 """ 164 jud = 0 165 for i in range(list_co.shape[1]): 166 167 if x[0] + j == list_co[0, i] and x[1] + q == list_co[1, i]: 168 169 jud = jud + 1 170 else: 171 jud = jud 172 # if a != 0: 173 # continue 174 return jud 175 176 def draw_path_closed(self): 177 """ 178 画出closed表中的坐标点图 179 :return: 180 """ 181 map_closed = copy.deepcopy(map_grid) 182 for i in range(self.closed.shape[1]): 183 x = self.closed[:, i] 184 185 map_closed[int(x[0]), int(x[1])] = 5 186 187 plt.imshow(map_closed, cmap=plt.cm.hot, interpolation='nearest', vmin=0, vmax=10) 188 # plt.colorbar() 189 xlim(-1, 20) # 设置x轴范围 190 ylim(-1, 20) # 设置y轴范围 191 my_x_ticks = numpy.arange(0, 20, 1) 192 my_y_ticks = numpy.arange(0, 20, 1) 193 plt.xticks(my_x_ticks) 194 plt.yticks(my_y_ticks) 195 plt.grid(True) 196 # plt.show() 197 198 def draw_init_map(self): 199 """ 200 画出起点终点图 201 :return: 202 """ 203 204 plt.imshow(map_grid, cmap=plt.cm.hot, interpolation='nearest', vmin=0, vmax=10) 205 # plt.colorbar() 206 xlim(-1, 20) # 设置x轴范围 207 ylim(-1, 20) # 设置y轴范围 208 my_x_ticks = numpy.arange(0, 20, 1) 209 my_y_ticks = numpy.arange(0, 20, 1) 210 plt.xticks(my_x_ticks) 211 plt.yticks(my_y_ticks) 212 plt.grid(True) 213 # plt.show() 214 215 def draw_path_open(self): 216 """ 217 画出open表中的坐标点图 218 :return: 219 """ 220 map_open = copy.deepcopy(map_grid) 221 for i in range(self.closed.shape[1]): 222 x = self.closed[:, i] 223 224 map_open[int(x[0]), int(x[1])] = 1 225 226 plt.imshow(map_open, cmap=plt.cm.hot, interpolation='nearest', vmin=0, vmax=10) 227 # plt.colorbar() 228 xlim(-1, 20) # 设置x轴范围 229 ylim(-1, 20) # 设置y轴范围 230 my_x_ticks = numpy.arange(0, 20, 1) 231 my_y_ticks = numpy.arange(0, 20, 1) 232 plt.xticks(my_x_ticks) 233 plt.yticks(my_y_ticks) 234 plt.grid(True) 235 # plt.show() 236 237 def draw_three_axes(self): 238 """ 239 将三张图画在一个figure中 240 :return: 241 """ 242 plt.figure() 243 ax1 = plt.subplot(221) 244 245 ax2 = plt.subplot(222) 246 ax3 = plt.subplot(223) 247 plt.sca(ax1) 248 self.draw_init_map() 249 plt.sca(ax2) 250 self.draw_path_open() 251 plt.sca(ax3) 252 self.draw_path_closed() 253 plt.show() 254 255 def main(self): 256 """ 257 main函数 258 :return: 259 """ 260 self.open = numpy.column_stack((self.open, self.start)) # 起点放入open 261 self.current_point = self.start # 起点放入当前点,作为父节点 262 # self.closed 263 ite = 1 264 while ite <= 2000: 265 266 # open列表为空,退出 267 if self.open.shape[1] == 0: 268 print('没有搜索到路径!') 269 return 270 271 last_point = self.current_point # 上一个目标点不断取得更新 272 273 while True: 274 275 index, self.current_point = self.min_f() # 判断open表中f值 276 print('检验第%s次当前点坐标' % ite) 277 print(self.current_point) 278 279 # 选取open表中最小f值的节点作为best,放入closed表 280 self.closed = numpy.c_[self.closed, self.current_point] 281 282 if self.current_point[0] == 15 and self.current_point[1] == 15: # 如果best是目标点,退出 283 print('搜索成功!') 284 return 285 286 tem_open_shape = self.child_point(self.current_point) # 生成子节点并判断数目 287 self.open = delete(self.open, index, axis=1) # 删除open中最优点 288 289 if tem_open_shape == 0: 290 self.closed = delete(self.closed, -1, axis=1) # 删除closed中不合理的点 291 self.taboo = numpy.c_[self.taboo, self.current_point] # 将撞墙点加入禁忌表 292 self.current_point = last_point 293 self.g = self.g + self.g_value_tem(self.current_point, last_point) 294 continue 295 else: 296 break 297 298 # print(self.open) 299 300 301 302 ite = ite+1 303 304 305 if __name__ == '__main__': 306 307 a1 = AStar() 308 a1.main() 309 a1.draw_three_axes()