c语言可以说是高级计算机语言之母。之前学校有开c语言课程,但是几乎没有听过。期末考也是突击两小时。写java也有一年多了,总感觉只是停在用的基础上,没有办法去深究它到底是怎么样组织数据的。所以在一直想重新来一遍C语言。这算是一个开始。
# include <stdio.h> int main() { float weight; float value; printf("Are you worth your weight in platinum? "); printf("Let's check it out. "); printf("Please enter your weight in pounds: "); //scanf() 方法用于读取键盘的输入, %f 表明要读取的是浮点数, &weight表示 把scanf()方法读取的浮点数赋值给 weight。 scanf("%f", &weight); value = 1700.0 * weight * 14.5833; //在printf() 方法中,使用 %f 来输出浮点数。%.2f 用于精确控制输出,只输出小数点后两位 printf("Your weight in platinum is worth $%.2f. ", value); printf("You are easily worth that ! If platinum price drop, "); printf("eat more to maintain your value. "); }
输出

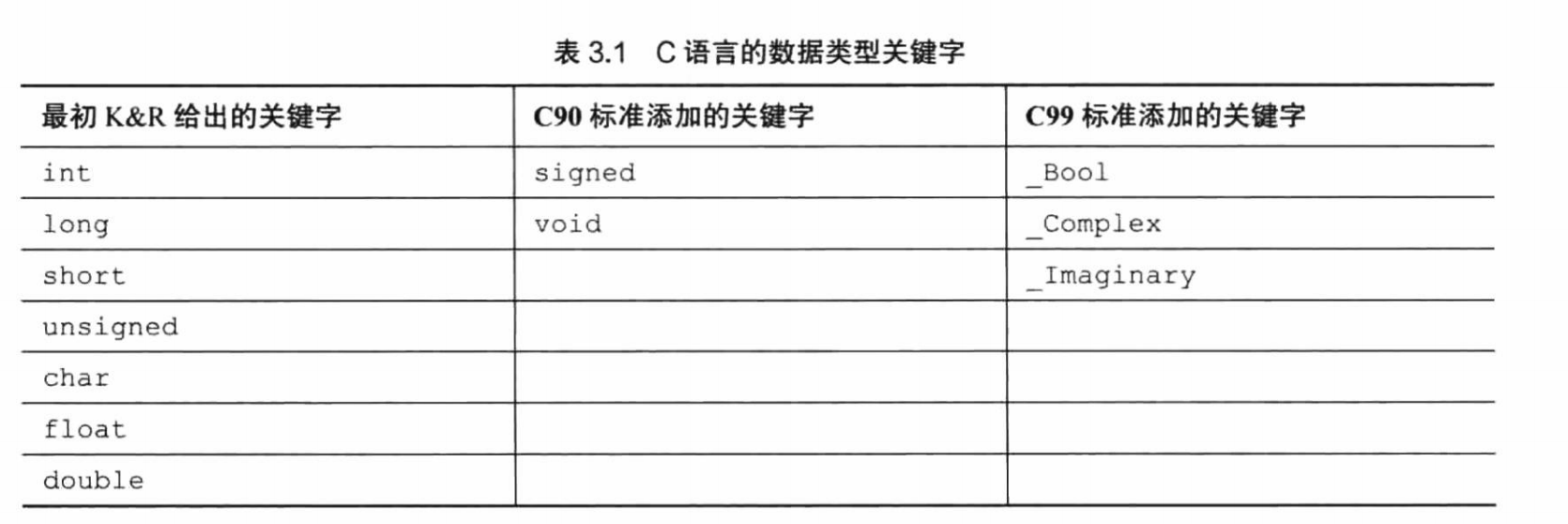
C语言数据类型关键字
内存:
位:bit 最小的存储单位,可以存储0或1.位是计算机内存的基本构建块;
字节: byte 对于几乎所有的机器,1字节均为8位,这是字节的标准定义。有2^8种组合
字: word 设计计算机时给定的自然 存储单位,对于8位的微型计算机,1个字长只有8位。 现在个人计算机增至16位,32位,64位。计算机的字长越大,其数据转移越快,允许的内存访问也越多。
整数存储结构

浮点数存储结构:

数据类型
1. int(整型):
int的大小为一个字长,而字长取决于计算机的设定。我现在的计算机是64位的,所以我这里一个int的大小为64位,也就是8个byte。但是我下面用sizeof(int) = 4, sizeof(int*)=8这就很尴尬了。
//声明 int age; //声明一个 int count, amount, plat; //声明多个 //初始化 int age = 12; //声明时初始化 int count; count = 5; //先声明,后进行初始化 int dogs = 23, cats = 24; //声明多个并初始化 int dogs, cats = 55; //正确,但不推荐。格式糟糕 /* 声明时为变量进行内存分配,初始化时为变量赋值 */
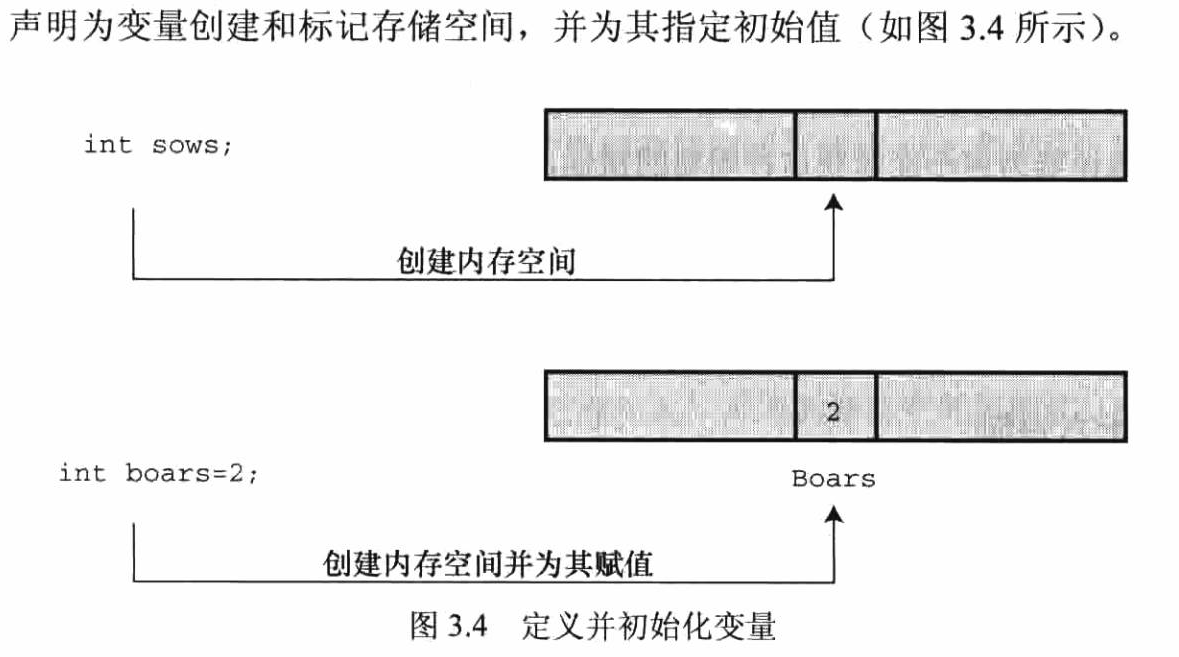
#include <stdio.h> int main() { int ten = 10; int two = 2; printf("正确打印方式: "); printf("%d 减去 %d 等于 %d ", ten, two, ten - two); printf("错误方式: "); printf("%d 减去 %d 等于 %d ", ten); //遗漏2个参数 return 0; }
输出
显示进制输出
#include<stdio.h> int main() { int x = 100; printf("一个整型的大小为%d ",sizeof(int)); printf("一个整型指针的大小为%d ",sizeof(int*)); printf("dec =%d; octal = %o; hex = %x ", x, x, x); printf("dec =%d; octal = %#o; hex = %#x ", x, x, x); return 0; } /* output: 一个整型的大小为4 一个整型指针的大小为8 dec =100; octal = 144; hex = 64 dec =100; octal = 0144; hex = 0x64 */
其他整型
1. short int 或 short: 占用的空间可能比int小
2. long int 或long : 占用的空间可能比int大
3. long long int 或 long long : 占用的空间可能比long大,至少为64位
4. unsigned 无符号
5. 为什么说 short i可能比 int 小。因为只规定了short占用的空间不能大于int,int占用的空间不能大于long.。所以它们有可能是相等的
整数溢出:
#include<stdio.h> int main() { int x = 2147483647; unsigned int y = 4294967295; printf("%d; %d; %d ", x, x+1, x+2); printf("%d; %d; %d ", y, y+1, y+2); return 0; } /* output: 2147483647; -2147483648; -2147483647 -1; 0; 1 */