20165315 第四次考试课下补做
一、相关知识点的总结
- 泛型
- 主要目的是可以建立具有类型安全的集合框架,如链表、散列映射等数据结构
- 泛型类声明
- 可以使用
class 名称<泛型列表>声明一个类,为了和普通的类有所区别,这样声明的类称作泛型类,没有指定E是何种类型的数据,它可以是任何对象或接口,但不能是基本类型数据
- 可以使用
- 使用泛型类声明对象
- 泛型类声明和创建对象时,类名后多了一对“<>”,而且必须要用具体的类型替换“<>”中的泛型
- 链表
- 链表是由若干个称作节点的对象组成的一种数据结构,每个节点含有一个数据和下一个节点的引用
LinkedList<E>泛型类- LinkedList
泛型类创建的对象以链表结构存储数据,习惯上称LinkedList类创建的对象为链表对象 LinkedList<String> mylist=new LinkedList<String>();创建一个空双链表add(E obj)向链表依次增加节点
- 常用方法
- LinkedList
泛型类实现Lis 泛型接口中的一些常用方法 public boolean add(E element)向链表末尾添加一个新的节点,该节点中的数据是参数elememt指定的数据public void add(int index ,E element)向链表的指定位置添加一个新的节点,该节点中的数据是参数elememt指定的数据public void clear()删除链表的所有节点,使当前链表成为空链表public E remove(int index)删除指定位置上的节点public boolean remove(E element)删除首次出现含有数据elemen的节点public E get(int index)得到链表中指定位置处节点中的数据
- LinkedList
泛型类本身新增加的一些常用方法 public void addFirst(E element)向链表的头添加新节点,该节点中的数据是参数elememt指定的数据public void addLast(E element)向链表的末尾添加新节点,该节点中的数据是参数elememt指定的数据public E getFirst()得到链表中第一个节点中的数据public E getLast()得到链表中最后一个节点中的数据public E removeFirst()删除第一个节点,并返回这个节点中的数据
- LinkedList
- 遍历链表
- 当用户需要遍历集合中的对象时,应当使用该集合提供的迭代器,而不是让集合本身来遍历其中的对象
- 链表对象可以使用
iterator()方法获取一个Iterator对象,该对象就是针对当前链表的迭代器
- 排序与查找
Collections类提供的用于排序和查找的类方法如下:public static sort(List<E> list): 该方法可以将list中的元素升序排列int binarySearch(List<T> list, T key,CompareTo<T> c): 使用折半法查找list是否含有和参数key相等的元素,如果key链表中某个元素相等,方法返回和key相等的元素在链表中的索引位置(链表的索引位置从0考试),否则返回-1
- 洗牌与旋转
Collections类还提供了将链表中的数据重新随机排列的类方法以及旋转链表中数据的类方法public static void shuffle(List<E> list)将list中的数据按洗牌算法重新随机排列static void rotate(List<E> list, int distance)旋转链表中的数据public static void reverse(List<E> list)翻转list中的数据
- LinkedList
- 堆栈
- 堆栈是一种“后进先出”的数据结构,只能在一端进行输入或输出数据的操作
- Stack
泛型类创建一个堆栈对象,堆栈对象常用方法: public E push(E item);实现压栈操作public E pop();实现弹栈操作public boolean empty();判断堆栈是否还有数据public E peek();获取堆栈顶端的数据,但不删除该数据public int search(Object data);获取数据在堆栈中的位置
- 散列映射
- HashMap<K,V>泛型类
- HashMap<K,V>对象采用散列表这种数据结构存储数据,习惯上称HashMap<K,V>对象为散列映射
- 相关方法:
public V put(K key,V value)将键/值对数据存放到散列映射中,该方法同时返回键所对应的值 - 常用方法:
public void clear()清空散列映射public Object clone()返回当前散列映射的一个克隆public boolean containsKey(Object key)如果散列映射有“键/值”对使用了参数指定的键,方法返回true,否则返回falsepublic boolean containsValue(Object value)如果散列映射有“键/值”对的值是参数指定的值public V get(Object key)返回散列映射中使用key做键的“键/值”对中的值public boolean isEmpty()如果散列映射不含任何“键/值”对,方法返回true,否则返回falsepublic V remove(Object key)删除散列映射中键为参数指定的“键/值”对,并返回键对应的值public int size()返回散列映射的大小,即散列映射中“键/值”对的数目
- HashMap<K,V>泛型类
- 树集
TreeSet<E>泛型类- TreeSet
类创建的对象称作树集 TreeSet<String> mytree=new TreeSe<String>();mytree.add("boy");使用add方法为树集添加节点
- TreeSet
TreeSet类的常用方法public boolean add(E o)向树集添加加节点public void clear()删除树集中的所有节点public void contains(Object o)如果树集中有包含参数指定的对象,该方法返回true,否则返回falsepublic E first()返回树集中的第一个节点中的数据(最小的节点)public E last()返回最后一个节点中的数据(最大的节点)public isEmpty()判断是否是空树集,如果树集不含任何节点,该方法返回truepublic boolean remove(Object o)删除树集中的存储参数指定的对象的最小节点public int size()返回树集中节点的数目
二、课上内容的补做,结果截图
针对下面的Student类,使用Comparator编程完成以下功能:
- 在测试类StudentTest中新建学生列表,包括自己和学号前后各两名学生,共5名学生,给出运行结果(排序前,排序后)
- 对这5名同学分别用学号和总成绩进行增序排序,提交两个Comparator的代码
- 课下提交代码到码云
- 示例代码:
class Student {
private String id;//表示学号
private String name;//表示姓名
private int age;//表示年龄
private double computer_score;//表示计算机课程的成绩
private double english_score;//表示英语课的成绩
private double maths_score;//表示数学课的成绩
private double total_score;// 表示总成绩
private double ave_score; //表示平均成绩
public Student(String id, String name){
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public Student(String id, String name, char sex, int age){
this(id, name);
this.sex = sex;
this.age = age;
}
public String getId(){
return id;
}//获得当前对象的学号,
public double getComputer_score(){
return computer_score;
}//获得当前对象的计算机课程成绩,
public double getMaths_score(){
return maths_score;
}//获得当前对象的数学课程成绩,
public double getEnglish_score(){
return english_score;
}//获得当前对象的英语课程成绩,
public void setId(String id){
this.id=id;
}// 设置当前对象的id值,
public void setComputer_score(double computer_score){
this.computer_score=computer_score;
}//设置当前对象的Computer_score值,
public void setEnglish_score(double english_score){
this.english_score=english_score;
}//设置当前对象的English_score值,
public void setMaths_score(double maths_score){
this.maths_score=maths_score;
}//设置当前对象的Maths_score值,
public double getTotalScore(){
return computer_score+maths_score+english_score;
}// 计算Computer_score, Maths_score 和English_score 三门课的总成绩。
public double getAveScore(){
return getTotalScore()/3;
}// 计算Computer_score, Maths_score 和English_score 三门课的平均成绩。
}
class Undergraduate extends Student{
private String classID;
public Undergraduate(String id, String name, char sex, int age,String classID){
super(id,name,sex,age);
this.classID=classID;
}
public String getClassID(){
return classID;
}
public void setClassID(String classID){
this.classID=classID;
}
}
- 设计思路:
最开始使用的是书上例子9中的代码进行修改,得到满足老师运行结果要求的代码:
import java.sql.SQLOutput;
import java.util.*;
class StudentKey implements Comparable {
double d = 0;
String s = "";
StudentKey(double d) {
this.d = d;
}
StudentKey(String s) {
this.s = s;
}
public int compareTo(Object b) {
StudentKey st = (StudentKey) b;
if ((this.d - st.d) == 0)
return -1;
else
return (int) ((this.d - st.d) * 1000);
}
}
class StudentIF {
String name = null;
int ID ;
double math, english, computer, total, aver;
StudentIF(String n, int id,double m, double e, double f, double a, double b) {
name = n;
ID = id;
math = m;
english = e;
computer = f;
total = a;
aver = b;
}
}
public class Student {
public static void main(String args[]) {
TreeMap<StudentKey, StudentIF> treemap = new TreeMap<StudentKey, StudentIF>();
String name[] = {"张晨晖", "陈由章", "阎含", "孙勖哲", "宁心宇"};
int ID[] = {20165313,20165314,20165315,20165316,20165317};
double math[] = {66,77,88,99,100};
double english[] = {100,99,88,77,66};
double computer[] = {60,70,80,90,99};
double total[] = new double[5];
double aver[] = new double[5];
StudentIF student[] = new StudentIF[5];
for (int k = 0; k < student.length; k++) {
total[k] = math[k] + english[k] + computer[k];
aver[k] = total[k] / 3;
}
for (int k = 0; k < student.length; k++) {
student[k] = new StudentIF(name[k], ID[k] , math[k], english[k], computer[k], total[k], aver[k]);
}
StudentKey key[] = new StudentKey[5];
for (int k = 0; k < key.length; k++) {
key[k] = new StudentKey(student[k].total);
}
for (int k = 0; k < student.length; k++) {
treemap.put(key[k], student[k]);
}
int number = treemap.size();
System.out.println("树映射中有" + number + "个对象,按总成绩排序:");
Collection<StudentIF> collection = treemap.values();
Iterator<StudentIF> iter = collection.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
StudentIF stu = iter.next();
System.out.println("姓名 " + stu.name + " 学号 "+ stu.ID + " 总成绩 " + stu.total);
}
treemap.clear();
StudentKey key2[] = new StudentKey[5];
for (int k = 0; k < key2.length; k++) {
key2[k] = new StudentKey(student[k].ID);
}
for (int k = 0; k < student.length; k++) {
treemap.put(key2[k], student[k]);
}
System.out.println("树映射中有" + number + "个对象,按学号排序:");
Collection<StudentIF> collection2 = treemap.values();
Iterator<StudentIF> iter2 = collection2.iterator();
while (iter2.hasNext()) {
StudentIF stu2 = iter2.next();
System.out.println("姓名 " + stu2.name + " 学号 " + stu2.ID + " 总成绩 " + stu2.total);
}
}
}
运行截图:
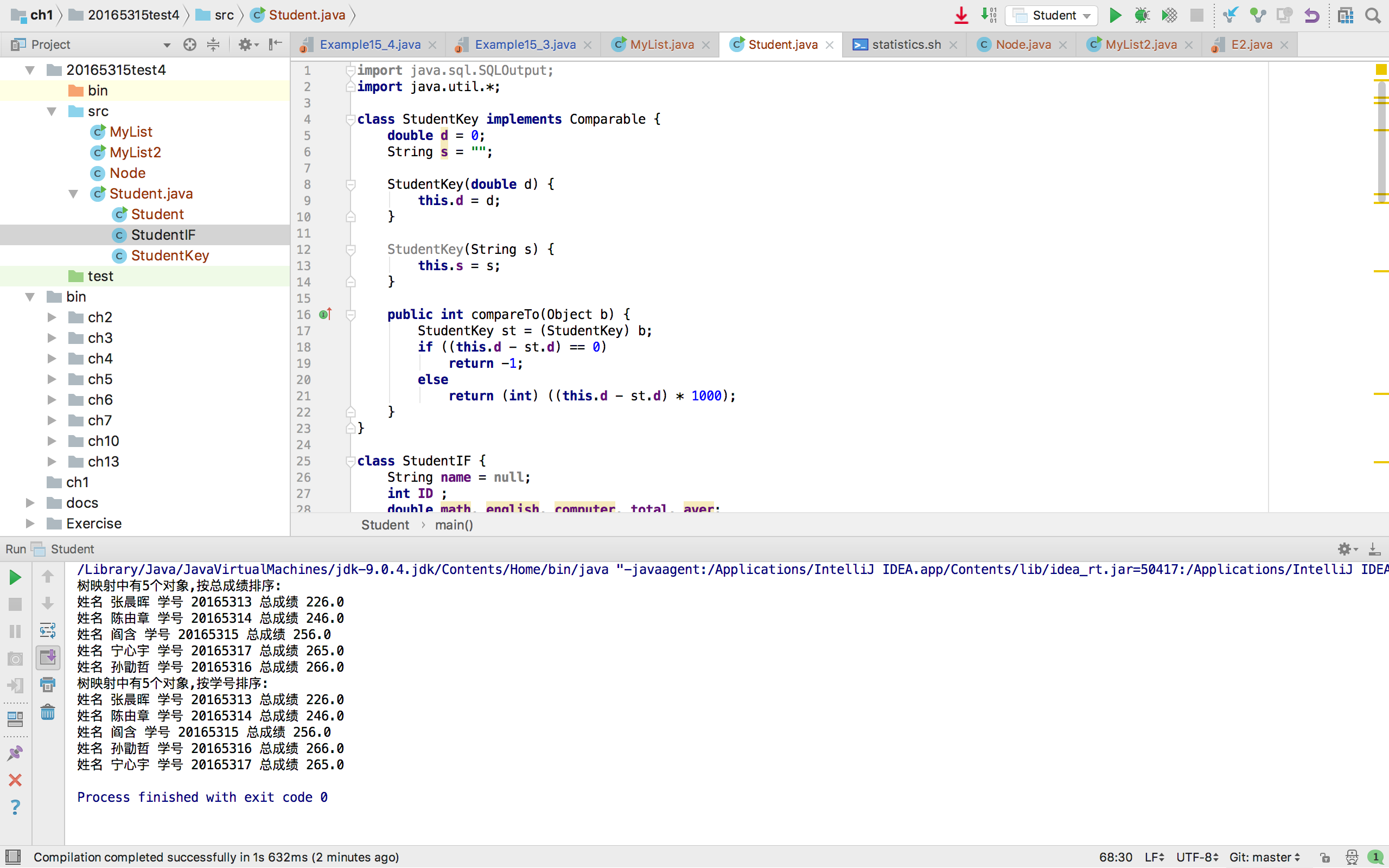
虽然此方法可行,但是不满足老师给出的要求,即应该用Comparator代码,我在课下补写了对应代码:
import java.util.*;
public class MyComparator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<StudentIF> list = new LinkedList<>();
StudentIF stu1=new StudentIF(20165313,"张晨晖","male",20,55,77,88);
StudentIF stu2=new StudentIF(20165314,"陈由章","male",20,88,100,66);
StudentIF stu3=new StudentIF(20165315,"阎 含","female",20,77,88,66);
StudentIF stu4=new StudentIF(20165316,"孙勖哲","male",20,99,77,88);
StudentIF stu5=new StudentIF(20165317,"宁心宇","male",20,66,99,77);
stu1.getAveScore();
stu2.getAveScore();
stu3.getAveScore();
stu4.getAveScore();
stu5.getAveScore();
list.add(stu1);
list.add(stu2);
list.add(stu3);
list.add(stu4);
list.add(stu5);
System.out.println("排序前链表中的数据:");
Iterator<StudentIF> iter=list.iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
StudentIF studentIF=iter.next();
System.out.println(studentIF.toString());
}
IDComparator idComparator = new IDComparator();
Collections.sort(list, idComparator);
System.out.println("根据学生学号升序排序后链表中的数据:");
Iterator<StudentIF> iter2=list.iterator();
while(iter2.hasNext()) {
StudentIF studentIF=iter2.next();
System.out.println(studentIF.toString());
}
ScoreComparator scoreComparator = new ScoreComparator();
Collections.sort(list, scoreComparator);
System.out.println("根据学生成绩升序排序后链表中的数据:");
Iterator<StudentIF> iter3=list.iterator();
while(iter3.hasNext()) {
StudentIF studentIF=iter3.next();
System.out.println(studentIF.toString());
}
}
}
class IDComparator implements Comparator {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
StudentIF st1 = (StudentIF)o1;
StudentIF st2 = (StudentIF)o2;
return (st1.getId()-st2.getId());
}
}
class ScoreComparator implements Comparator{
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2){
StudentIF st1 = (StudentIF)o1;
StudentIF st2 = (StudentIF)o2;
return (int)(st1.getTotalScore()-st2.getTotalScore());
}
}
class StudentIF {
private int id;//表示学号
private String name;//表示姓名
private int age;//表示年龄
private String sex;//表示性别
private double computer_score;//表示计算机课程的成绩
private double english_score;//表示英语课的成绩
private double maths_score;//表示数学课的成绩
private double total_score;// 表示总成绩
private double ave_score; //表示平均成绩
@Override
public String toString() {
return "姓名:"+name+",年龄:"+age+",学号:"+id+",总分:"+total_score;
}
public StudentIF(int id, String name, String sex, int age,double computer_score,
double english_score,double maths_score) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
this.age = age;
this.computer_score = computer_score;
this.english_score = english_score;
this.maths_score = maths_score;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}//获得当前对象的学号,
public double getComputer_score() {
return computer_score;
}//获得当前对象的计算机课程成绩,
public double getMaths_score() {
return maths_score;
}//获得当前对象的数学课程成绩,
public double getEnglish_score() {
return english_score;
}//获得当前对象的英语课程成绩,
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}// 设置当前对象的id值,
public void setComputer_score(double computer_score) {
this.computer_score = computer_score;
}//设置当前对象的Computer_score值,
public void setEnglish_score(double english_score) {
this.english_score = english_score;
}//设置当前对象的English_score值,
public void setMaths_score(double maths_score) {
this.maths_score = maths_score;
}//设置当前对象的Maths_score值,
public double getTotalScore() {
total_score=computer_score + maths_score + english_score;
return total_score;
}// 计算Computer_score, Maths_score 和English_score 三门课的总成绩。
public double getAveScore() {
return getTotalScore() / 3;
}// 计算Computer_score, Maths_score 和English_score 三门课的平均成绩。
}
运行截图:
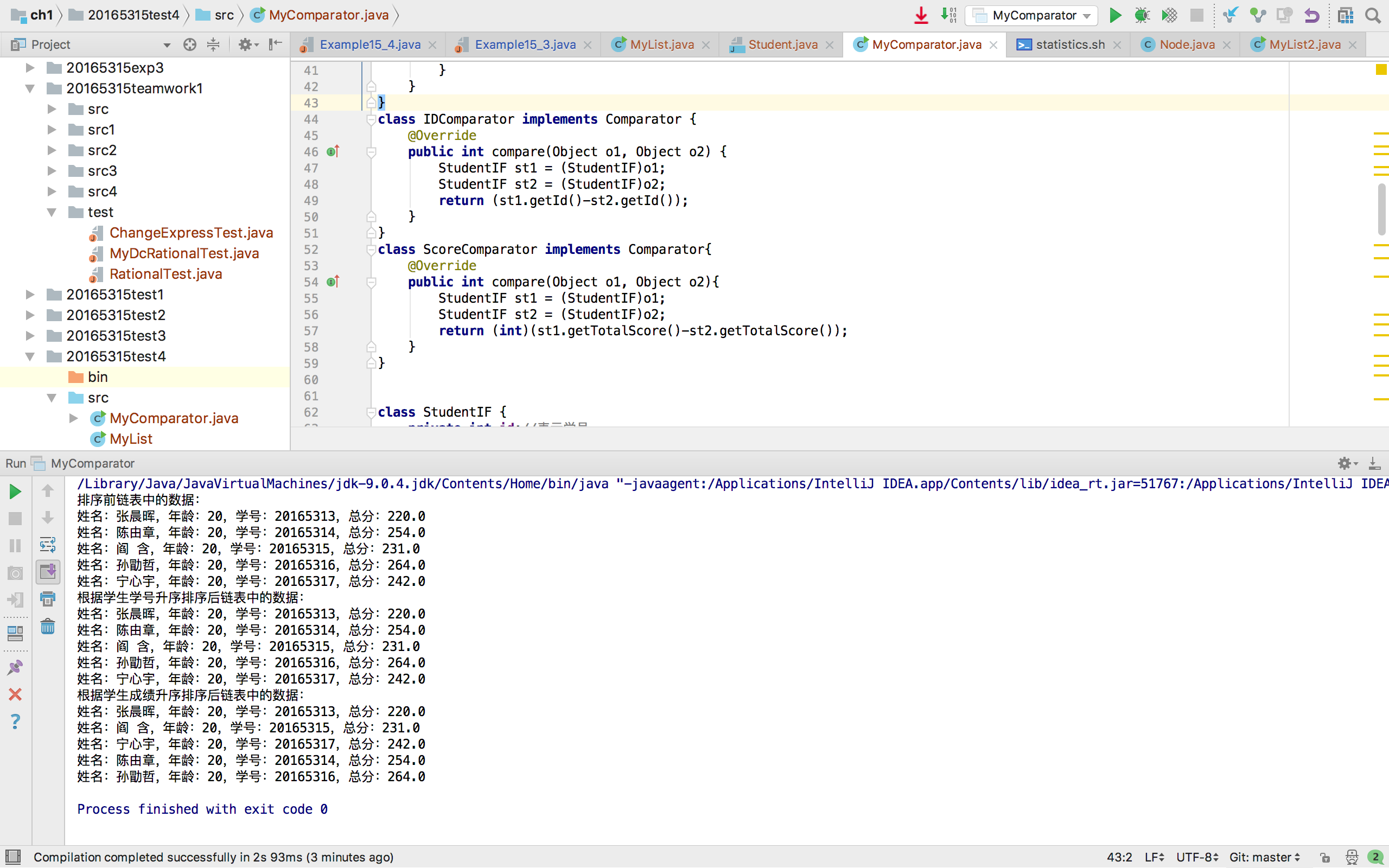
补充MyList.java的内容
- 示例代码:
public class MyList {
public static void main(String [] args) {
//选用合适的构造方法,用你学号前后各两名同学的学号创建四个结点
//把上面四个节点连成一个没有头结点的单链表
//遍历单链表,打印每个结点的
//把你自己插入到合适的位置(学号升序)
//遍历单链表,打印每个结点的
//从链表中删除自己
//遍历单链表,打印每个结点的
}
}
public class Node<T> //单链表结点类,T指定结点的元素类型
{
public T data; //数据域,存储数据元素
public Node<T> next; //地址域,引用后继结点
public Node(T data, Node<T> next) //构造结点,data指定数据元素,next指定后继结点
{
this.data = data; //T对象引用赋值
this.next = next; //Node<T>对象引用赋值
}
public Node()
{
this(null, null);
}
public String toString() //返回结点数据域的描述字符串
{
return this.data.toString();
}
}
- 设计思路:
根据老师给出的伪代码,我先是根据书上例子4中的代码改写出了如下代码:
import java.util.*;
public class MyList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//选用合适的构造方法,用你学号前后各两名同学的学号创建四个结点
List<String> list = new LinkedList<String>();
list.add(new String("20165313"));
list.add(new String("20165314"));
list.add(new String("20165316"));
list.add(new String("20165317"));
//把上面四个节点连成一个没有头结点的单链表
System.out.println("打印初始链表");
//遍历单链表,打印每个结点
Iterator<String> iter = list.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
String ID = iter.next();
System.out.println(ID);
}
//把你自己插入到合适的位置(学号升序)
list.add(new String("20165315"));
Collections.sort(list);
//遍历单链表,打印每个结点
System.out.println("打印插入后的链表");
Iterator<String> iter2 = list.iterator();
while (iter2.hasNext()) {
String ID = iter2.next();
System.out.println(ID);
}
//从链表中删除自己
list.remove("20165315");
//遍历单链表,打印每个结点的
System.out.println("打印删除后的链表");
Iterator<String> iter3 = list.iterator();
while (iter3.hasNext()) {
String ID = iter3.next();
System.out.println(ID);
}
}
}
运行截图:
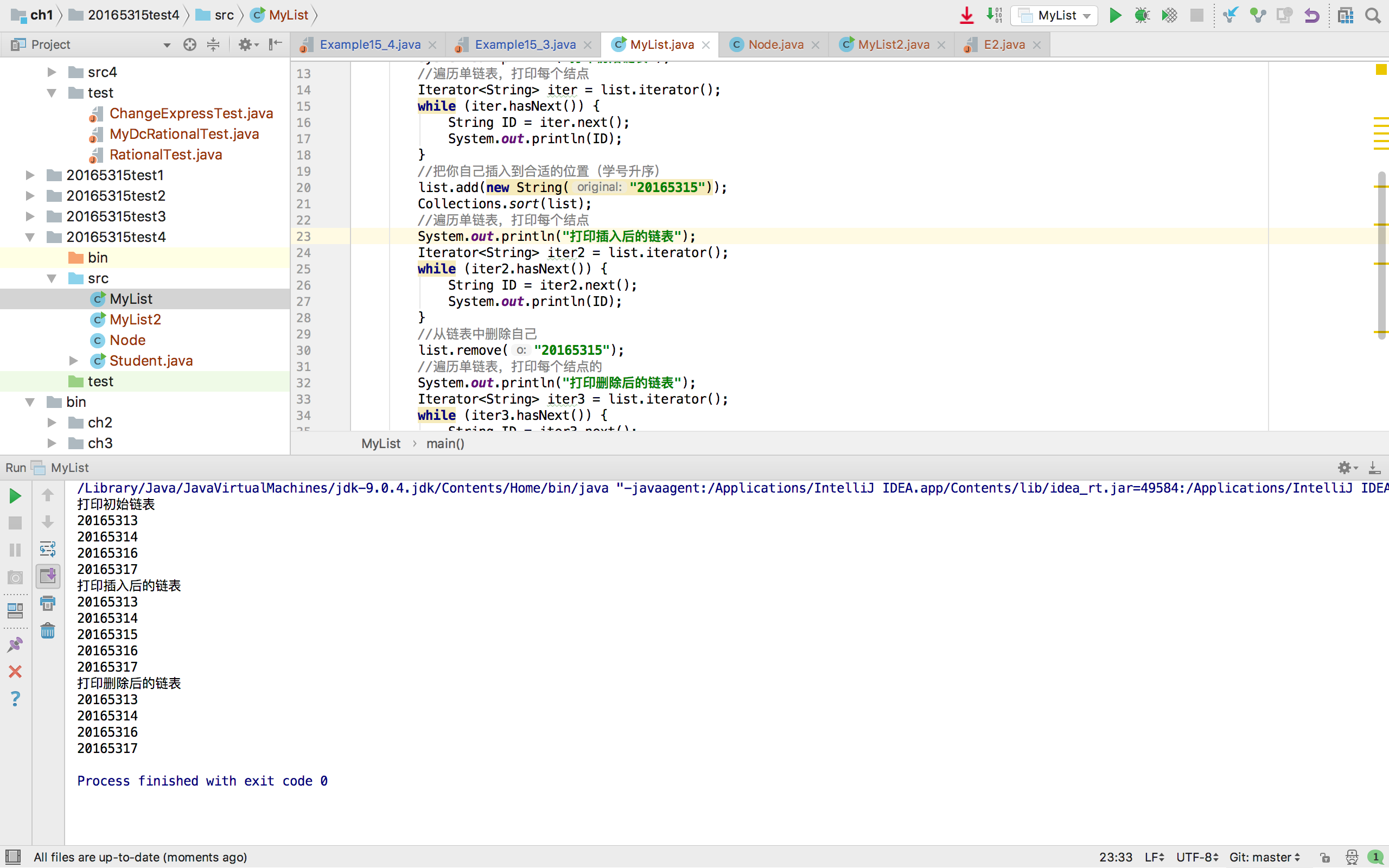
后来仔细阅读题目要求,发现此代码并不符合题意,没有用到Node<T>,也没有删除头节点,于是我在课下改写了上述代码使之符合题意:
public class Node<T>
//单链表结点类,T指定结点的元素类型
{
public T data;
//数据域,存储数据元素
public Node<T> next;
//地址域,引用后继结点
public Node(T data, Node<T> next)
//构造结点,data指定数据元素,next指定后继结点
{
this.data = data;
//T对象引用赋值
this.next = next;
//Node<T>对象引用赋值
}
public Node()
{
this(null, null);
}
@Override
public String toString()
//返回结点数据域的描述字符串
{
return this.data.toString();
}
}
public class MyList2 {
public static void main(String [] args) {
//选用合适的构造方法,用你学号前后各两名同学的学号创建四个结点
Node<Integer> S1 = new Node<Integer>(20165313, null);
Node<Integer> S2 = new Node<Integer>(20165314, null);
Node<Integer> S3 = new Node<Integer>(20165316, null);
Node<Integer> S4 = new Node<Integer>(20165317, null);
//把上面四个节点连成一个没有头结点的单链表
S1.next=S2;
S2.next=S3;
S3.next=S4;
//遍历单链表,打印每个结点
Node<Integer> oriList=S1;
System.out.println("打印初始链表");
while(oriList!=null){
System.out.println(oriList.data);
oriList=oriList.next;
}
//把你自己插入到合适的位置(学号升序)
Node<Integer> S5=new Node<Integer>(20165315,null);
Node<Integer> oriAddList=S1;
while (oriAddList != null) {
if(oriAddList.data < S5.data && oriAddList.next.data > S5.data){
S5.next=oriAddList.next;
oriAddList.next=S5;
break;
}
else{
oriAddList=oriAddList.next;
}
}
//遍历单链表,打印每个结点的
Node<Integer> addList=S1;
System.out.println("打印插入后的链表");
while(addList!=null){
System.out.println(addList.data);
addList=addList.next;
}
//从链表中删除自己
Node<Integer> oriDeleteList=S1;
while(oriDeleteList!=null){
if(oriDeleteList.next.data.equals(S5.data)){
oriDeleteList.next=S5.next;
break;
}
oriDeleteList=oriDeleteList.next;
}
//遍历单链表,打印每个结点的
Node<Integer> deleteList=S1;
System.out.println("打印删除后的链表");
while(deleteList!=null){
System.out.println(deleteList.data);
deleteList=deleteList.next;
}
}
}
运行截图:

三、 教材第十五章的代码分析
- 例子1:使用泛型类Cone声明了一个圆锥对象和一个方锥对象,并计算它们的体积,并且不考虑底的类型
- 例子2:分别使用迭代器和
get()方法遍历链表,通过调用currentTimeMillis()方法比较二者所用的时间 - 例子3:创建一个链表,加入两个节点,将节点类型强制转换后输出
- 例子4:创建一个链表,加入姓名、身高等数据,利用
sort方法(调用compareTo方法)对链表中的数据按身高排序,如果有身高相同的情况,则输出身高相同的姓名 - 例子5:使用
shuffle()、rotate()方法分别对链表中的数据进行随机排列、向右旋转一次,最后输出 - 例子6:使用压栈弹栈操作输出斐波那次递归序列
- 例子7:
wordPolice类使用Scanner解析Word.txt中的单词,然后将英文单词-汉语翻译作为建/值存储到散列映射中用户查询 - 例子8:使用
add(V value)方法对树集中的数据value按英语成绩进行升序排序,并且compareTo方法不允许有成绩相同的结点 - 例子9:使用
put(K key,V value)方法对树映射中的数据````value按关键字key进行升序排列,并且compareTo```方法允许有成绩相同的结点 - 例子10:使用
ArrayList<T>对链表中数据进行自动装箱(add()方法)和自动拆箱(get()方法) - 例子11:使用对象流实现商品库存的录入与显示系统,程序将
Goods类的对象作为链表的结点,并将链表写入文件
四、补做教材第十五章的编程题目
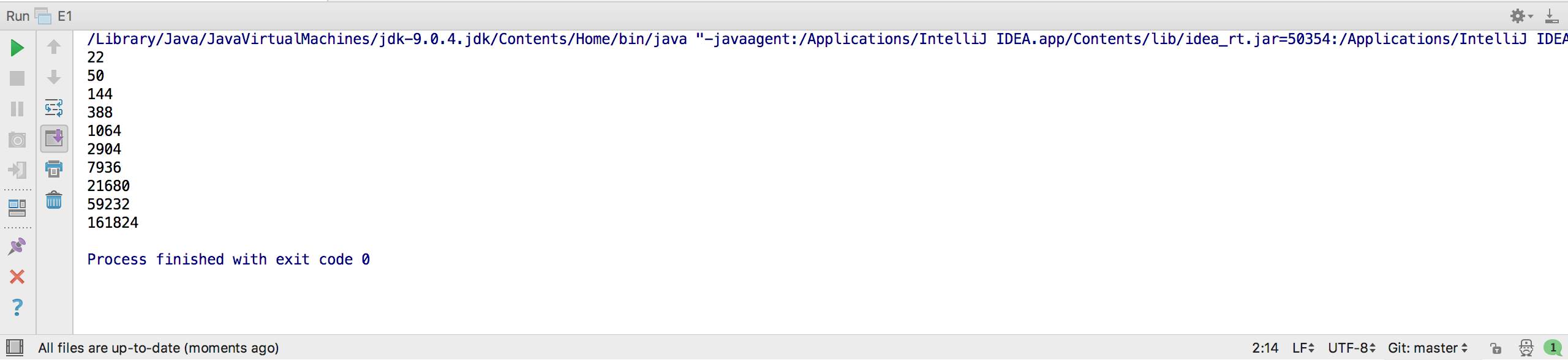
- 用堆栈结构输出an的若干项,其中an=2an-1+2an-2,a1=3,a2=8
import java.util.*;
public class E1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<Integer> stack=new Stack<Integer>();
stack.push(new Integer(3));
stack.push(new Integer(8));
int k=1;
while(k<=10){
for(int i =1;i<=2;i++){
Integer F1=stack.pop();
int f1=F1.intValue();
Integer F2=stack.pop();
int f2=F2.intValue();
Integer temp=new Integer(2*f1+2*f2);
System.out.println(""+temp.toString());
stack.push(temp);
stack.push(F2);
k++;
}
}
}
}
运行结果截图:
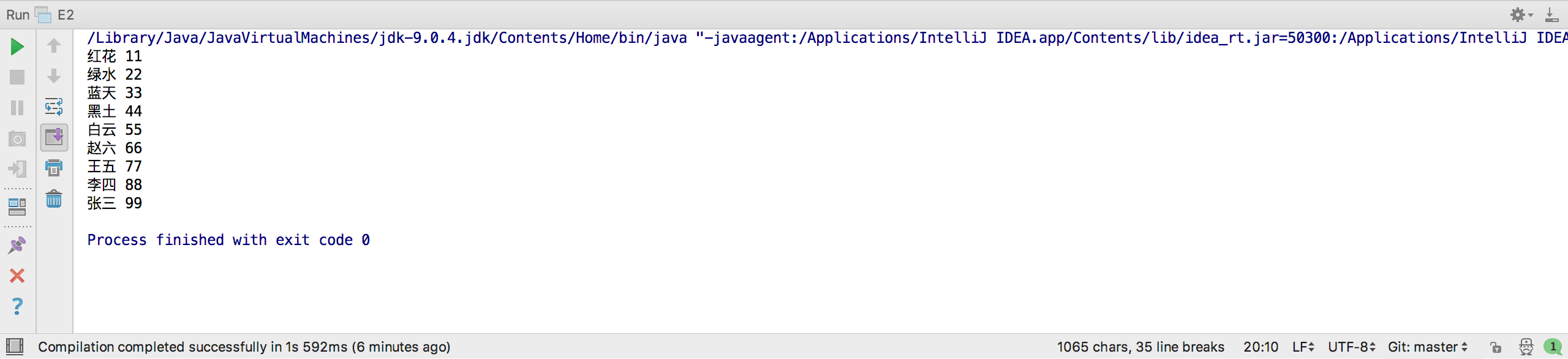
- 编写一个程序,将链表中的学生英语成绩单存放到一个树集中,使得按成绩自动排序,并输出排序结果
import java.util.*;
public class E2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Student> list=new LinkedList<Student>();
int score[]={99,88,77,66,55,44,33,22,11};
String name[]={"张三","李四","王五","赵六","白云","黑土","蓝天","绿水","红花"};
for(int i=0;i<score.length;i++){
list.add(new Student(score[i],name[i]));
}
Iterator<Student> iter=list.iterator();
TreeSet<Student> mytree=new TreeSet<Student>();
while(iter.hasNext()){
Student stu=iter.next();
mytree.add(stu);
}
Iterator<Student> te=mytree.iterator();
while(te.hasNext()){
Student stu=te.next();
System.out.println(""+stu.name+" "+stu.english);
}
}
}
class Student implements Comparable{
int english=0;
String name;
Student(int english,String name){
this.name=name;
this.english=english;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Object b){
Student st=(Student)b;
return (this.english-st.english);
}
}
运行结果截图:
- 有10个U盘,有两个重要的属性:价格和容量。编写一个应用程序,使用TreeMap<K,V>类,分别按照价格和容量排序输出10个U盘的详细信息
import java.util.*;
class UDiscKey implements Comparable {
double key = 0;
UDiscKey(double d) {
this.key = d;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Object b) {
UDiscKey discKey = (UDiscKey) b;
if ((this.key - discKey.key) == 0) {
return -1;
}
else {
return (int) ((this.key - discKey.key) * 1000);
}
}
}
class UDisc {
int amount;
double price;
UDisc(int a,double p) {
amount=a;
price=p;
}
}
public class E3 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
TreeMap<UDiscKey,UDisc> treemap = new TreeMap<UDiscKey, UDisc>();
int amount[]={100,200,300,400,500,600,700,800,900,1000};
double price[]={111,222,333,444,555,666,777,888,999,1000};
UDisc uDisc[] = new UDisc[10];
for (int k = 0; k < uDisc.length; k++) {
uDisc[k] = new UDisc(amount[k],price[k]);
}
UDiscKey key[] = new UDiscKey[10];
for (int k = 0; k < key.length; k++) {
key[k] = new UDiscKey(uDisc[k].amount);
}
for (int k = 0; k < uDisc.length; k++) {
treemap.put(key[k], uDisc[k]);
}
int number = treemap.size();
System.out.println("树映射中有" + number + "个对象,按容量排序:");
Collection<UDisc> collection = treemap.values();
Iterator<UDisc> iter = collection.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
UDisc disc = iter.next();
System.out.println(" 容量 " + disc.amount);
}
treemap.clear();
for (int k = 0; k < key.length; k++) {
key[k] = new UDiscKey(uDisc[k].price);
}
for (int k = 0; k < uDisc.length; k++) {
treemap.put(key[k], uDisc[k]);
}
number = treemap.size();
System.out.println("树映射中有" + number + "个对象:按价格排序:");
collection = treemap.values();
iter = collection.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
UDisc disc = (UDisc) iter.next();
System.out.println(" 价格 " + disc.price);
}
}
}
运行结果截图:

五、码云链接
https://gitee.com/BESTI-IS-JAVA-2018/ch1/tree/master/20165315test4/src