习题 33: While 循环
接下来是一个更在你意料之外的概念: while-loop``(while 循环)。``while-loop 会一直执行它下面的代码片段,直到它对应的布尔表达式为 False 时才会停下来。
等等,你还能跟得上这些术语吧?如果你的某一行是以 : (冒号, colon)结尾,那就意味着接下来的内容是一个新的代码片段,新的代码片段是需要被缩进的。只有将代码用这样的方式格式化,Python 才能知道你的目的。如果你不太明白这一点,就回去看看“if 语句”和“函数”的章节,直到你明白为止。
接下来的练习将训练你的大脑去阅读这些结构化的代码。这和我们将布尔表达式烧录到你的大脑中的过程有点类似。
回到 while 循环,它所作的和 if 语句类似,也是去检查一个布尔表达式的真假,不一样的是它下面的代码片段不是只被执行一次,而是执行完后再调回到 while 所在的位置,如此重复进行,直到 while 表达式为 False 为止。
While 循环有一个问题,那就是有时它会永不结束。如果你的目的是循环到宇宙毁灭为止,那这样也挺好的,不过其他的情况下你的循环总需要有一个结束点。
为了避免这样的问题,你需要遵循下面的规定:
- 尽量少用 while-loop,大部分时候 for-loop 是更好的选择。
- 重复检查你的 while 语句,确定你测试的布尔表达式最终会变成 False 。
- 如果不确定,就在 while-loop 的结尾打印出你要测试的值。看看它的变化。
在这节练习中,你将通过上面的三样事情学会 while-loop :

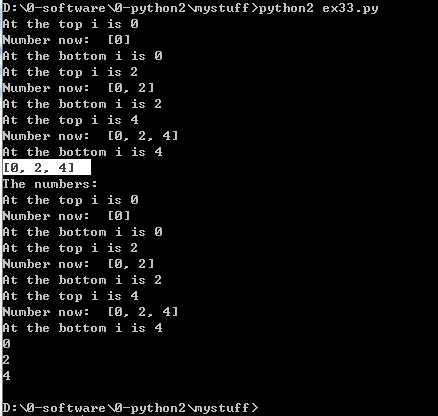
1 i = 0 2 numbers = [] 3 4 while i < 6: 5 print "At the top i is %d" % i 6 numbers.append(i) 7 8 i = i + 1 9 print "Number now: ",numbers 10 print "At the bottom i is %d" % i 11 12 13 print "The numbers: " 14 15 for num in numbers: 16 print num
你应该看到的结果
加分习题
- 将这个 while 循环改成一个函数,将测试条件(i < 6)中的 6 换成一个变量。
- 使用这个函数重写你的脚本,并用不同的数字进行测试。
- 为函数添加另外一个参数,这个参数用来定义第 8 行的加值 + 1 ,这样你就可以让它任意加值了。
- 再使用该函数重写一遍这个脚本。看看效果如何。
- 接下来使用 for-loop 和 range 把这个脚本再写一遍。你还需要中间的加值操作吗?如果你不去掉它,会有什么样的结果?
很有可能你会碰到程序跑着停不下来了,这时你只要按着 CTRL 再敲 c (CTRL-c),这样程序就会中断下来了。
习题练习
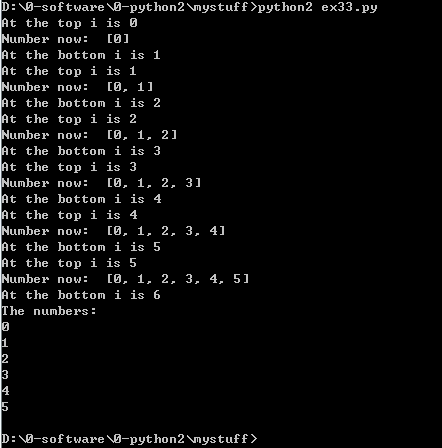
1.
1 def while_loop(n, n_add): 2 i = 0 3 numbers = [] 4 5 6 while i < n: 7 print "At the top i is %d" % i 8 numbers.append(i) 9 10 i = i + n_add 11 print "Number now: ",numbers 12 print "At the bottom i is %d" % i 13 return numbers 14 15 while_loop(6, 1) 16 print "The numbers: " 17 18 numbers = while_loop(6, 1) 19 for num in numbers: 20 print num
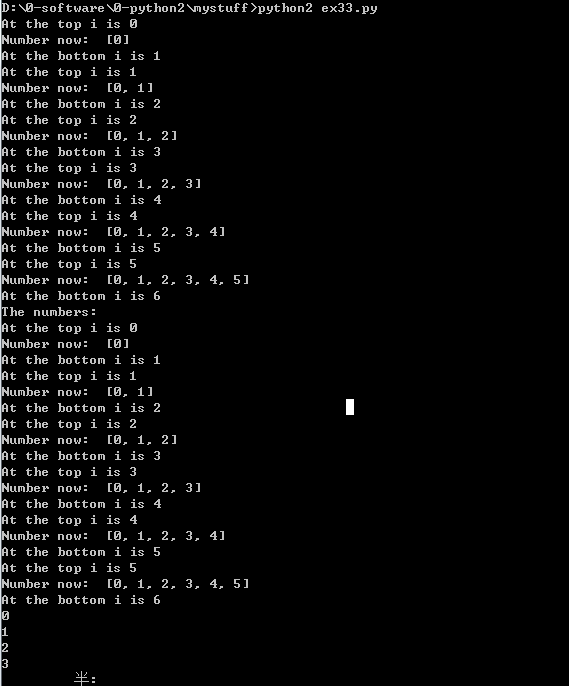
2.
1 def while_loop(n, n_add): 2 i = 0 3 numbers = [] 4 5 6 for i in range(0,n + 1,n_add): 7 print "At the top i is %d" % i 8 numbers.append(i) 9 10 print "Number now: ",numbers 11 print "At the bottom i is %d" % i 12 return numbers 13 14 print while_loop(4, 2) 15 print "The numbers: " 16 17 numbers = while_loop(4, 2) 18 for num in numbers: 19 print num