参考:
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000006746409
https://waylau.com/mockito-quick-start/
1.引入依赖
下面这个最新版本匹配似乎有问题
testCompile group: 'org.mockito', name: 'mockito-core', version: '3.7.7'
testCompile group: 'org.mockito', name: 'mockito-junit-jupiter', version: '3.7.7'
testCompile group: 'org.junit.jupiter', name: 'junit-jupiter', version: '5.7.0'
改用下面的旧版本测试成功
testCompile group: 'org.mockito', name: 'mockito-core', version: '2.18.3'
testCompile group: 'org.mockito', name: 'mockito-junit-jupiter', version: '2.18.3'
testCompile group: 'org.junit.jupiter', name: 'junit-jupiter-engine', version: '5.2.0'
2.编写测试用例
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.mockito.ArgumentCaptor;
import org.mockito.InOrder;
import org.mockito.Mockito;
import java.util.*;
/**
* @author zhengqian
* @date 2021.01.22
*/
public class CommonTest {
@Test
public void createMockObject() {
// 使用 mock 静态方法创建 Mock 对象.
List mockedList = Mockito.mock(List.class);
Assertions.assertTrue(mockedList instanceof List);
// mock 方法不仅可以 Mock 接口类, 还可以 Mock 具体的类型.
ArrayList mockedArrayList = Mockito.mock(ArrayList.class);
Assertions.assertTrue(mockedArrayList instanceof List);
Assertions.assertTrue(mockedArrayList instanceof ArrayList);
}
@Test
public void configMockObject() {
List mockedList = Mockito.mock(List.class);
// 我们定制了当调用 mockedList.add("one") 时, 返回 true
Mockito.when(mockedList.add("one")).thenReturn(true);
// 当调用 mockedList.size() 时, 返回 1
Mockito.when(mockedList.size()).thenReturn(1);
Assertions.assertTrue(mockedList.add("one"));
// 因为我们没有定制 add("two"), 因此返回默认值, 即 false.
Assertions.assertFalse(mockedList.add("two"));
Assertions.assertEquals(mockedList.size(), 1);
Iterator i = Mockito.mock(Iterator.class);
Mockito.when(i.next()).thenReturn("Hello,").thenReturn("Mockito!");
String result = i.next() + " " + i.next();
//assert
Assertions.assertEquals("Hello, Mockito!", result);
}
@Test
public void testVerify() {
List mockedList = Mockito.mock(List.class);
mockedList.add("one");
mockedList.add("two");
mockedList.add("three times");
mockedList.add("three times");
mockedList.add("three times");
Mockito.when(mockedList.size()).thenReturn(5);
Assertions.assertEquals(mockedList.size(), 5);
// mockedList.add("one") 至少被调用了 1 次(atLeastOnce)
Mockito.verify(mockedList, Mockito.atLeastOnce()).add("one");
// mockedList.add("two") 被调用了 1 次(times(1))
Mockito.verify(mockedList, Mockito.times(1)).add("two");
// mockedList.add("three times") 被调用了 3 次(times(3))
Mockito.verify(mockedList, Mockito.times(3)).add("three times");
// mockedList.isEmpty() 从未被调用(never)
Mockito.verify(mockedList, Mockito.never()).isEmpty();
}
@Test
public void testSpy() {
List list = new LinkedList();
// 使用 spy() 部分模拟对象
List spy = Mockito.spy(list);
// 对 spy.size() 进行定制.
Mockito.when(spy.size()).thenReturn(100);
spy.add("one");
spy.add("two");
// 因为我们没有对 get(0), get(1) 方法进行定制,
// 因此这些调用其实是调用的真实对象的方法.
Assertions.assertEquals(spy.get(0), "one");
Assertions.assertEquals(spy.get(1), "two");
Assertions.assertEquals(spy.size(), 100);
}
@Test
public void testCaptureArgument() {
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("1", "2");
List mockedList = Mockito.mock(List.class);
ArgumentCaptor<List> argument = ArgumentCaptor.forClass(List.class);
mockedList.addAll(list);
// 获取 mockedList.addAll 方法所传递的实参 list.
Mockito.verify(mockedList).addAll(argument.capture());
Assertions.assertEquals(2, argument.getValue().size());
Assertions.assertEquals(list, argument.getValue());
}
@Test
public void testArgumentMatcher() {
List mockedList = Mockito.mock(List.class);
//stubbing using built-in anyInt() argument matcher
Mockito.when(mockedList.get(Mockito.anyInt())).thenReturn("element");
//stubbing using custom matcher (let's say isValid() returns your own matcher implementation):
// when(mockedList.contains(argThat(isValid()))).thenReturn("element");
//following prints "element"
System.out.println(mockedList.get(999));
}
@Test
public void testThrowAndVoid() {
List mockedList = Mockito.mock(List.class);
Mockito.when(mockedList.get(1)).thenThrow(new RuntimeException());
//following throws runtime exception
System.out.println(mockedList.get(1));
Mockito.doThrow(new RuntimeException()).when(mockedList).clear();
//following throws RuntimeException:
mockedList.clear();
}
@Test
public void testInOrder() {
// A. Single mock whose methods must be invoked in a particular order
List singleMock = Mockito.mock(List.class);
//using a single mock
singleMock.add("was added first");
singleMock.add("was added second");
//create an inOrder verifier for a single mock
InOrder inOrder = Mockito.inOrder(singleMock);
//following will make sure that add is first called with "was added first, then with "was added second"
inOrder.verify(singleMock).add("was added first");
inOrder.verify(singleMock).add("was added second");
// B. Multiple mocks that must be used in a particular order
List firstMock = Mockito.mock(List.class);
List secondMock = Mockito.mock(List.class);
//using mocks
firstMock.add("was called first");
secondMock.add("was called second");
//create inOrder object passing any mocks that need to be verified in order
InOrder inOrder2 = Mockito.inOrder(firstMock, secondMock);
//following will make sure that firstMock was called before secondMock
inOrder2.verify(firstMock).add("was called first");
inOrder2.verify(secondMock).add("was called second");
}
@Test
public void testConsecutiveStubbing() {
List mockedList = Mockito.mock(List.class);
Mockito.when(mockedList.get(0))
.thenThrow(new RuntimeException())
.thenReturn("foo");
// 精简写法
// when(mockedList.get(0)).thenReturn("one", "two", "three");
//First call: throws runtime exception:
mockedList.get(0);
//Second call: prints "foo"
System.out.println(mockedList.get(0));
//Any consecutive call: prints "foo" as well (last stubbing wins).
System.out.println(mockedList.get(0));
}
@Test
public void testCallbackStubbing() {
List mockedList = Mockito.mock(List.class);
Mockito.when(mockedList.get(Mockito.anyInt())).thenAnswer(invocation -> {
Object[] args = invocation.getArguments();
return "called with arguments: " + args;
});
//the following prints "called with arguments: foo"
System.out.println(mockedList.get(111));
}
}
使用mock注解
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.ExtendWith;
import org.mockito.Mock;
import org.mockito.Mockito;
import org.mockito.junit.jupiter.MockitoExtension;
/**
* @author zhengqian
* @date 2021.01.27
*/
@ExtendWith(MockitoExtension.class)
public class UserServiceTest {
@Mock
private UserService userService;
@Test
public void testGet() {
Mockito.when(userService.get()).thenReturn("fake user");
Assertions.assertEquals(userService.get(), "fake user");
}
}
3. 其他JUnit5注解
@Test :表示方法是测试方法。但是与JUnit4的@Test不同,他的职责非常单一不能声明任何属性,拓展的测试将会由Jupiter提供额外测试
@ParameterizedTest :表示方法是参数化测试,下方会有详细介绍
@RepeatedTest :表示方法可重复执行,下方会有详细介绍
@DisplayName :为测试类或者测试方法设置展示名称
@BeforeEach :表示在每个单元测试之前执行
@AfterEach :表示在每个单元测试之后执行
@BeforeAll :表示在所有单元测试之前执行
@AfterAll :表示在所有单元测试之后执行
@Tag :表示单元测试类别,类似于JUnit4中的@Categories
@Disabled :表示测试类或测试方法不执行,类似于JUnit4中的@Ignore
@Timeout :表示测试方法运行如果超过了指定时间将会返回错误
@ExtendWith :为测试类或测试方法提供扩展类引用
补充
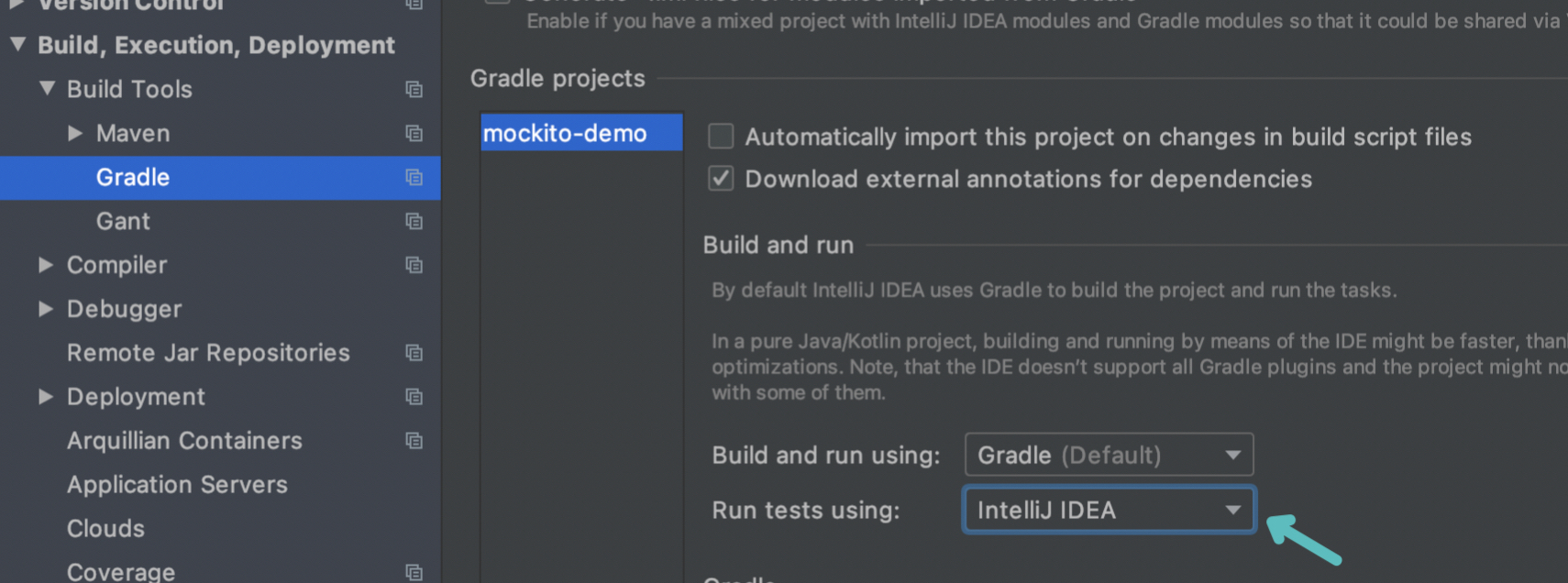
如果运行test遇到以下错误:
FAILURE: Build failed with an exception.
* What went wrong:
Execution failed for task ':test'.
> No tests found for given includes: [org.example.mockito.demo.service.UserServiceTest.configMockObject](filter.includeTestsMatching)
改一下IDEA配置