Spring的核心是ApplicationContext,它管理bean的完整生命周期。ApplicationContext在加载bean时发布某些类型的事件。例如,ContextStartedEvent当上下文启动,并公布ContextStoppedEvent当上下文停止出版。
ApplicationContext中的事件处理是通过ApplicationEvent类和ApplicationListener接口提供的。因此,如果bean实现了ApplicationListener,那么每次将ApplicationEvent发布到ApplicationContext时,都会通知该bean。

Spring的事件处理是单线程的,因此如果事件被发布,除非所有接收者都收到消息,否则流程将被阻止,流程将不会继续。因此,如果要使用事件处理,在设计应用程序时应该小心。
监听上下文事件
要监听上下文事件,bean应该实现ApplicationListener接口,该接口只有一个onApplicationEvent()方法。因此,让我们编写一个示例来查看事件如何传播以及如何使代码根据特定事件执行所需任务。
示例:
(1)编写HelloWorld.java
package com.tutorialspoint; public class HelloWorld { private String message; public void setMessage(String message){ this.message = message; } public void getMessage(){ System.out.println("Your Message : " + message); } }
(2)编写CStartEventHandler.java
package com.tutorialspoint; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener; import org.springframework.context.event.ContextStartedEvent; public class CStartEventHandler implements ApplicationListener<ContextStartedEvent>{ public void onApplicationEvent(ContextStartedEvent event) { System.out.println("ContextStartedEvent Received"); } }
(3)编写CStopEventHandler.java
package com.tutorialspoint; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener; import org.springframework.context.event.ContextStoppedEvent; public class CStopEventHandler implements ApplicationListener<ContextStoppedEvent>{ public void onApplicationEvent(ContextStoppedEvent event) { System.out.println("ContextStoppedEvent Received"); } }
(4)编写MainApp.java
package com.tutorialspoint; import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class MainApp { public static void main(String[] args) { ConfigurableApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Beans.xml"); // Let us raise a start event. context.start(); HelloWorld obj = (HelloWorld) context.getBean("helloWorld"); obj.getMessage(); // Let us raise a stop event. context.stop(); } }
(5)编写Beans.xml
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd"> <bean id = "helloWorld" class = "com.tutorialspoint.HelloWorld"> <property name = "message" value = "Hello World!"/> </bean> <bean id = "cStartEventHandler" class = "com.tutorialspoint.CStartEventHandler"/> <bean id = "cStopEventHandler" class = "com.tutorialspoint.CStopEventHandler"/> </beans>
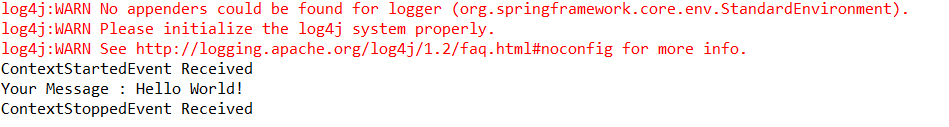
(6)运行MainApp.java中的main方法,结果如下: